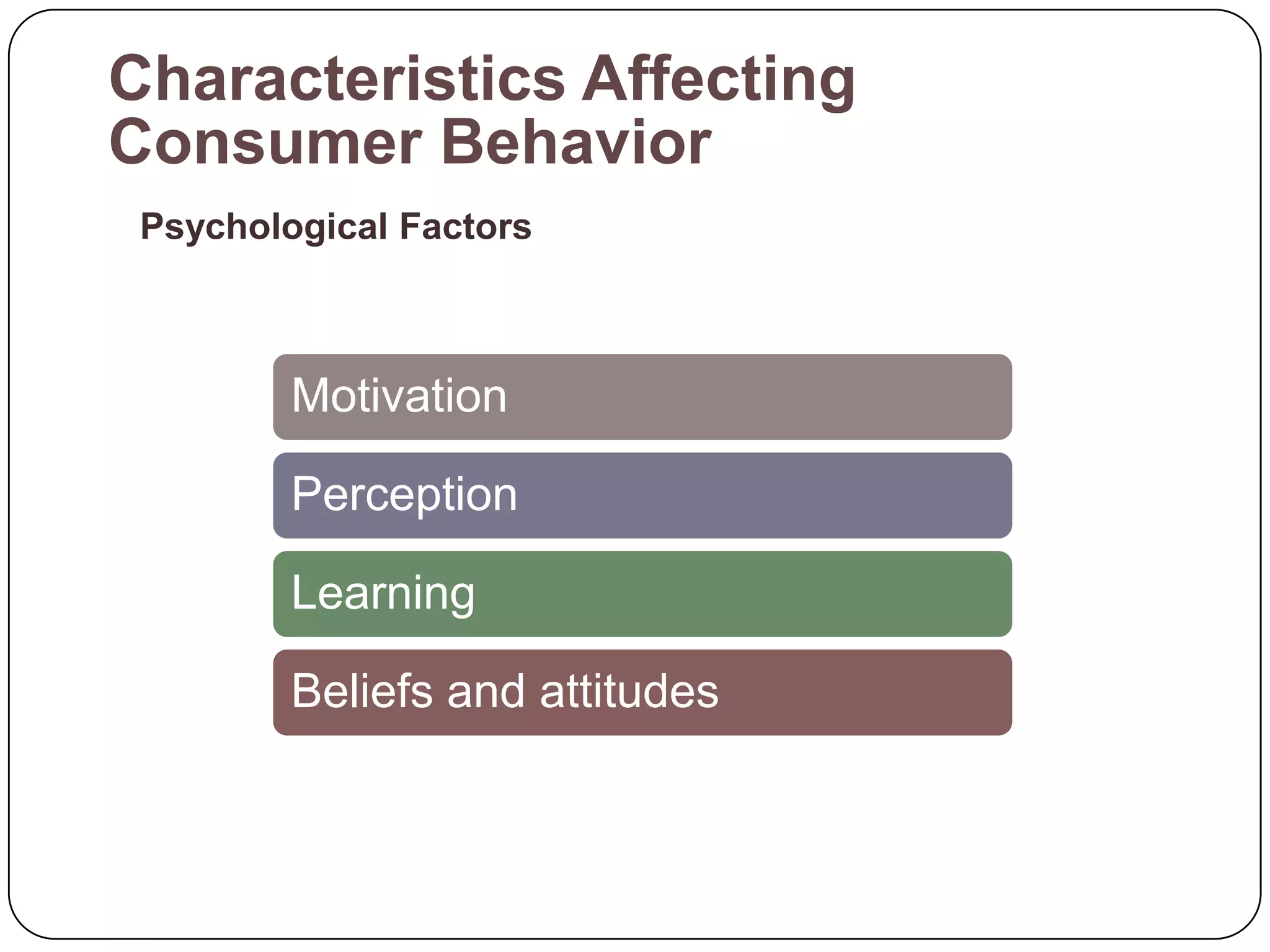
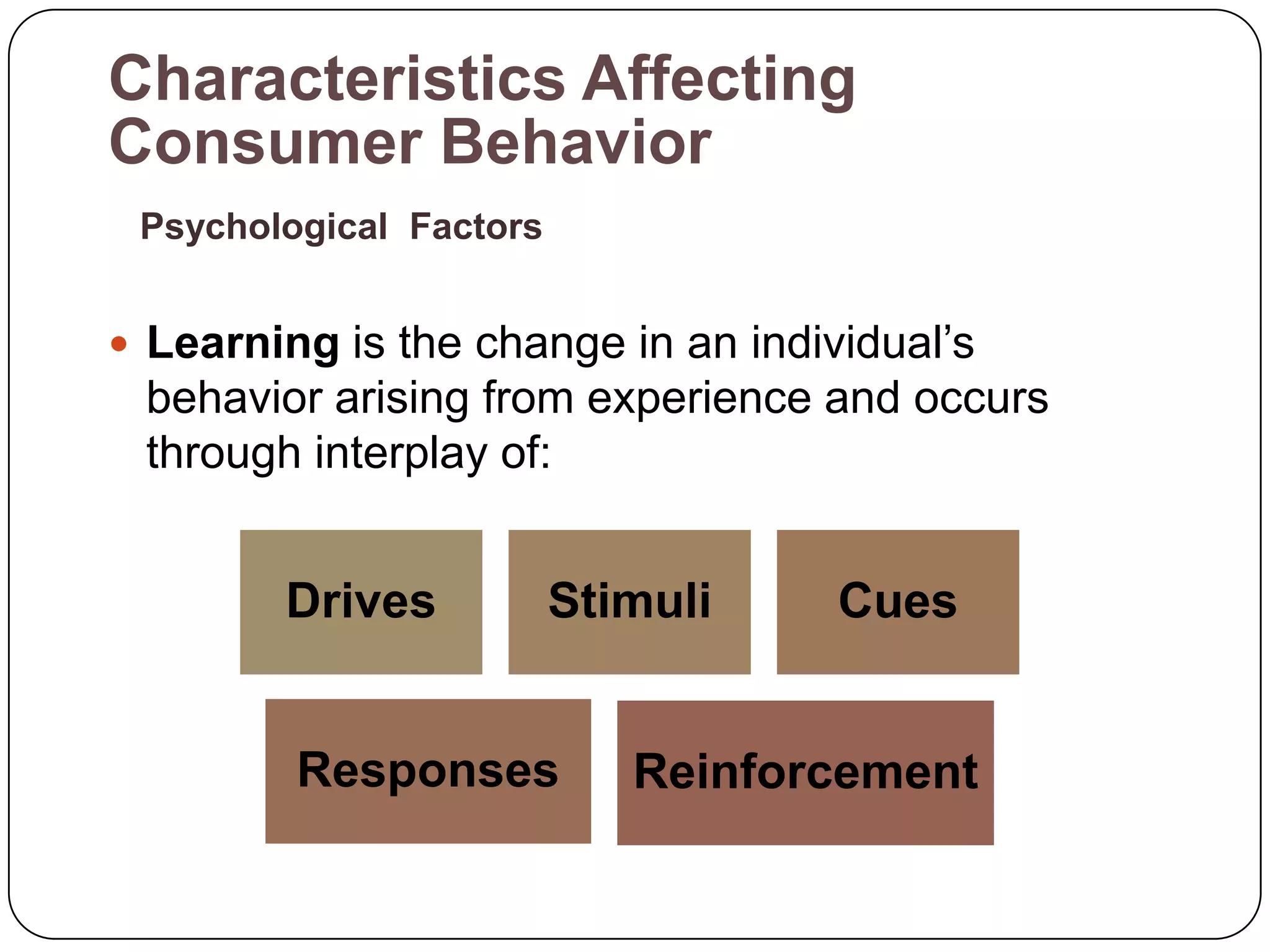
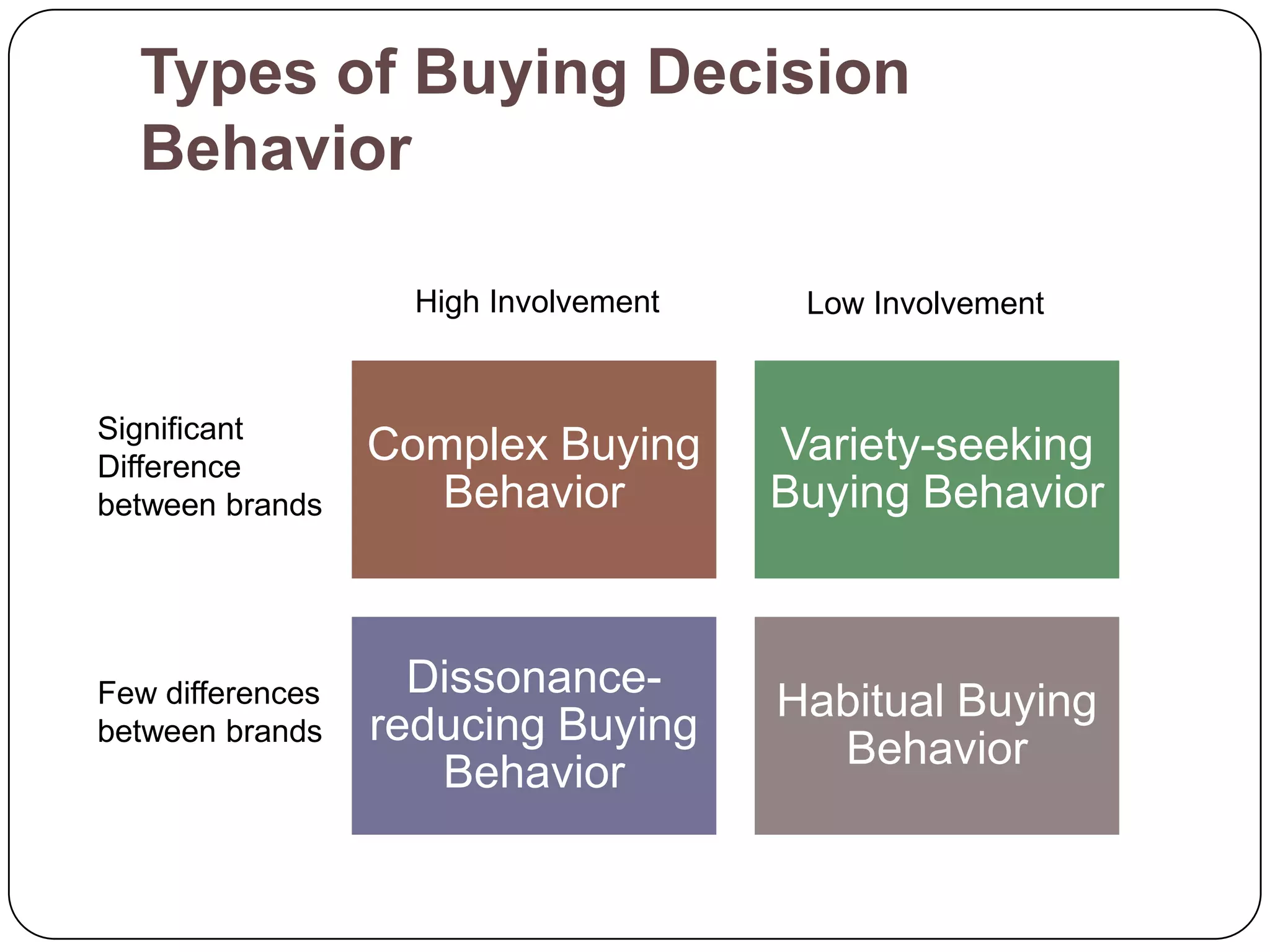
