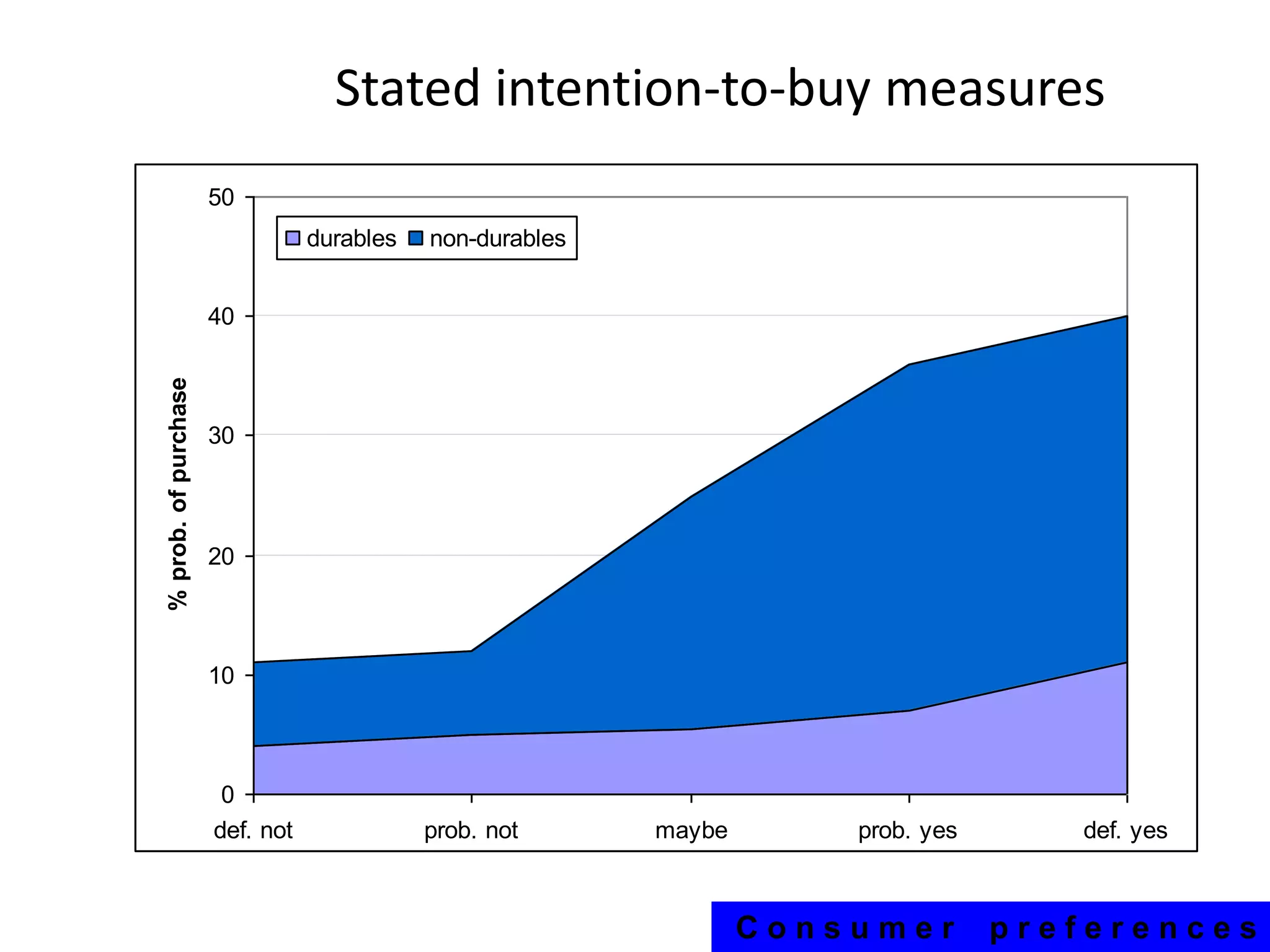
