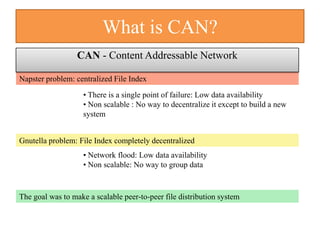
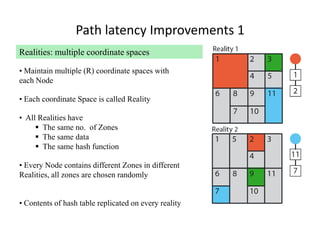
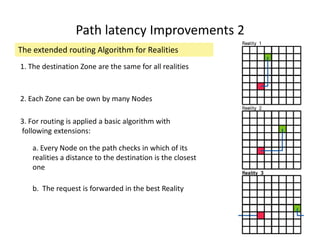
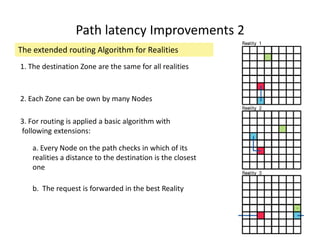
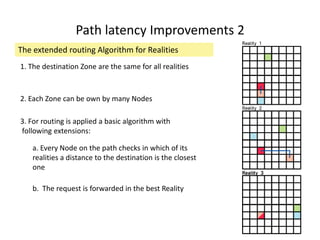
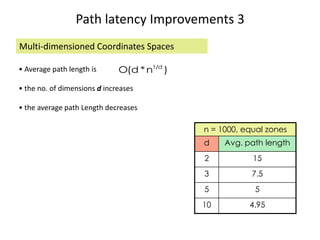
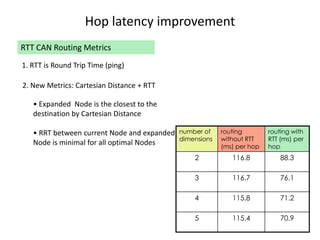
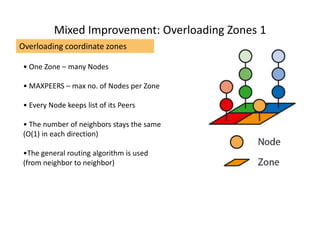
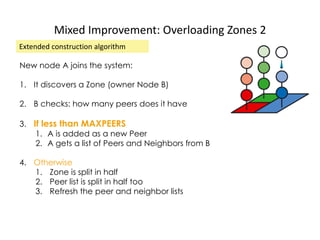
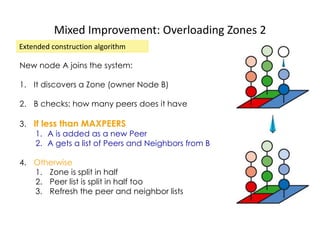
CAN is a distributed hash table that provides a scalable peer-to-peer architecture for data storage and retrieval. It addresses issues with centralized systems like Napster and completely decentralized systems like Gnutella by partitioning the network's virtual space among nodes. Nodes are responsible for zones in this space, and messages are routed through the network to the node responsible for a given zone. Several improvements were proposed to enhance CAN, such as using multiple coordinate spaces to improve routing latency and overloading zones to increase data availability. While powerful, CAN has some limitations regarding load balancing, query correctness, and susceptibility to attacks.


![CAN Routing
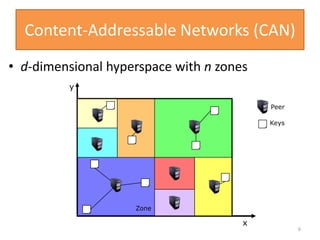
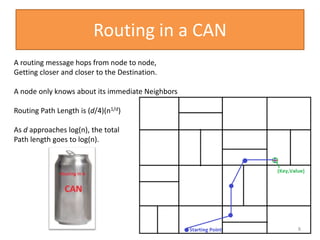
• d-dimensional space with n zones
• Two zones are neighbors if d-1 dimensions overlap
7
y
x
[x,y]
Peer
Keys
lookup([x,y])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canppt-140424113135-phpapp02/85/Can-ppt-7-320.jpg)
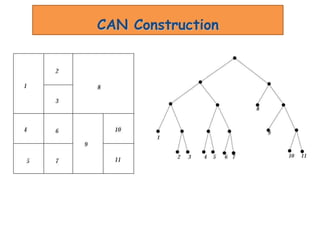
![CAN Construction
Joining CAN
1.Pick a new ID [x,y]
2.Contact a bootstrap
node
3.Route a message to
[x,y], discover the
current owner
4.Split owners zone in
half
5.Contact new
neighbors
9
y
x
New Node
[x,y]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canppt-140424113135-phpapp02/85/Can-ppt-9-320.jpg)

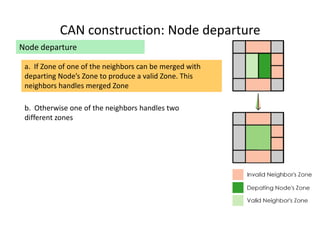
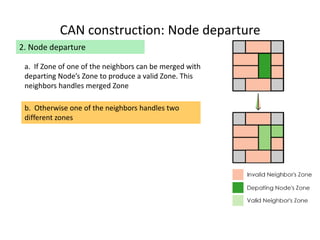
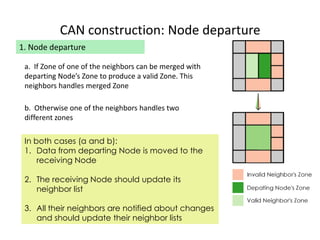




![REFERENCES
• [1] S. Ratnasamy, P. Francis, M. Handley, R. Karp, and S. Shenker. A Scalable Content-
Addressable Network. In ICSI Technical Report, Jan. 2001.
• [2] Balasubramanian, R.; Injong Rhee; Jaewoo Kang, "A scalable architecture for SIP
infrastructure using content addressable networks," Communications, 2005. ICC 2005. 2005
IEEE International Conference on , vol.2, no., pp.1314,1318 Vol. 2, 16-20 May 2005
• [3] Shidong Zhang; Bai Wang; Gengyu Wei; Chao Xin, "Web QoS Management Model
Based on CAN," Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), 2011 Fourth International
Symposium on , vol.1, no., pp.143,146, 28-30 Oct. 2011
• [4] Zhongtao Li; Weis, T., "Using zone code to manage a Content-Addressable Network for
Distributed Simulations," Communication Technology (ICCT), 2012 IEEE 14th International
Conference on , vol., no., pp.1350,1357, 9-11 Nov. 2012
• [5] Al-Omari, D.K.; Gurbani, V.K.; Anjali, T., "A novel architecture for a computer network
defense (CND) system using Content Addressable Networks (CAN)," Globecom Workshops
(GC Wkshps), 2012 IEEE , vol., no., pp.758,762, 3-7 Dec. 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canppt-140424113135-phpapp02/85/Can-ppt-36-320.jpg)
