Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




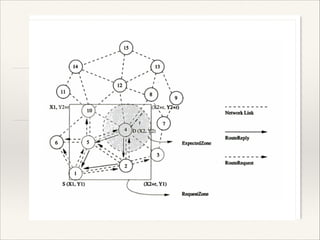

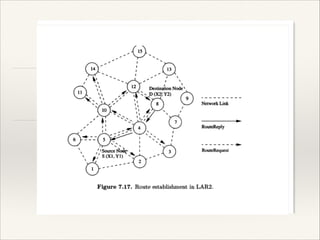




LAR utilizes location information to improve routing efficiency by reducing control overhead. It uses GPS to obtain geographical information. There are two zones in LAR - the ExpectedZone where the destination is expected to be, and the RequestZone which is the area where routing packets can propagate. PAR aims to minimize energy consumption per packet by calculating the sum of energy required at each hop. It also aims for maximum network connectivity and uniform distribution of power consumption across all nodes.