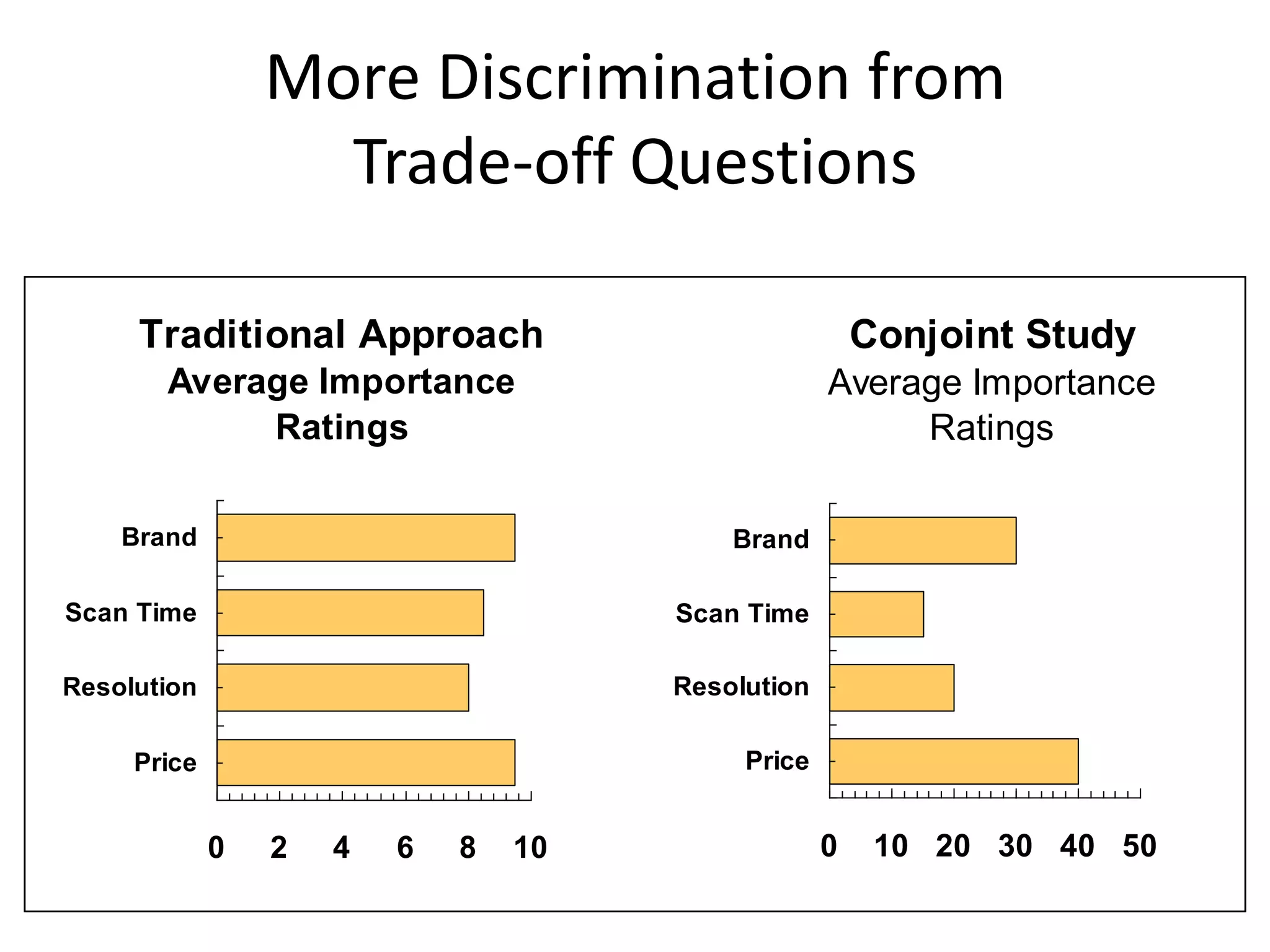
