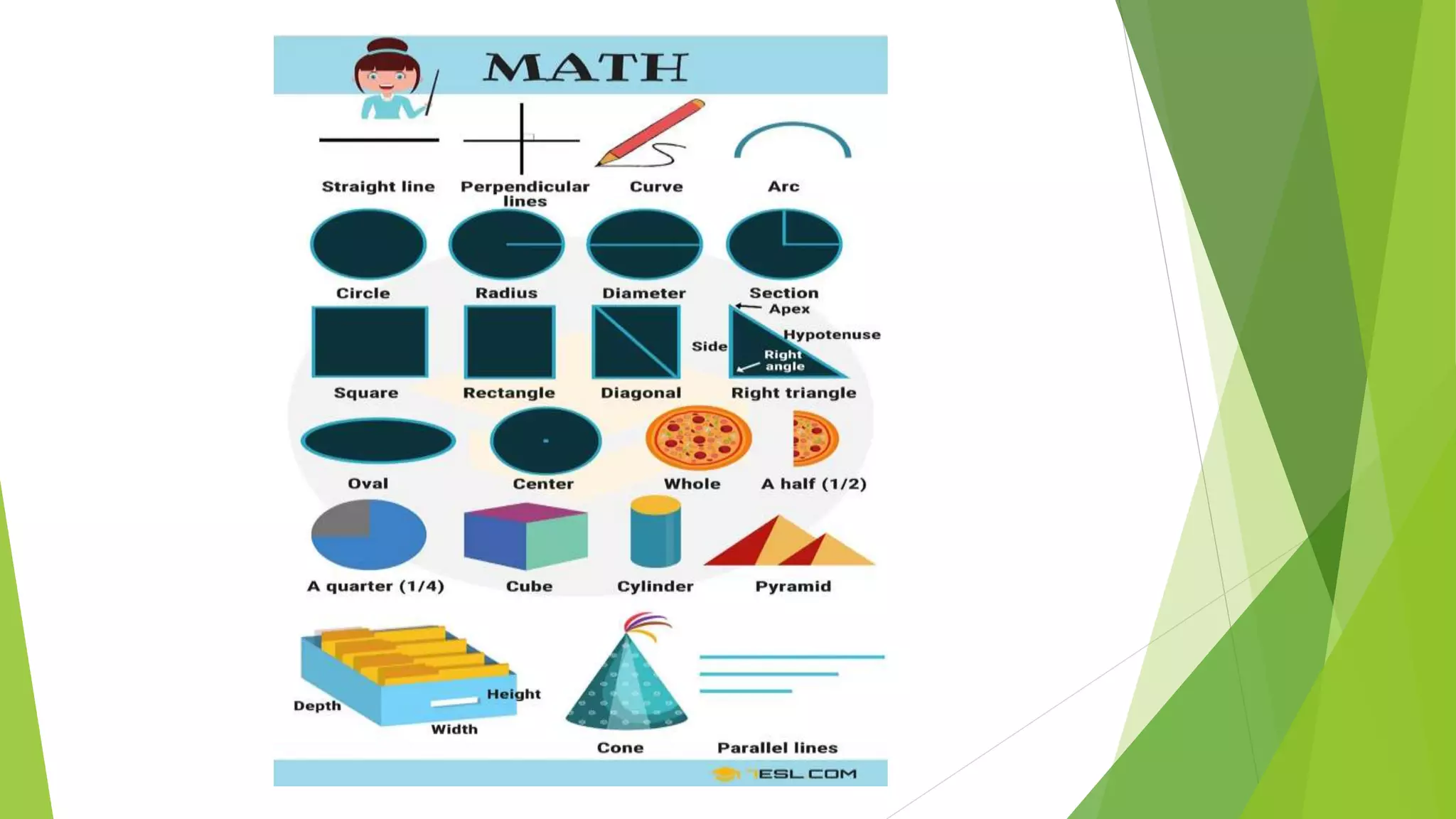
The document discusses the importance of mathematics in societal development, emphasizing its role in education and technological advancement. It defines mathematics as a systematic and precise science that encompasses various aspects, including quantity, measurement, and logical reasoning. The text also outlines the characteristics, terminology, notations, and algorithms associated with mathematics, highlighting its relevance in facilitating critical thinking and problem-solving skills.