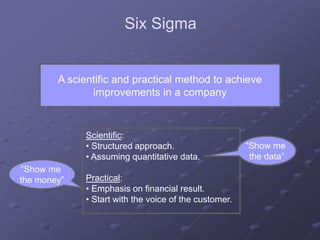
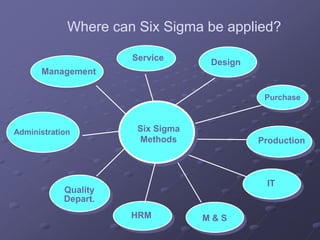
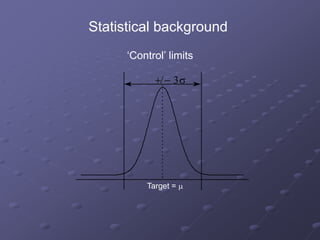
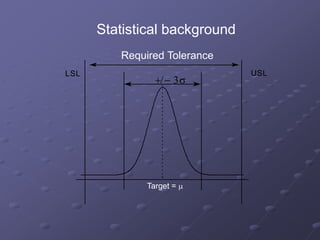
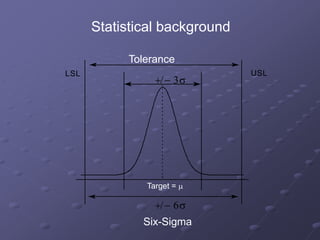
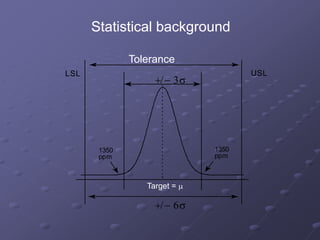
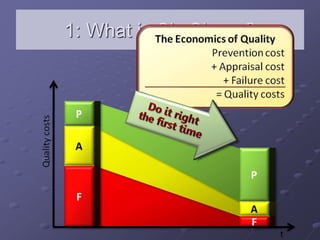
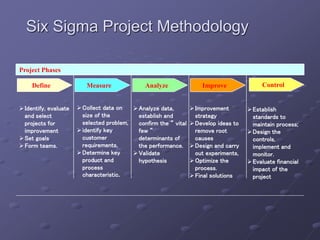
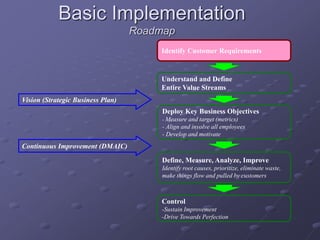
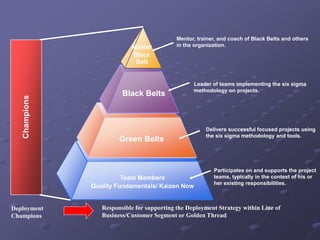
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology for improving processes by eliminating defects. It involves the following key aspects:
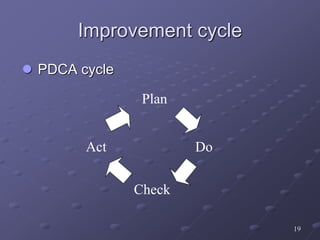
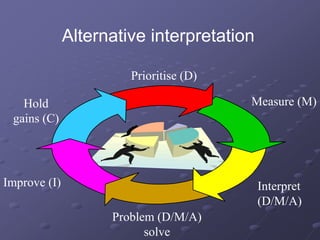
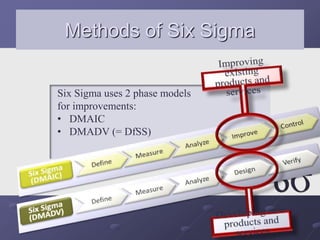
- A structured DMAIC methodology of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control phases to systematically solve problems.
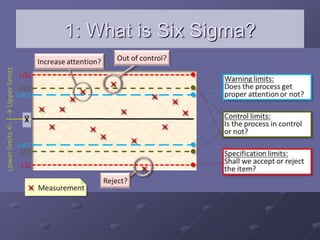
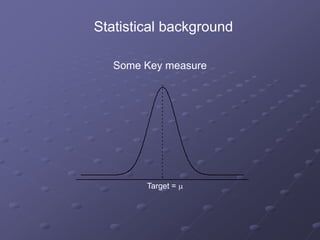
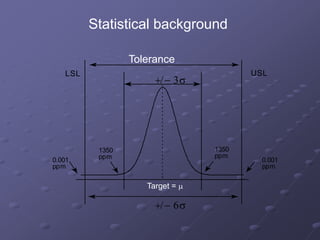
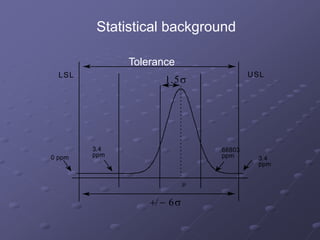
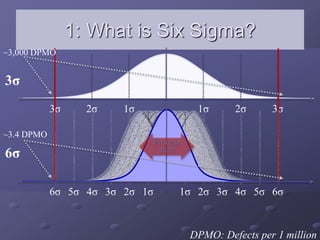
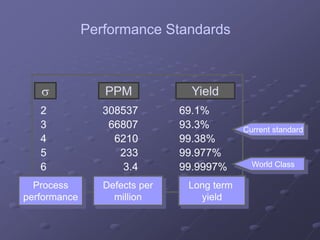
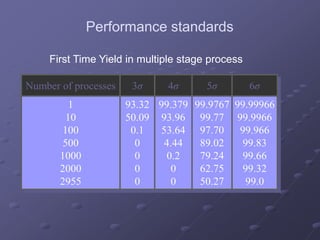
- A focus on processes capable of producing no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. This is derived from operating processes with no more than six standard deviations from the mean.
- Use of statistical tools during the Analyze phase to determine root causes of defects and during the Improve phase to develop and test solutions.
- An emphasis on controlling performance through statistical process controls after improvements are made to maintain results.