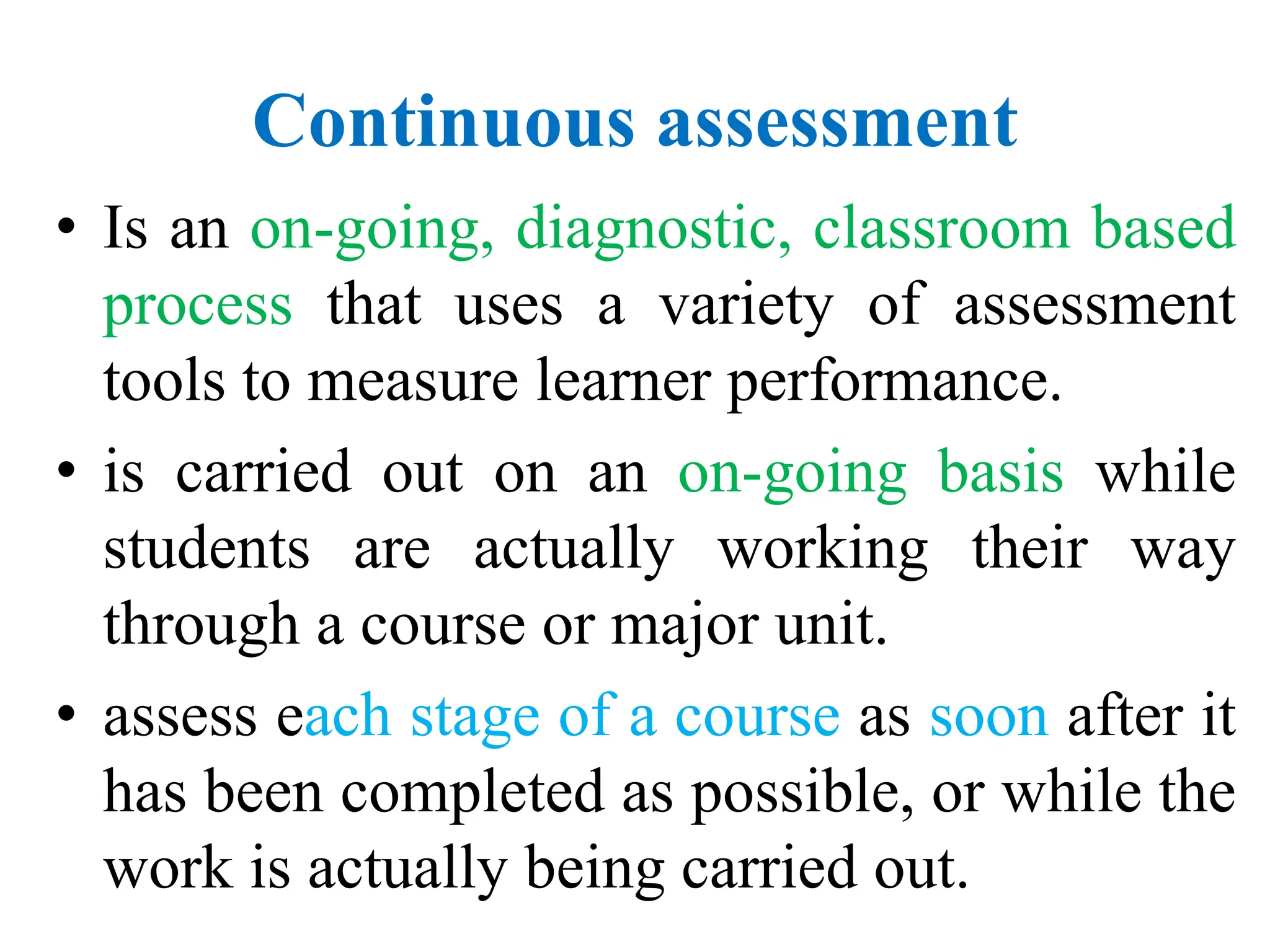
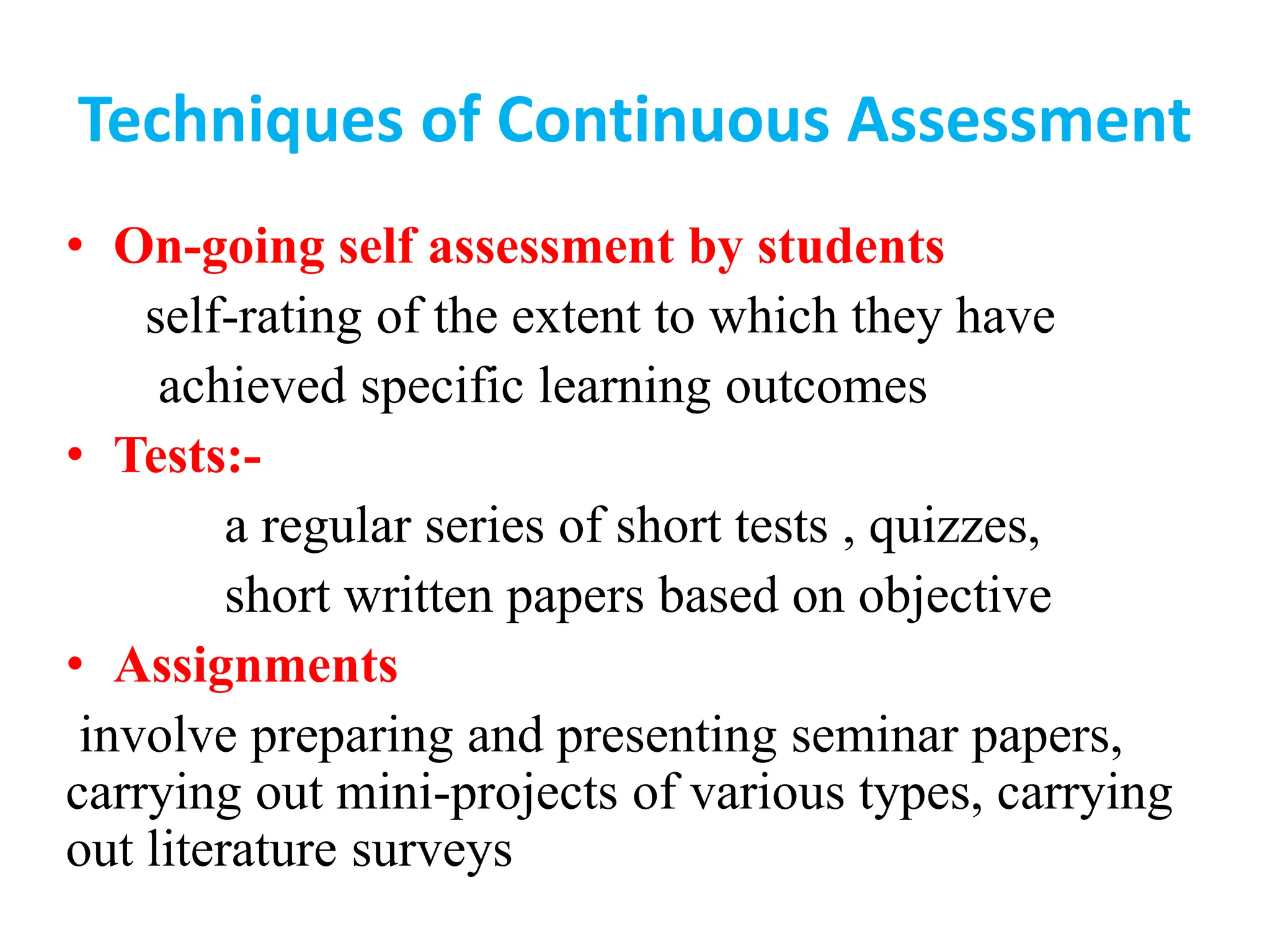
This document provides an overview of assessment concepts, types, and techniques used in educational settings, highlighting the distinctions between formative and summative assessments. It details various assessment methods, including quizzes, tests, and continuous assessment, and offers guidelines for constructing effective test items. Additionally, it discusses the importance of evaluation and feedback in enhancing learning outcomes.