Embed presentation
Downloaded 172 times

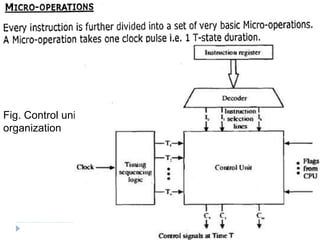

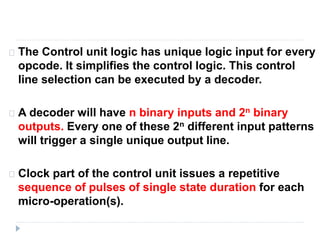



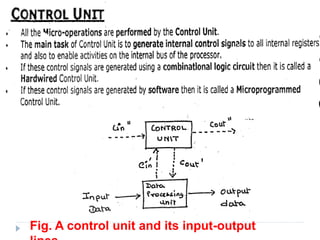
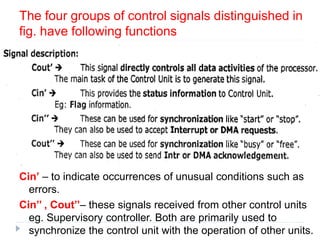
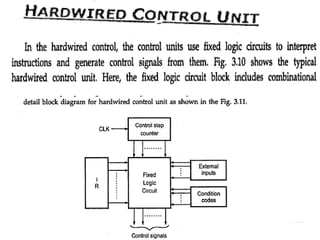

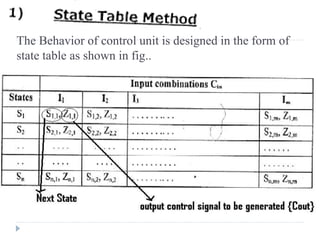



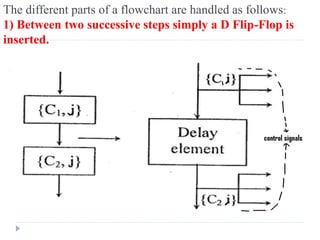
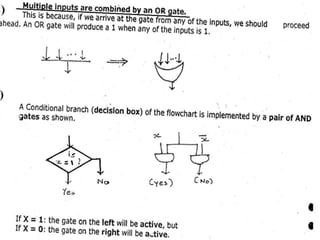
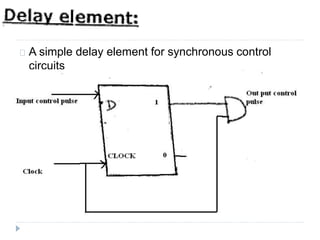
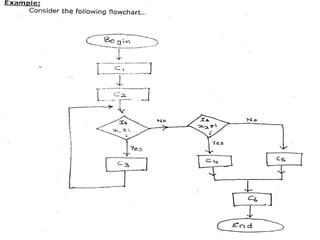
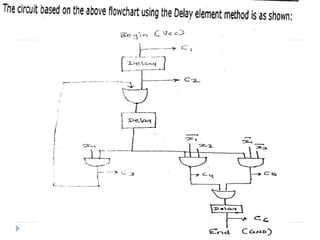


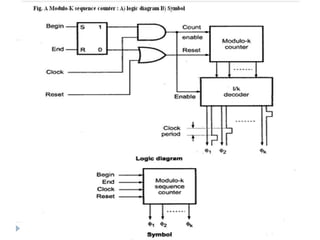
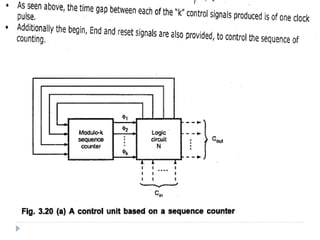
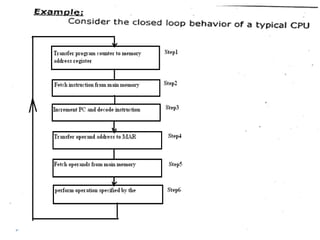

The document discusses the organization and design of a computer's control unit. It describes control units as being implemented as combinational logic circuits using gates, flip-flops, and decoders. The control unit uses the opcode of the instruction in the instruction register along with the clock and flags to determine the required control signals. A decoder is used to trigger a unique output line for each opcode input pattern. The control unit issues clock pulses to control the micro-operations and its behavior can be designed as a state table.


























