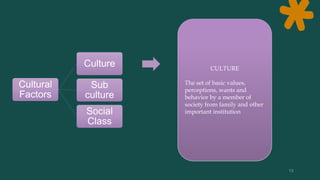
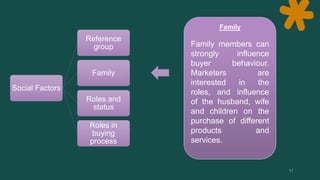
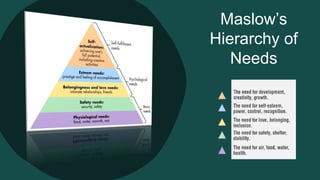
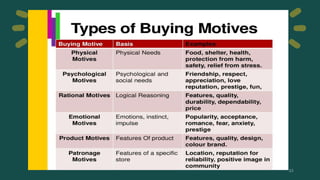
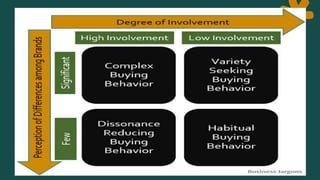
Consumer behavior involves how individuals search for, select, purchase, use, and dispose of products and services. It is defined as the activities people undertake when obtaining, consuming, and disposing of products and services. Consumer behavior is influenced by both external factors like culture, social groups, and internal factors like personal characteristics, psychology. Understanding consumer behavior helps marketers analyze opportunities, and make marketing mix decisions like product, price, place, and promotion.