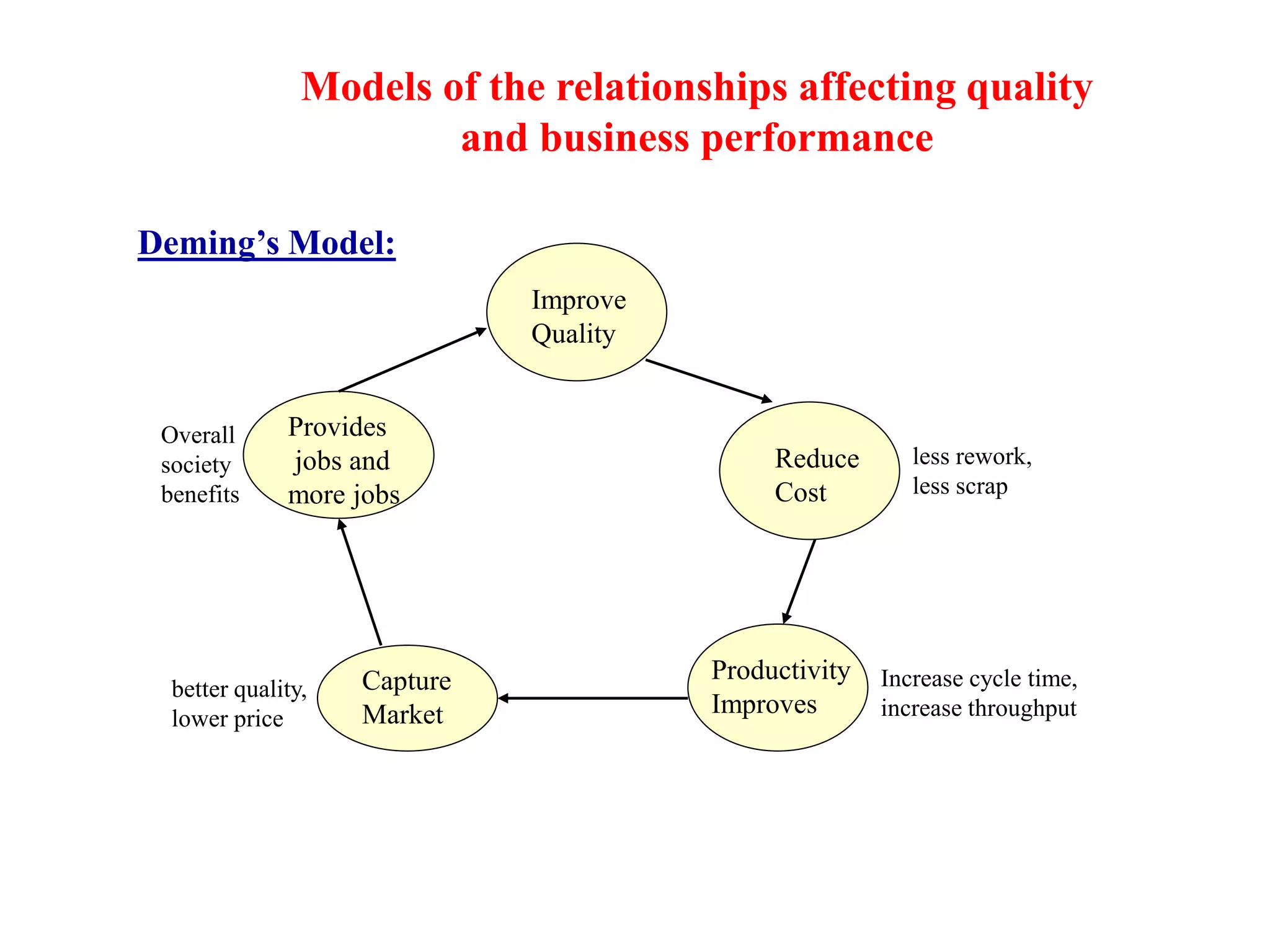
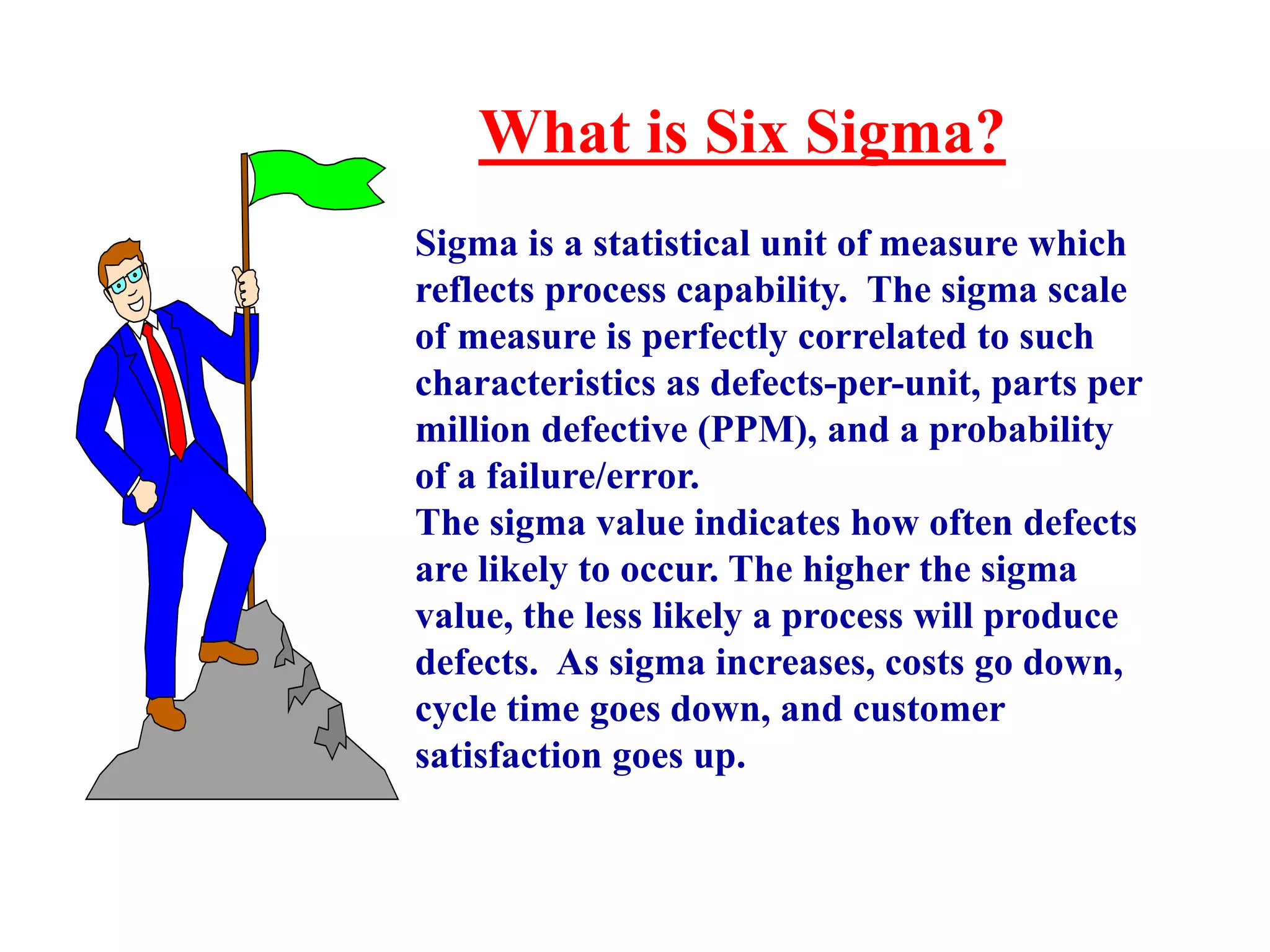
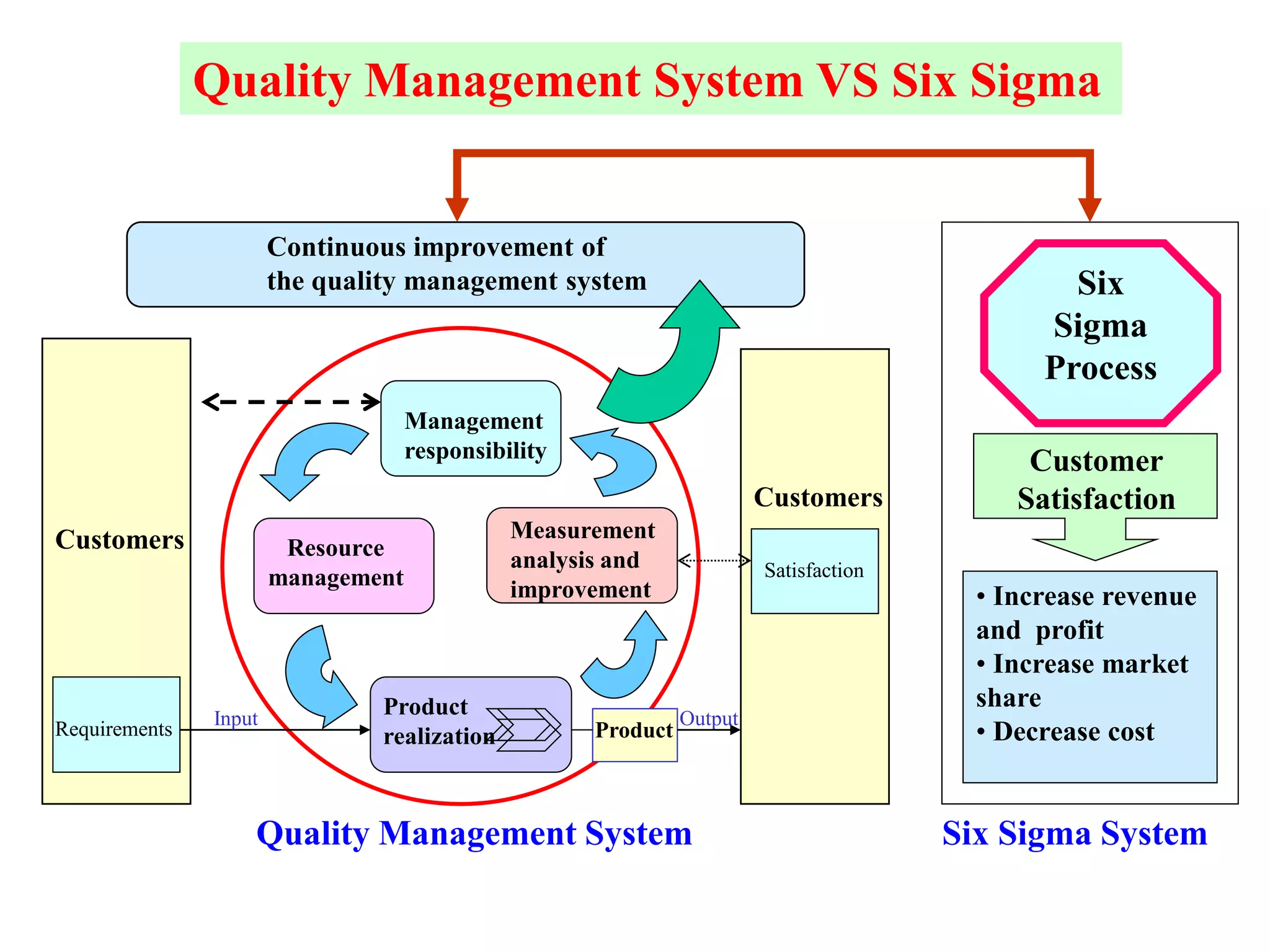
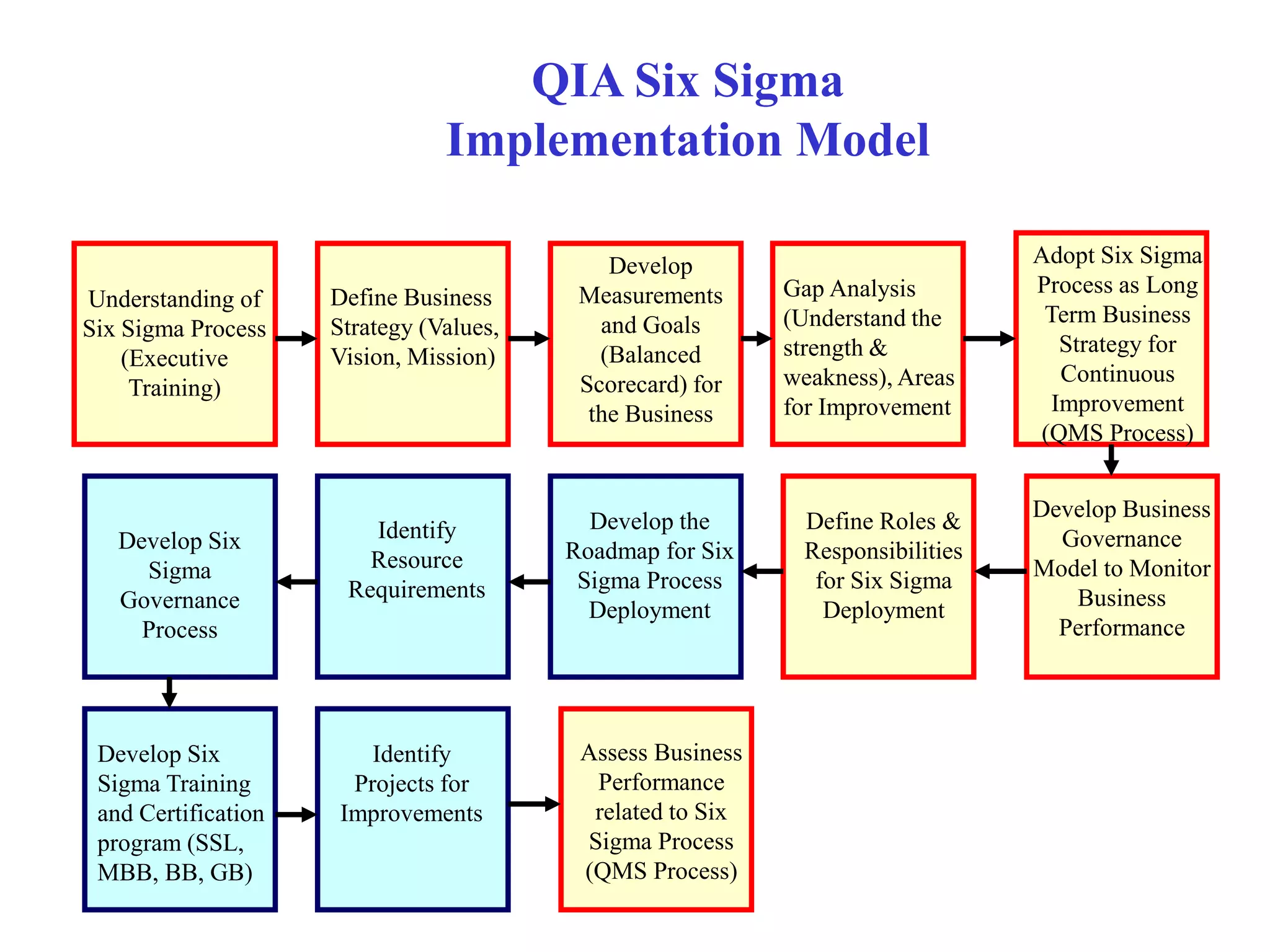
