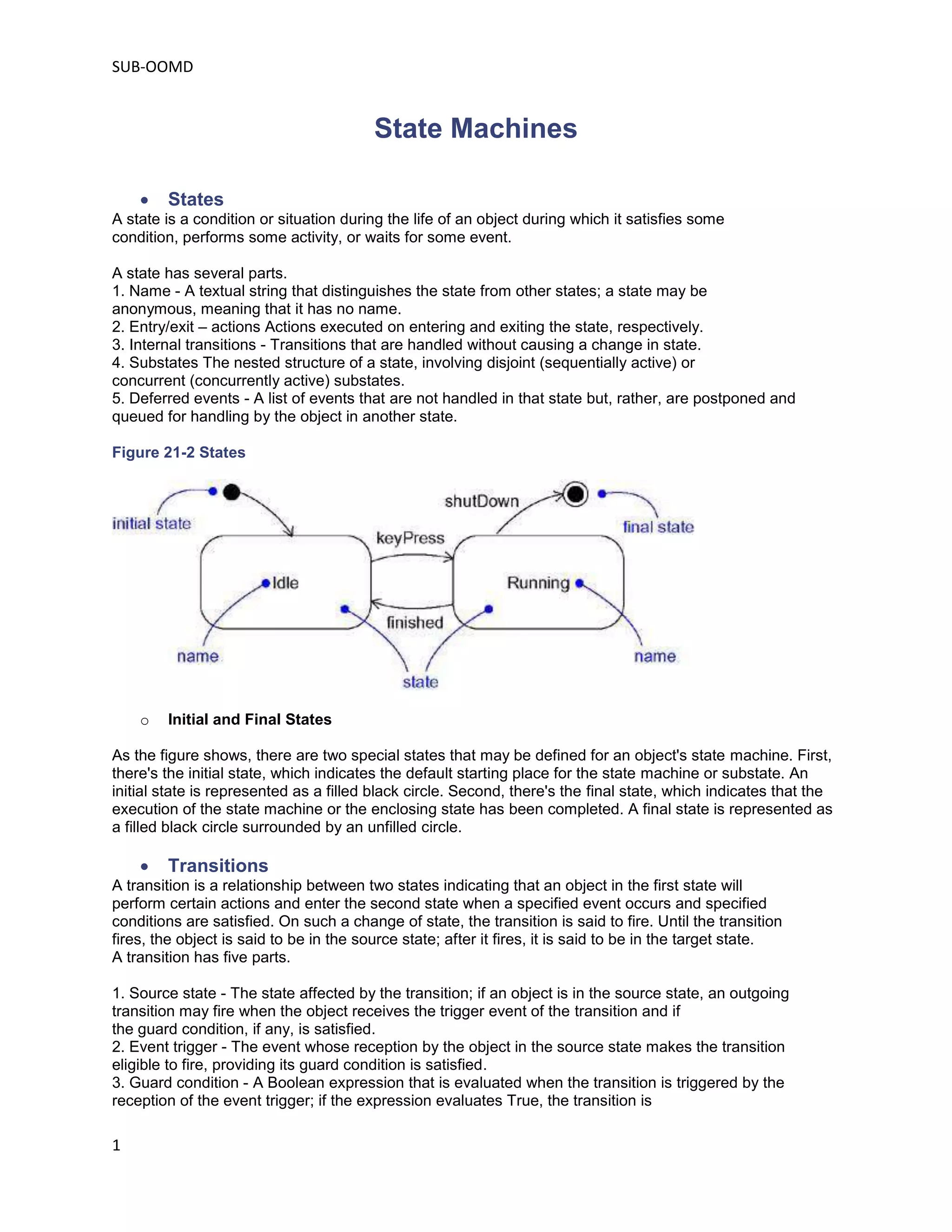
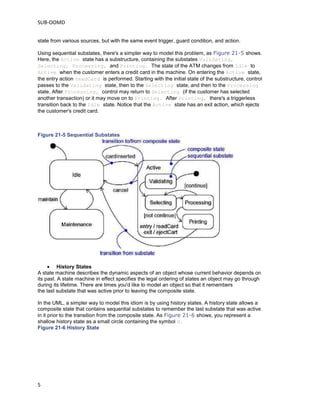
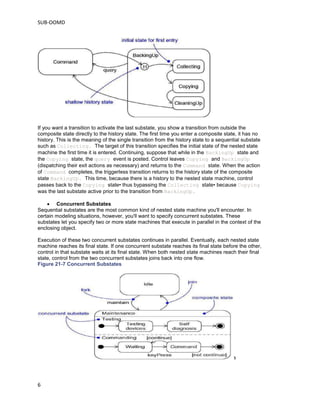
State machines model the different states an object can be in and the transitions between those states. A state represents a condition or situation during an object's lifetime. Transitions between states are triggered by events and may include actions. States can have substates that run either sequentially or concurrently. Sequential substates represent stages in a process, while concurrent substates run in parallel. Advanced state machine features like entry/exit actions, internal transitions, and history states help simplify complex models.