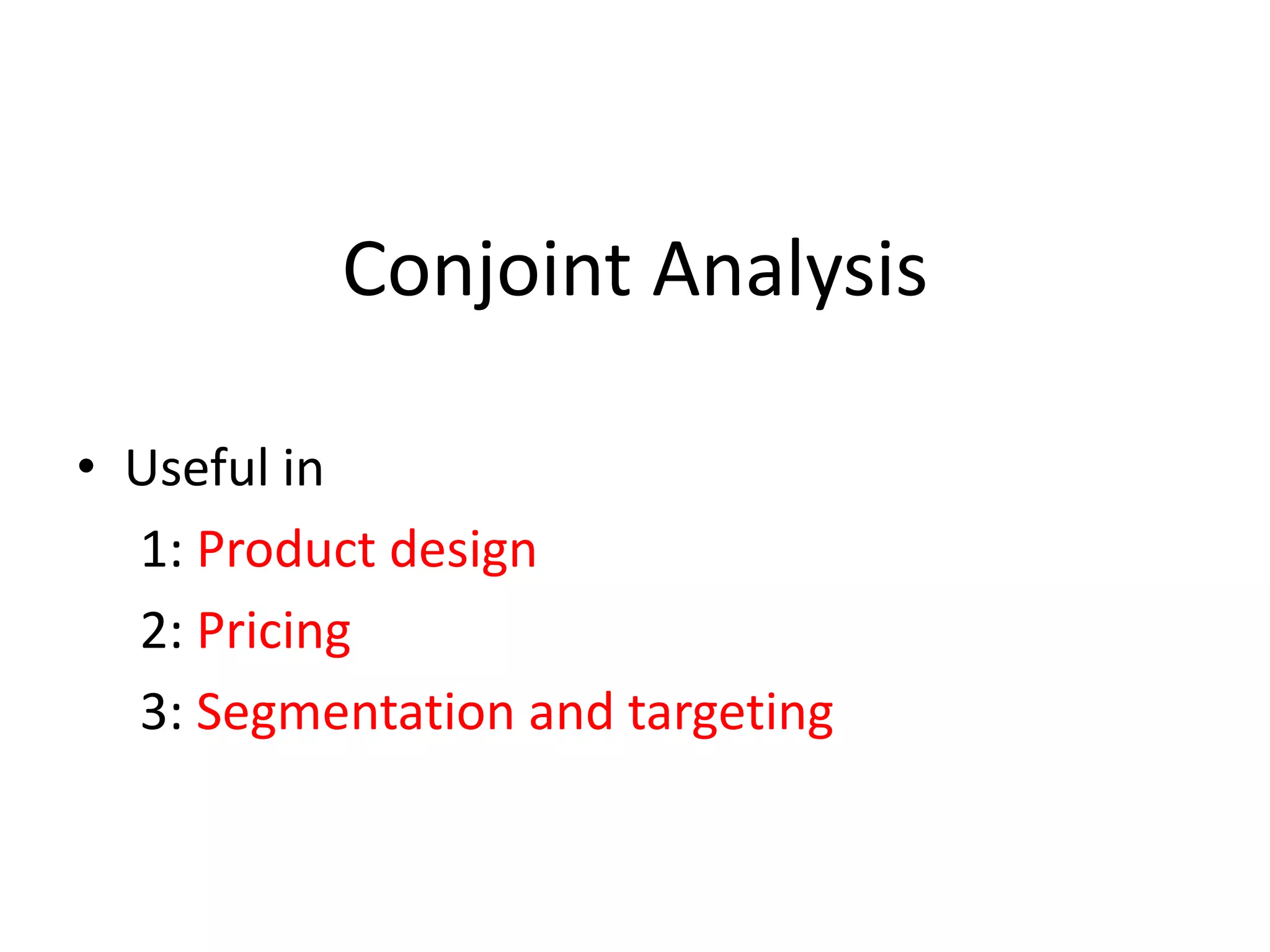