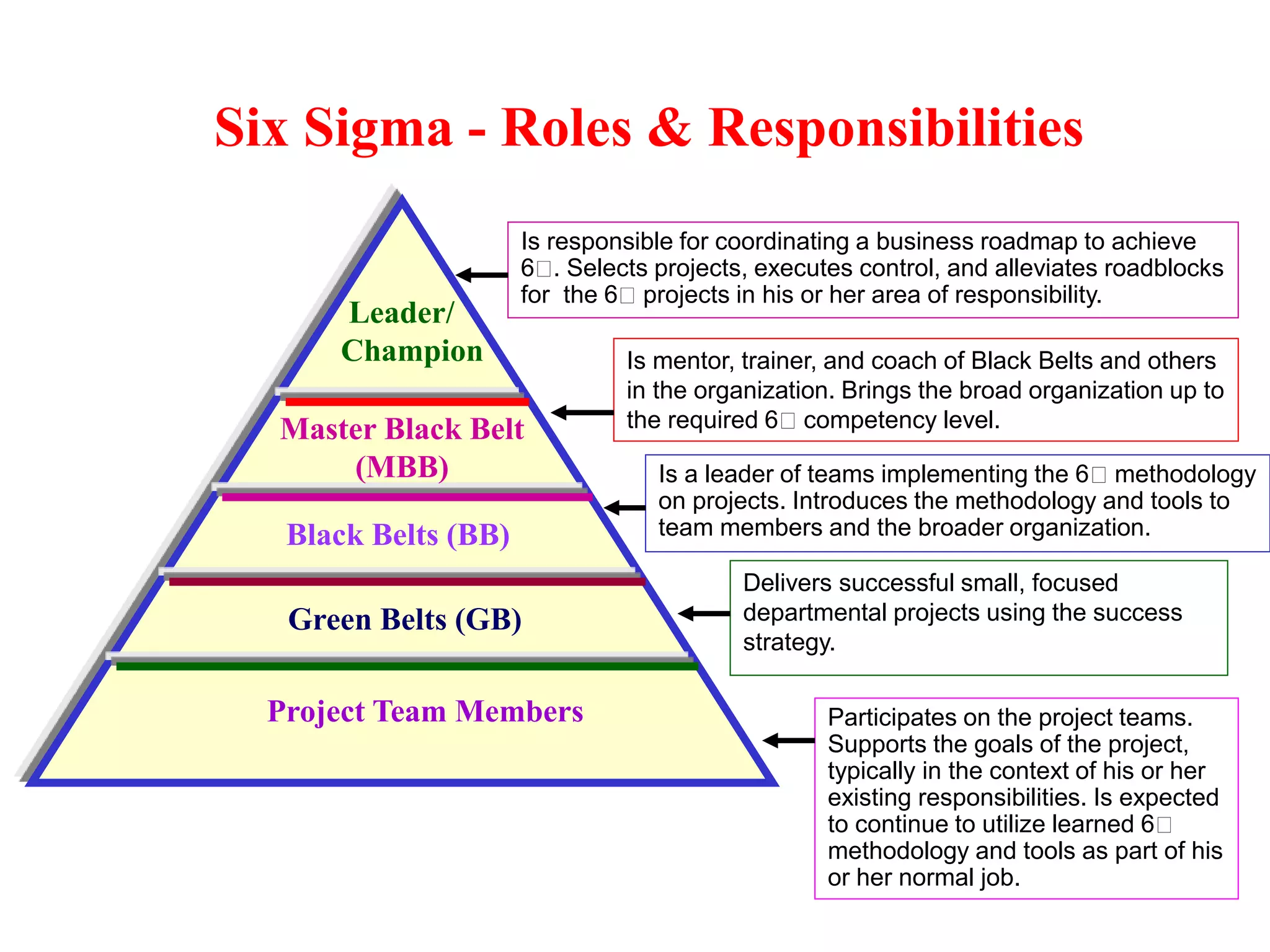
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology for improving processes by reducing variability, waste, and defects. It aims to achieve near-perfect process efficiency, accuracy, and quality. Key aspects of Six Sigma include defining and measuring quality in terms of defects per million opportunities, setting ambitious quality goals such as 3.4 defects per million, training Green and Black Belts to lead improvement projects, and delivering substantial financial returns and customer satisfaction gains. Implementing Six Sigma requires executive support, thorough training programs, establishing roles and responsibilities, identifying high-impact projects, and continuously measuring outcomes.