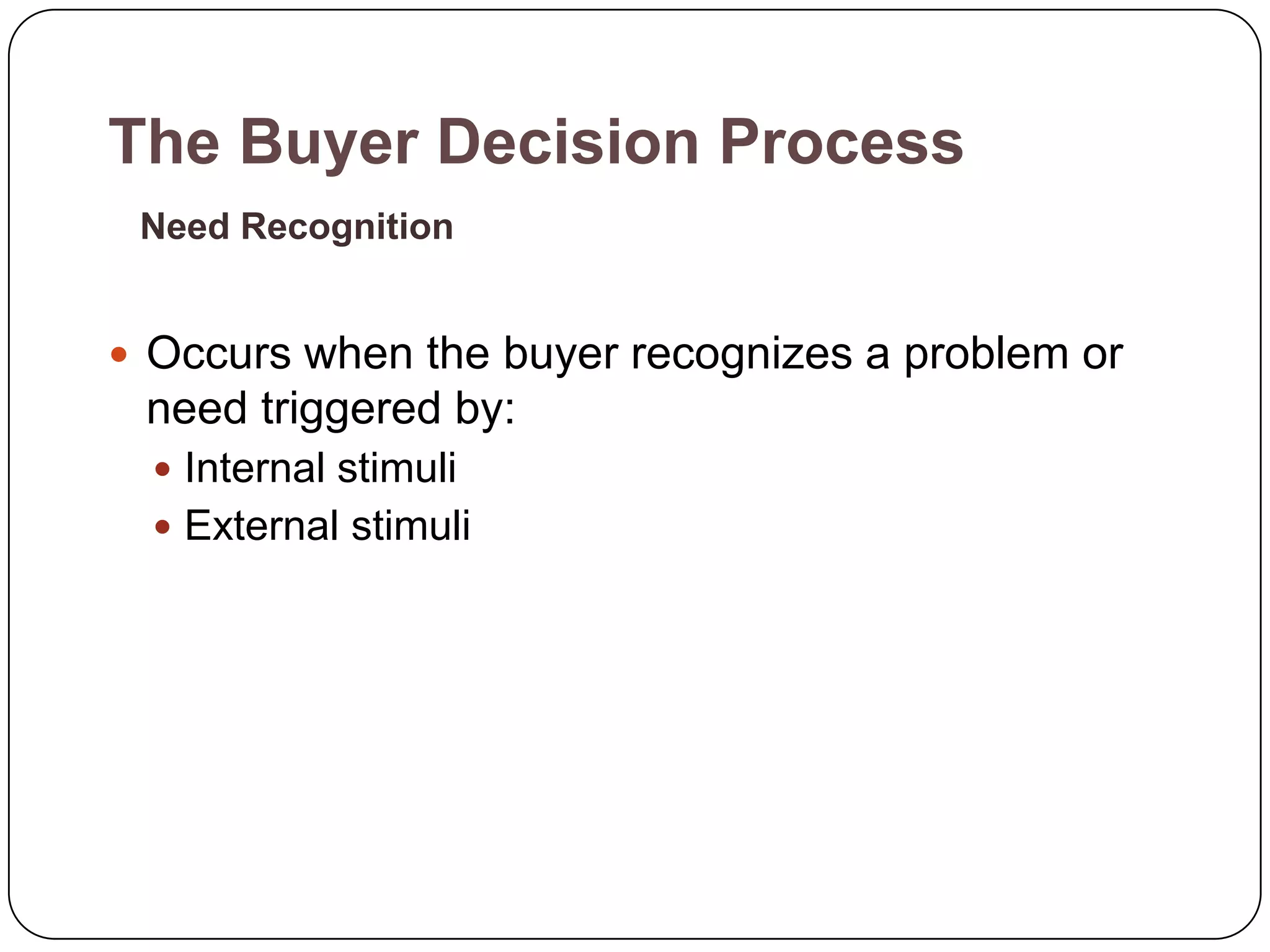
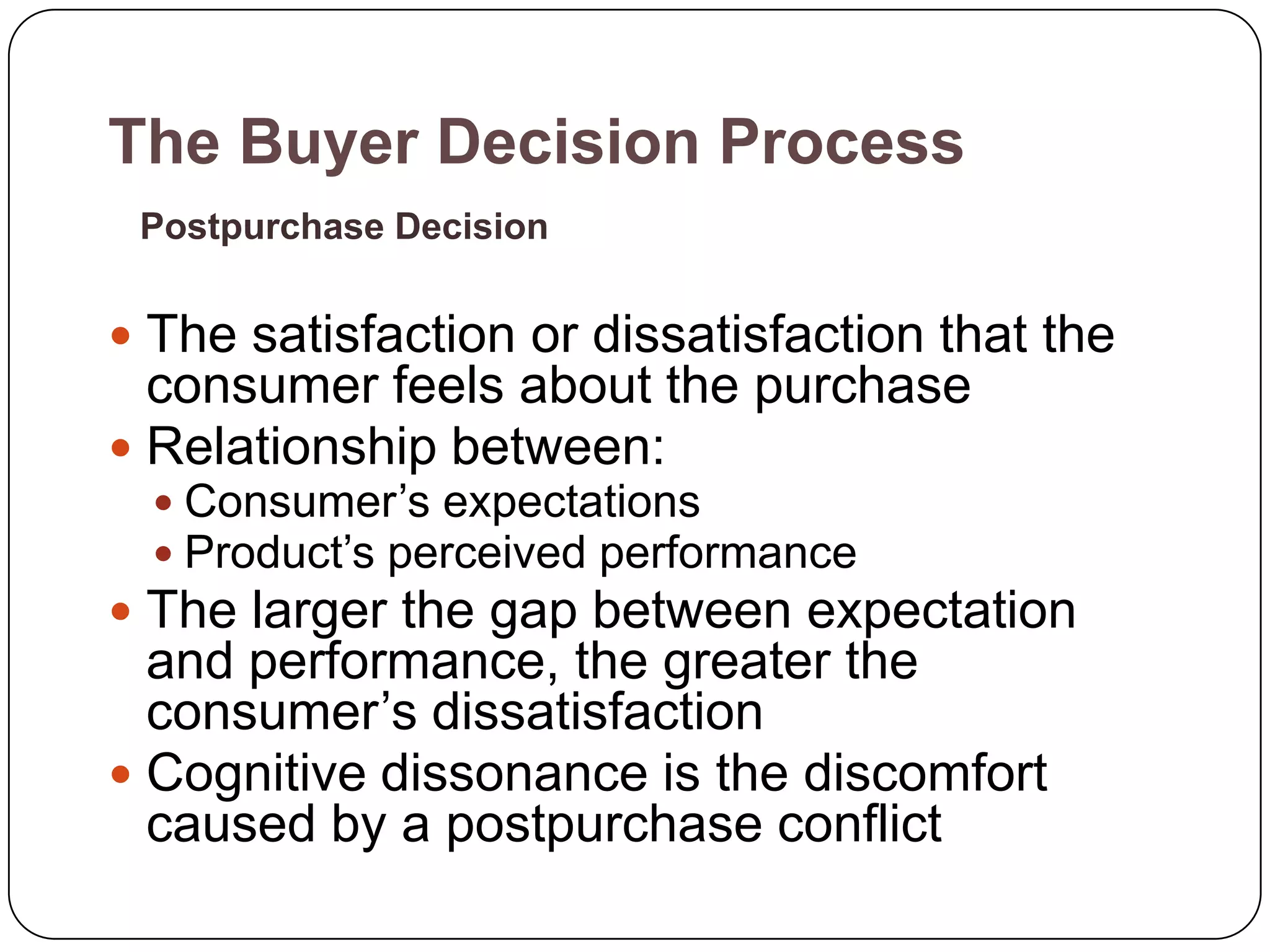
