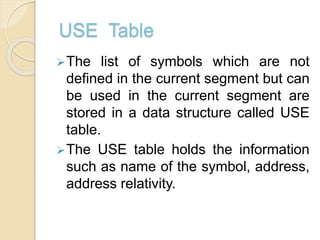
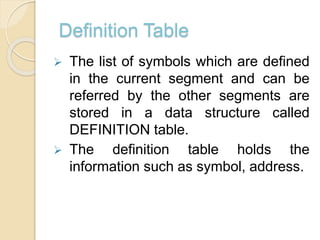
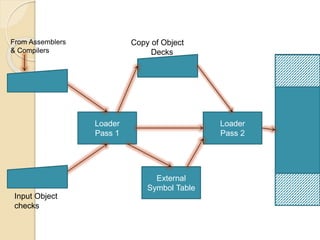
The document summarizes the key aspects of direct linking loaders. A direct linking loader allows for multiple procedure and data segments and flexible intersegment referencing. It provides assembler output with the length and symbol tables (USE and DEFINITION) to the loader. The loader performs two passes, building a Global External Symbol Table in Pass 1 and performing relocation and linking in Pass 2 using the object decks with External Symbol Dictionary, instructions/data, and relocation/linkage sections. This allows combining and executing object code from separate object programs.