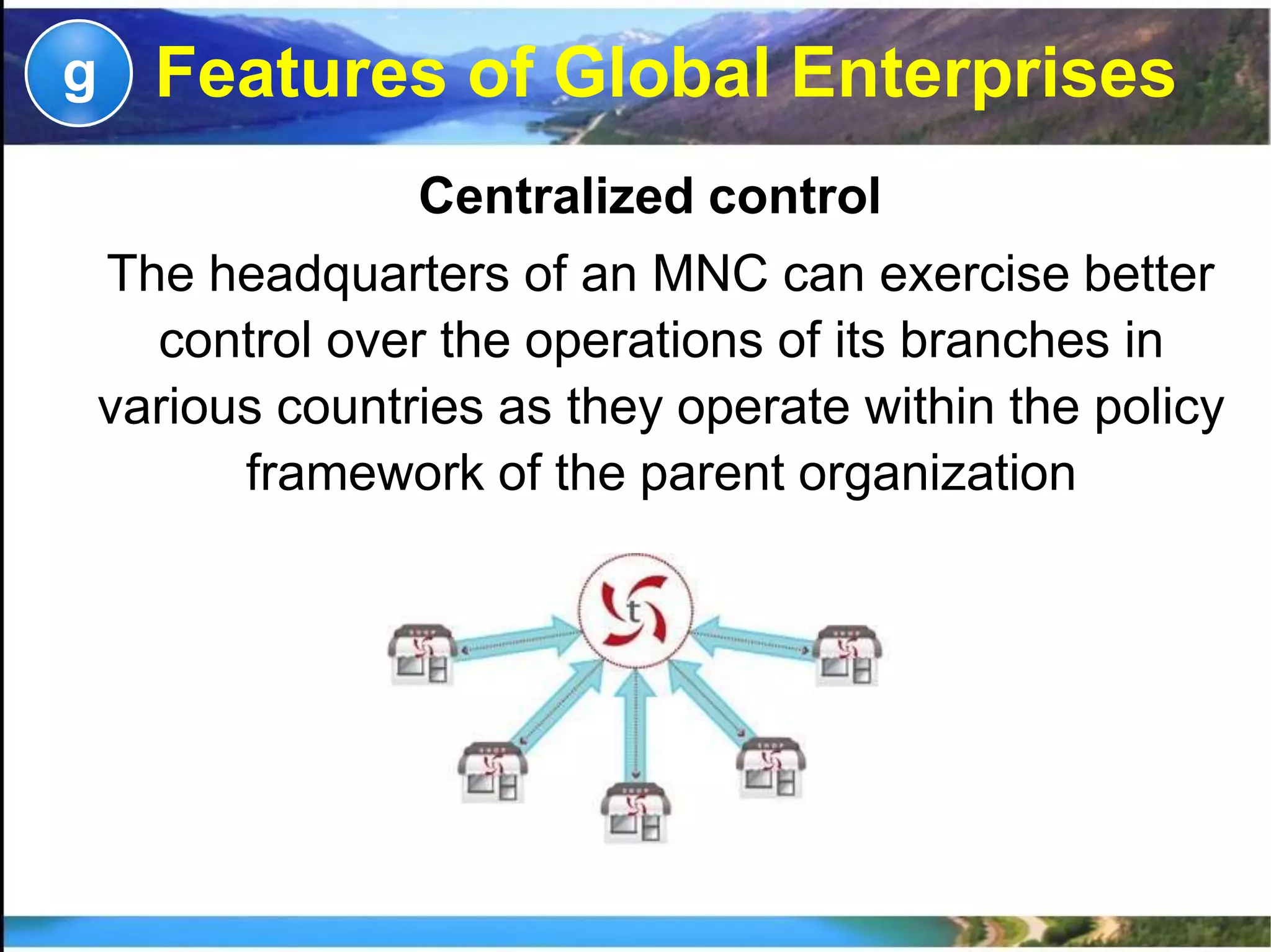
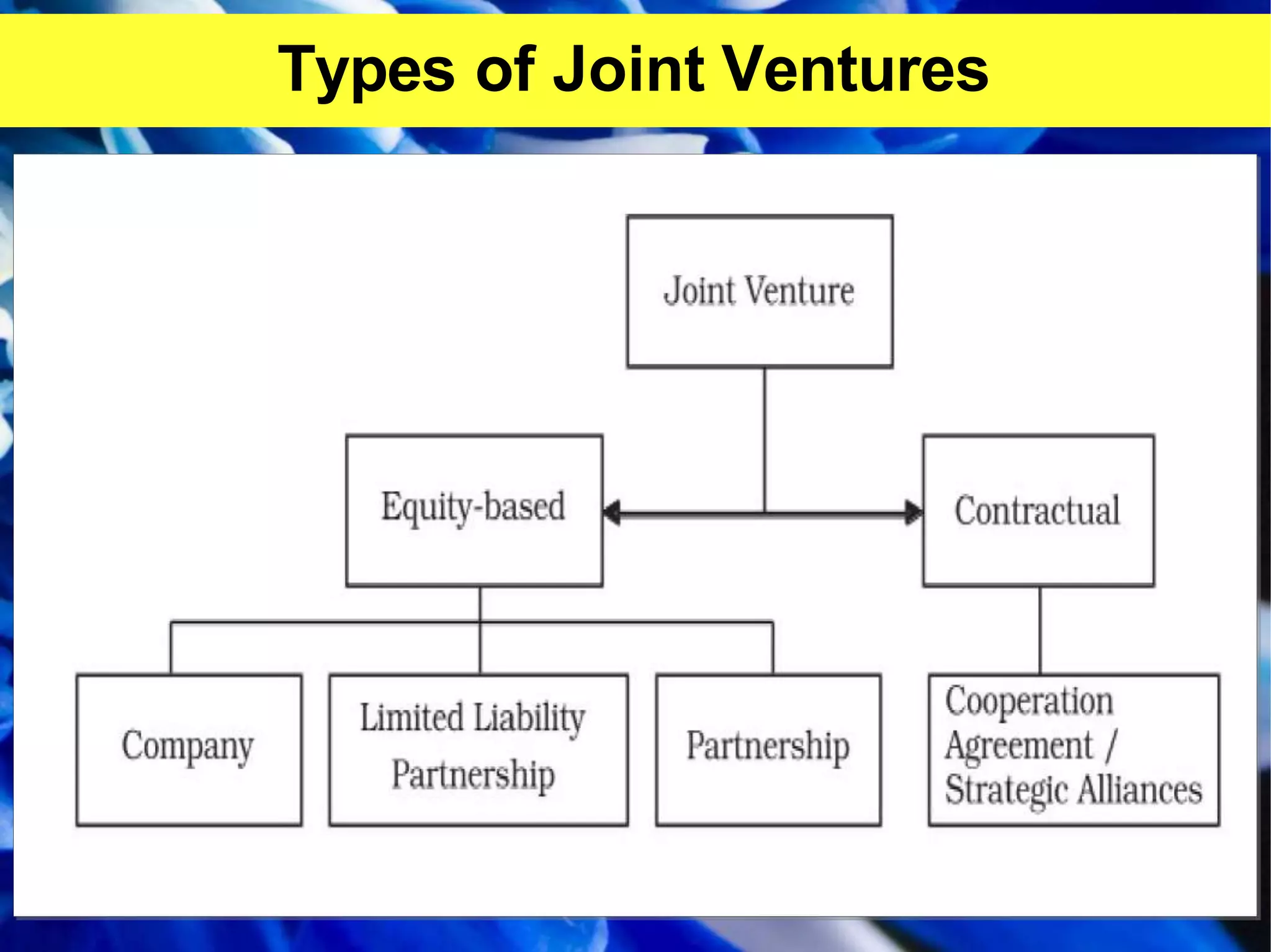
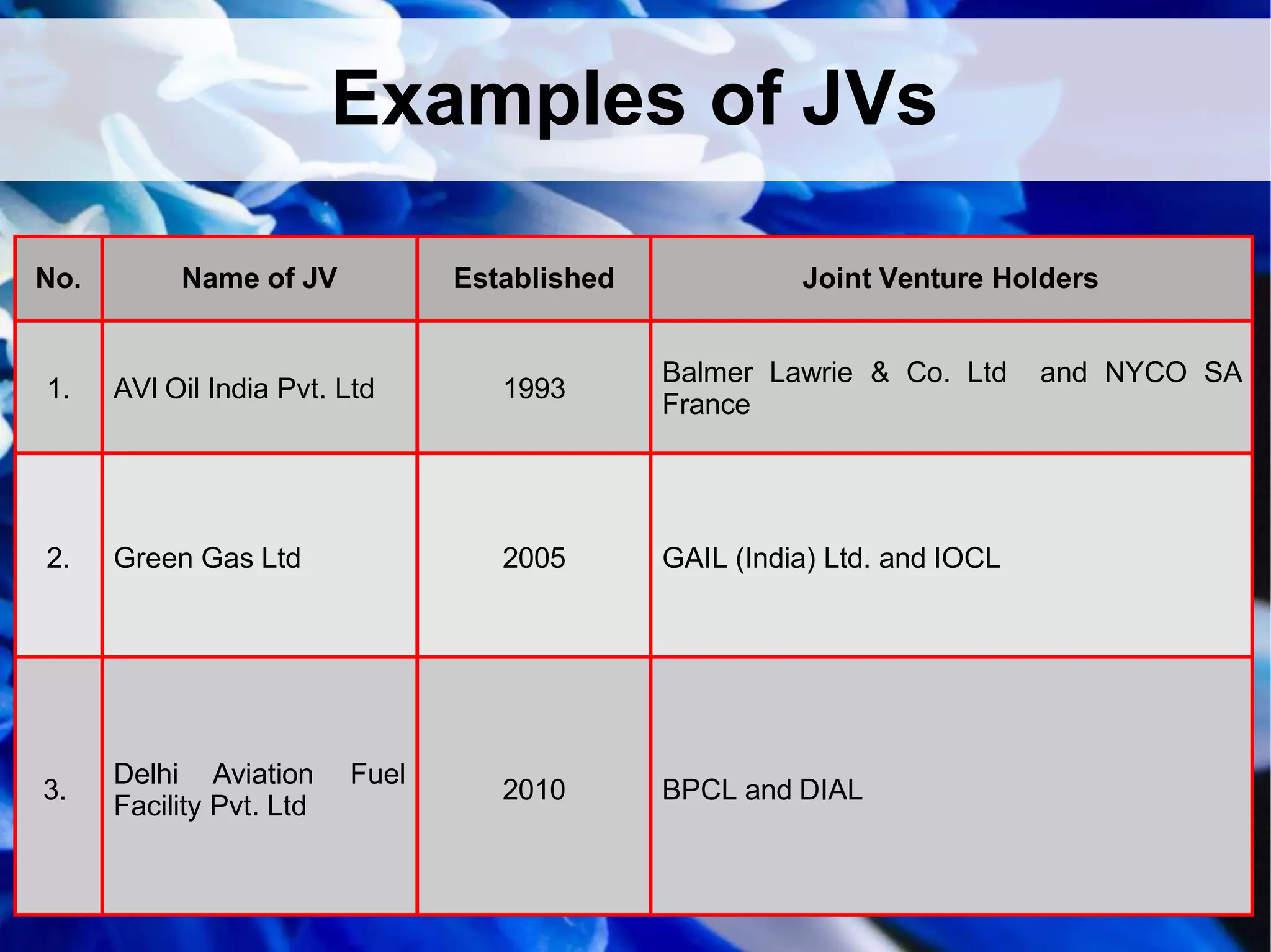
This document provides information on different types of business organizations including private sector enterprises, public