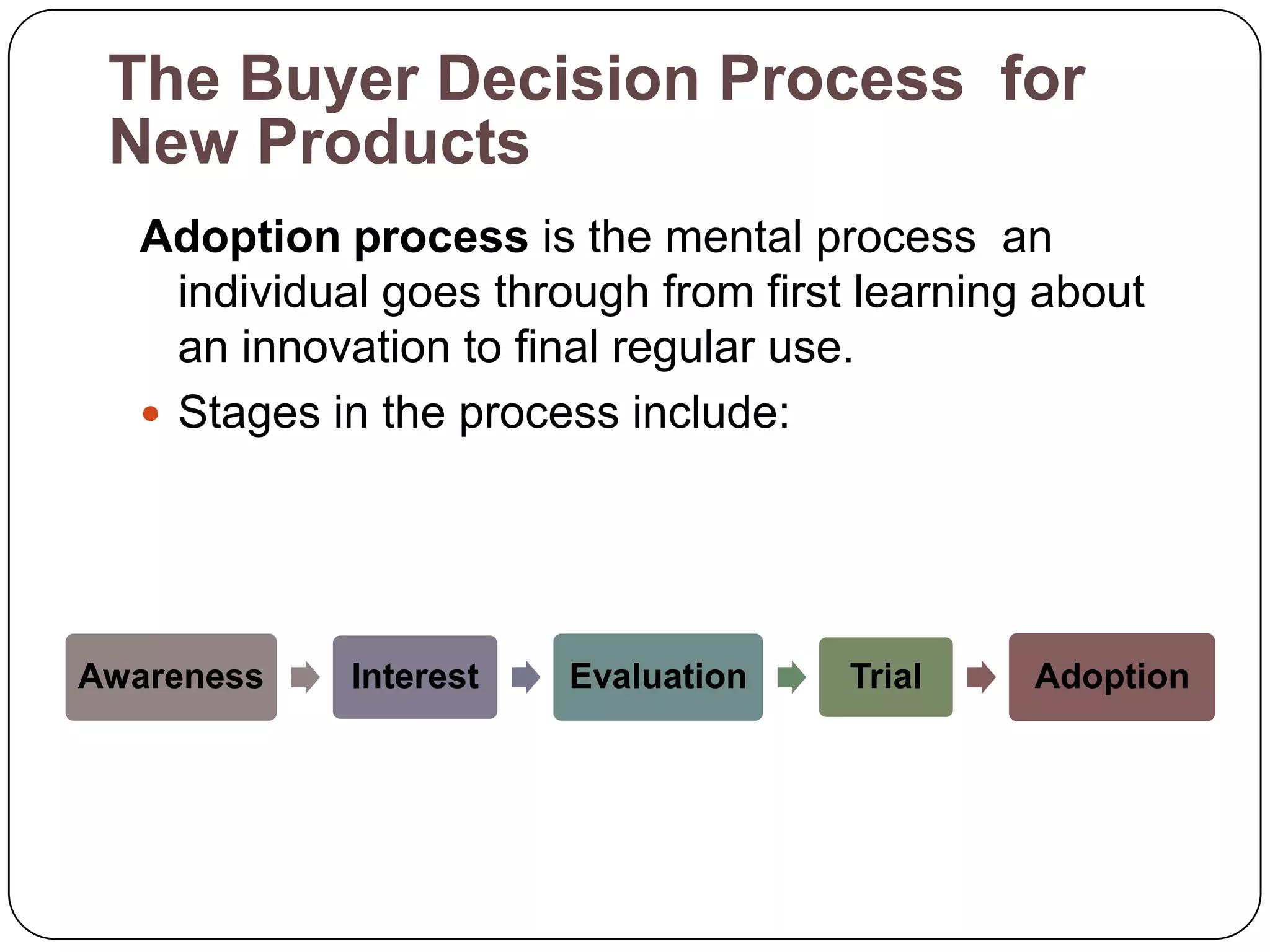
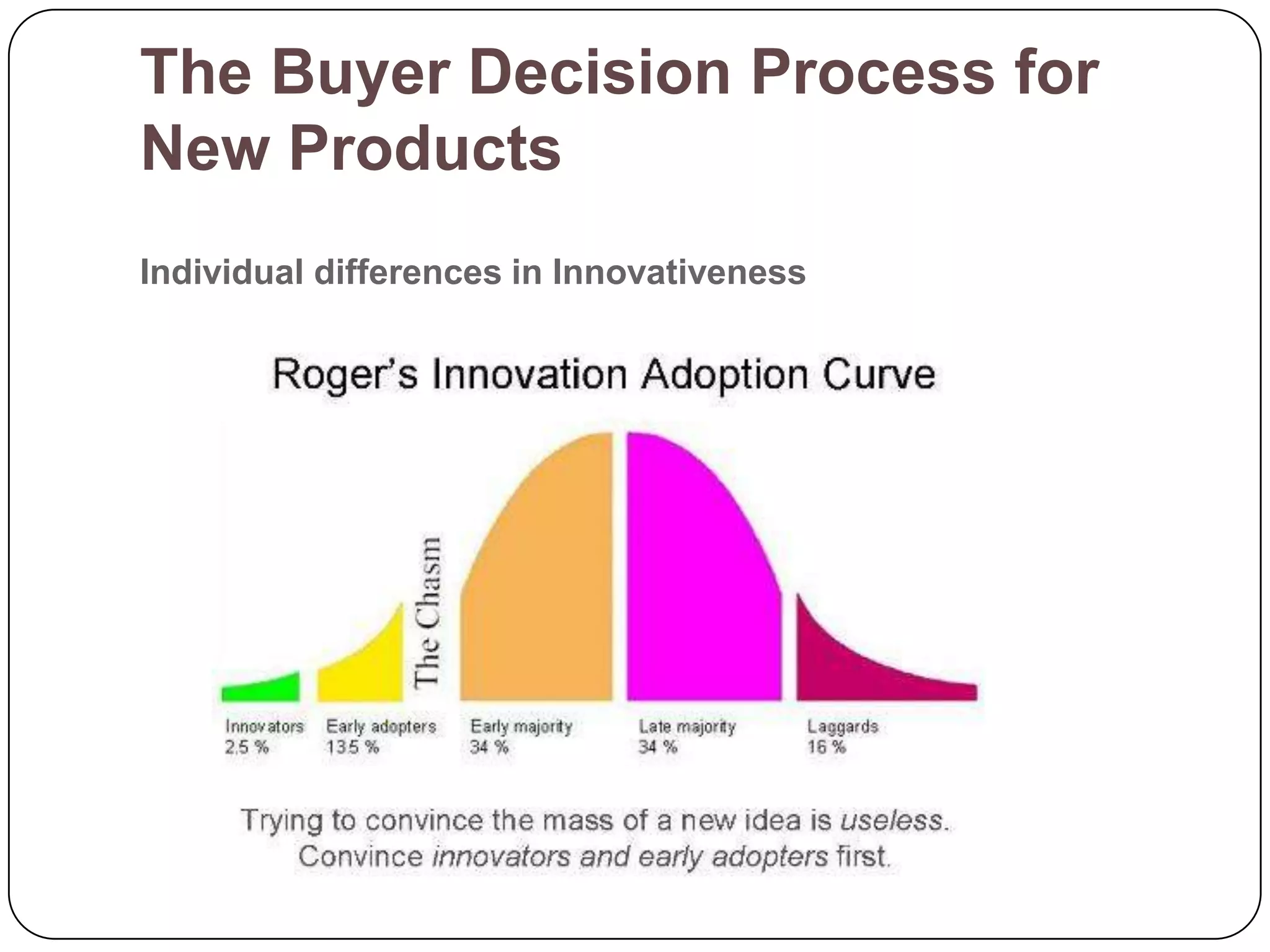
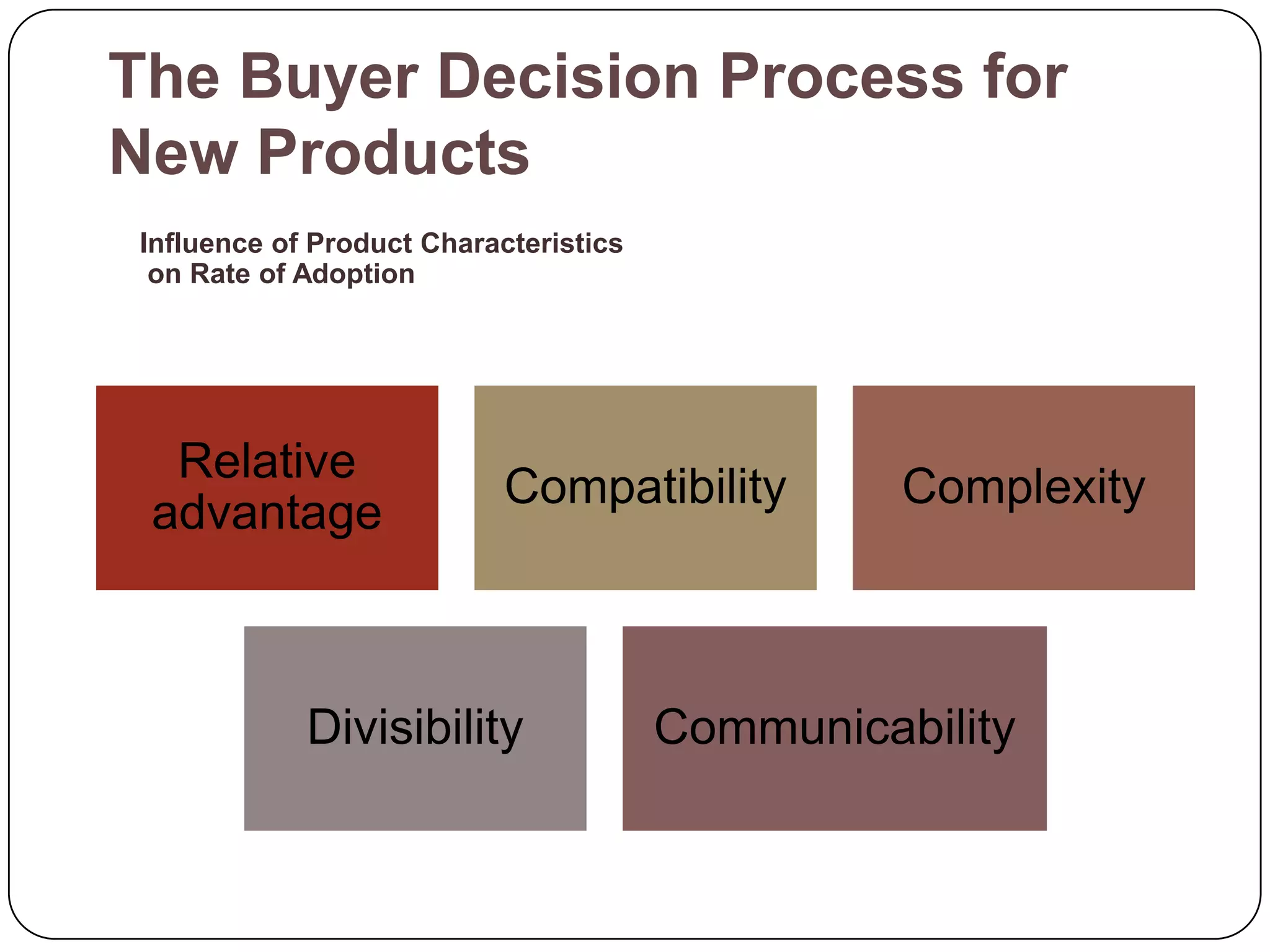
The document discusses psychological factors that affect consumer behavior, including motivation, perception, learning, and beliefs/attitudes. It also covers the buyer decision process, which involves need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase decision. The buyer decision process for new products includes stages from awareness to adoption, and is influenced by individual differences in innovativeness and characteristics of the product like relative advantage and compatibility.