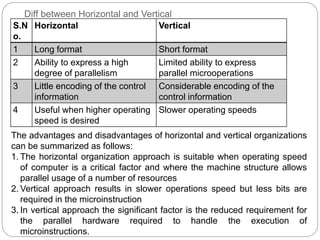
This document discusses hardwired control and microprogrammed control in computer processors. It provides details on:
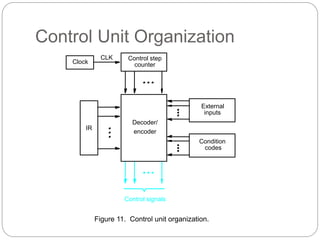
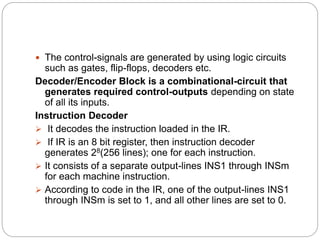
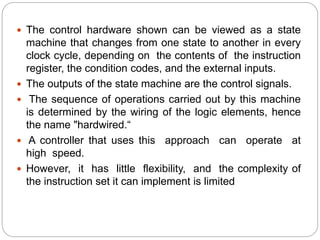
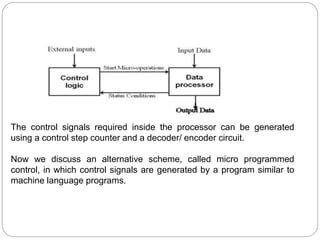
- Hardwired control generates control signals using logic circuits like gates and counters. It can operate at high speed but has little flexibility and complexity is limited.
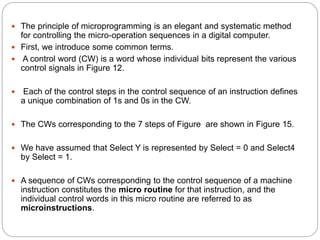
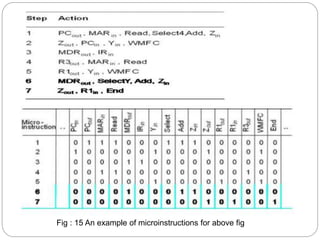
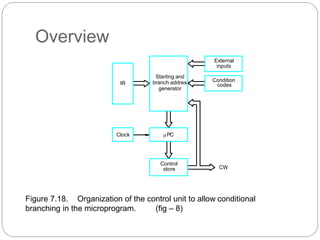
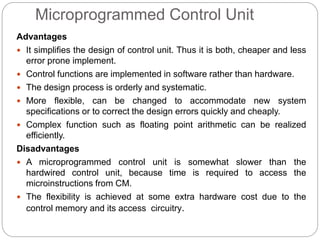
- Microprogrammed control stores sequences of control words (microinstructions) in a control store. It uses a microprogram counter to sequentially fetch microinstructions and generate control signals. This allows for more flexible control but is slower than hardwired.
- Key components of a microprogrammed control unit include the control store, microprogram counter, and starting address generator block to load addresses and support conditional branching in the microcode.