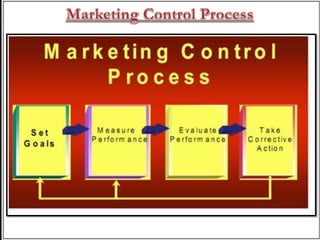
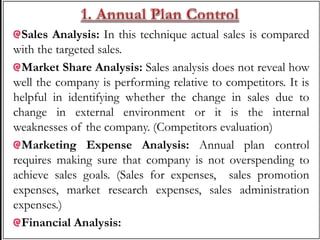
The document discusses various aspects of controlling marketing operations. It defines marketing control as monitoring marketing plans and adjusting as needed to achieve goals. There are four main steps to marketing control: 1) establishing performance standards, 2) measuring actual performance, 3) comparing performance to standards, and 4) taking corrective actions as needed. The document also outlines different types of marketing controls including annual plan control, profitability control, efficiency control, and strategic control, which involve analyzing sales, profits, expenses, financials, market share, and customer attitudes. Marketing audits provide in-depth analysis of a company's marketing environment, strategies, and activities to identify issues and improve performance.