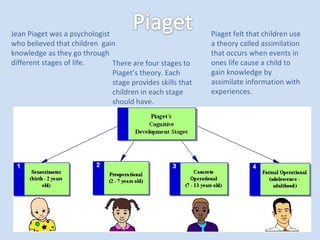
This document discusses constructivism as a learning theory where learners construct understanding through observation and interaction. It describes the theories of Piaget, Vygotsky, Bruner, and Dewey on cognitive development and the role of social interaction and experience in learning. The implications for the classroom are that teachers should use hands-on materials, ask open-ended questions, and scaffold instruction based on students' abilities while students work collaboratively and engage in experiential learning.







![Credits
ATHERTON J S (2010) Learning and Teaching; Constructivism in learning [On-
line] UK: Available:
http://www.learningandteaching.info/learning/constructivism.htm
Accessed: 22 November 2010
Shelly, Cashman, Gunter, & Gunter, . (2009). Integrating technology and
digital media in the classroom 6th ed.: teachers discovering computers.
Wood, K. C., Smith, H., Grossniklaus, D. (2001). Piaget's Stages of Cognitive
Development. In M. Orey (Ed.), Emerging perspectives on learning,
teaching, and technology. Retrieved <insert date>, from
http://projects.coe.uga.edu/epltt/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theoryteam7-101123082413-phpapp01/85/Theory-team-7-9-320.jpg)
![Credits
ATHERTON J S (2010) Learning and Teaching; Constructivism in learning [On-
line] UK: Available:
http://www.learningandteaching.info/learning/constructivism.htm
Accessed: 22 November 2010
Shelly, Cashman, Gunter, & Gunter, . (2009). Integrating technology and
digital media in the classroom 6th ed.: teachers discovering computers.
Wood, K. C., Smith, H., Grossniklaus, D. (2001). Piaget's Stages of Cognitive
Development. In M. Orey (Ed.), Emerging perspectives on learning,
teaching, and technology. Retrieved <insert date>, from
http://projects.coe.uga.edu/epltt/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theoryteam7-101123082413-phpapp01/85/Theory-team-7-10-320.jpg)