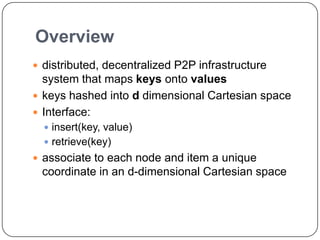
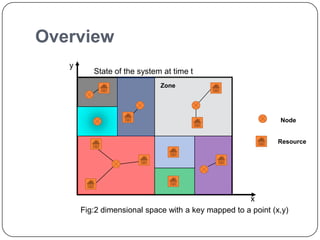
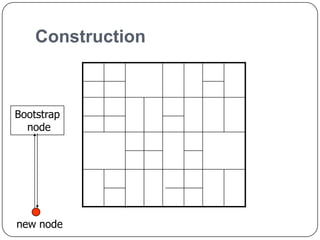
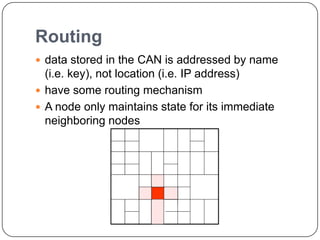
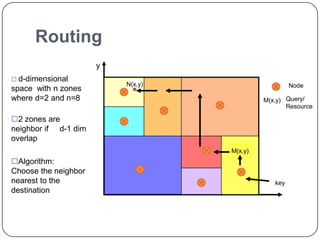
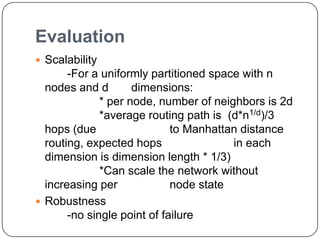
This document summarizes Content Addressable Network (CAN), a structured peer-to-peer network. CAN partitions a virtual d-dimensional space among nodes, with each node responsible for a zone. It allows keys to be mapped to values by hashing keys to points in the space. New nodes join by contacting an existing node and splitting its zone. Routing is done by forwarding requests to the node responsible for the zone containing the destination point. Zones are reassigned if neighboring nodes fail to send periodic alive messages. CAN scales well as routing path length increases slowly with number of nodes. Future work could involve increasing dimensions, caching, and zone overloading.