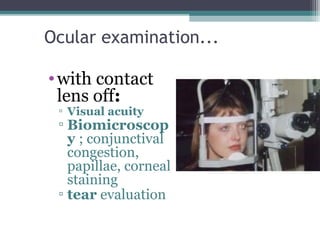
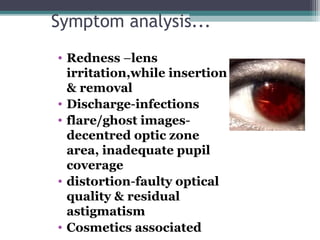
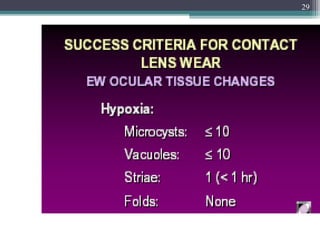
This document discusses the purpose and process of a contact lens aftercare visit. The goals are to maintain good lens performance, check for eye health issues caused by contact lens wear, and address any discomfort or vision problems. The visit involves taking a case history, examining the eyes with and without lenses, reviewing care and maintenance, resolving any identified problems, and providing advice or treatment. Examinations check vision, comfort, lens fit, and eye health using tools like a slit lamp. Common problems addressed include blurry vision, redness, discharge, and discomfort, which can indicate issues like improper lens power or fitting, solution toxicity, or infections. The criteria for a successful visit are meeting wearing time and comfort expectations and achieving good vision