sector enterprises, and global enterprises. It discusses sole proprietorships, partnerships, joint stock companies, departmental undertakings, public corporations, government companies, and multinational corporations. It also covers joint ventures and public-private partnerships. The key points are:
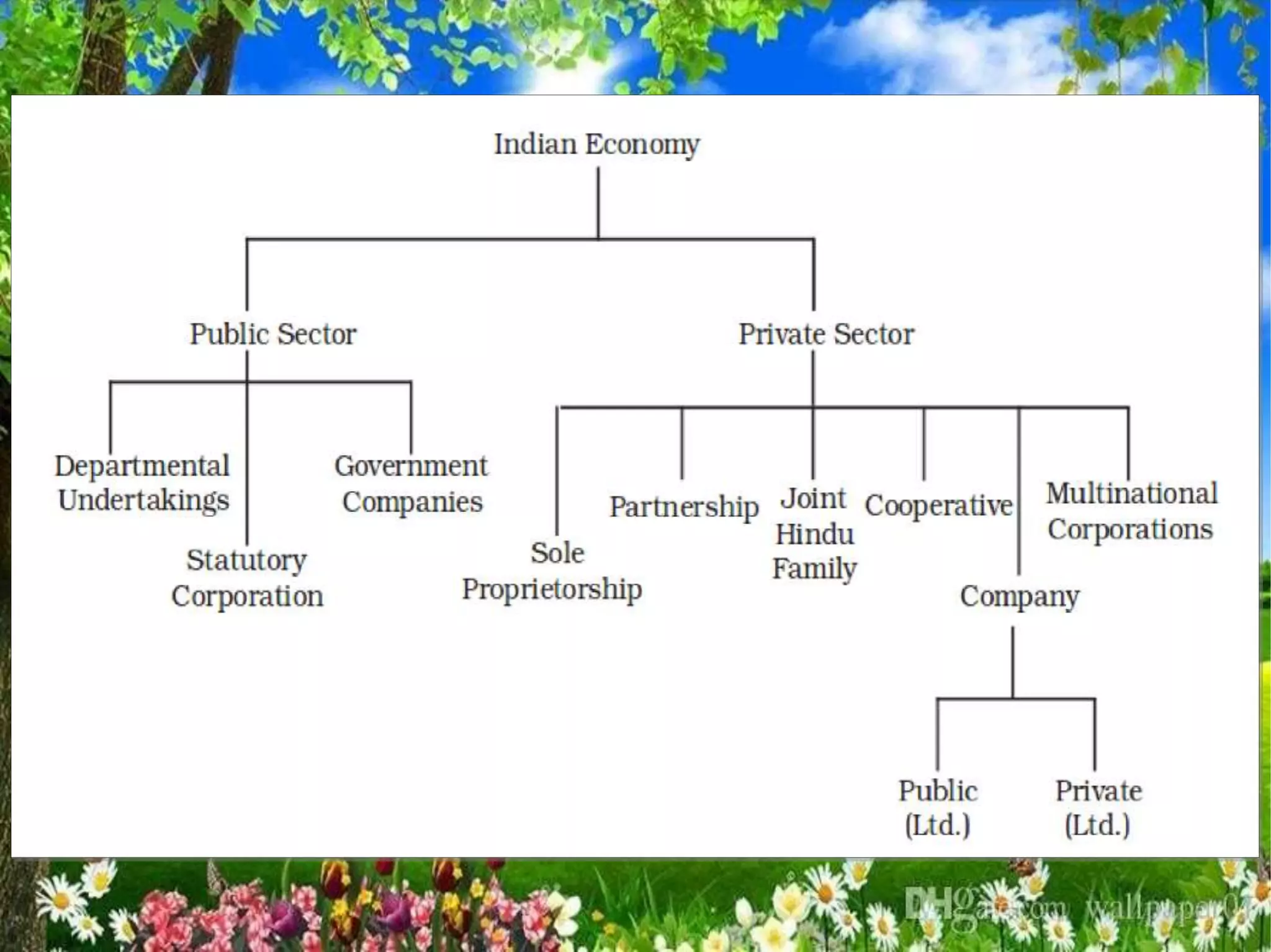
1. Private sector enterprises are owned and managed by private individuals/groups and aim to generate profits, while public sector enterprises are owned by the government and aim to provide services to society.
2. Public sector enterprises can take the form of departmental undertakings, public corporations, or government companies.
3. Global/multinational enterprises operate