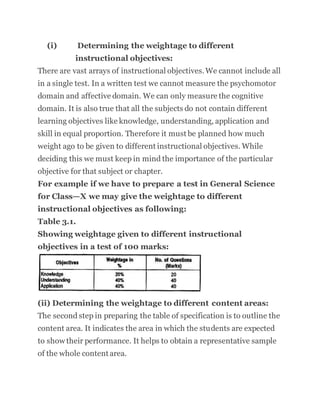
The document outlines the four main steps of standardized test construction: 1) Planning the test, 2) Preparing the test, 3) Trying out the test, and 4) Evaluating the test. It focuses on the first two steps. Step 1 involves determining test objectives, preparing test specifications including a table of specifications, and selecting item types. Step 2 is preparing test items according to the table of specifications, instructions for test takers, and a scoring key. Care must be taken to write clear, unbiased items that measure the intended objectives and cover the full content without technical flaws or irrelevant clues.