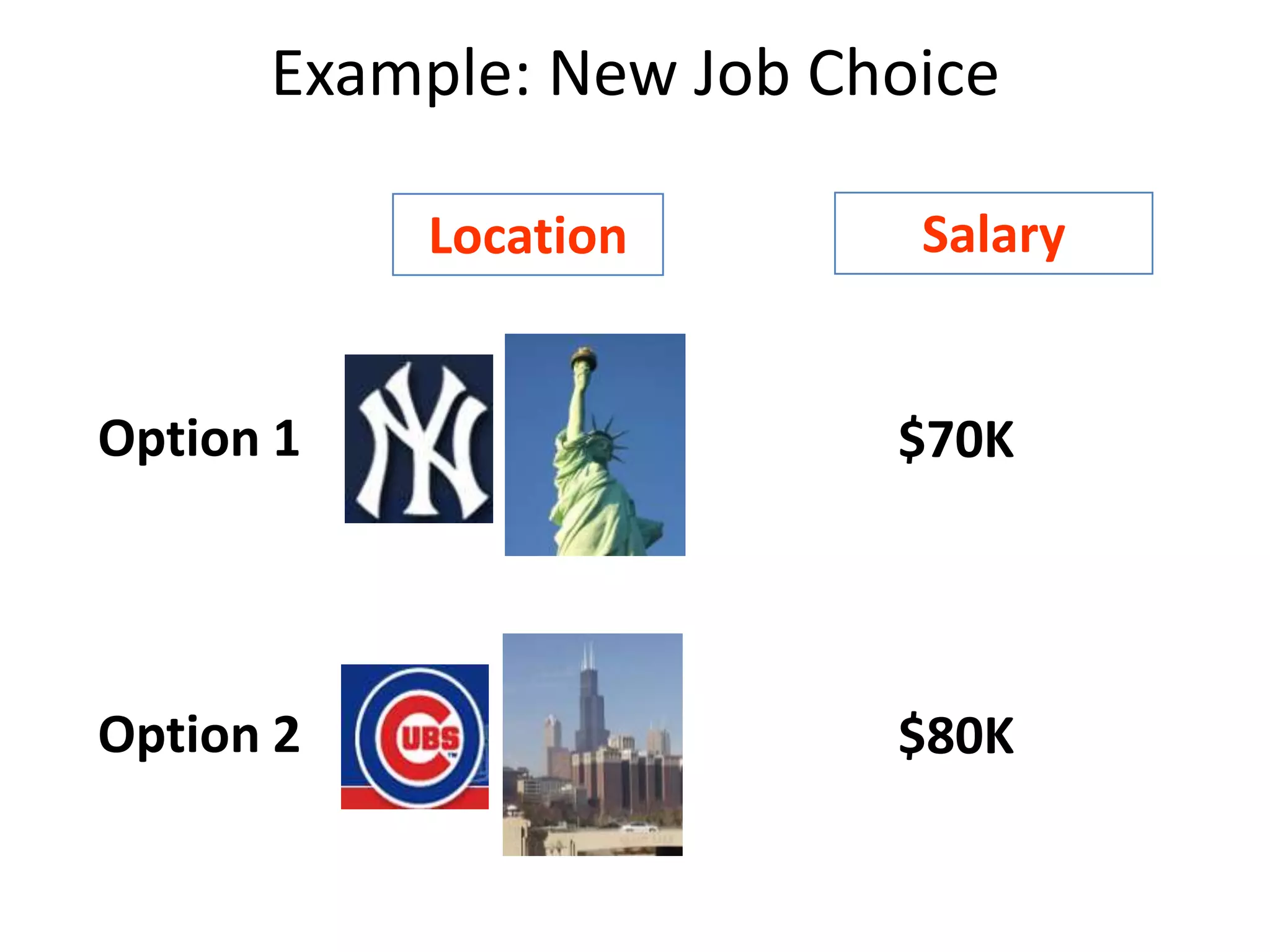
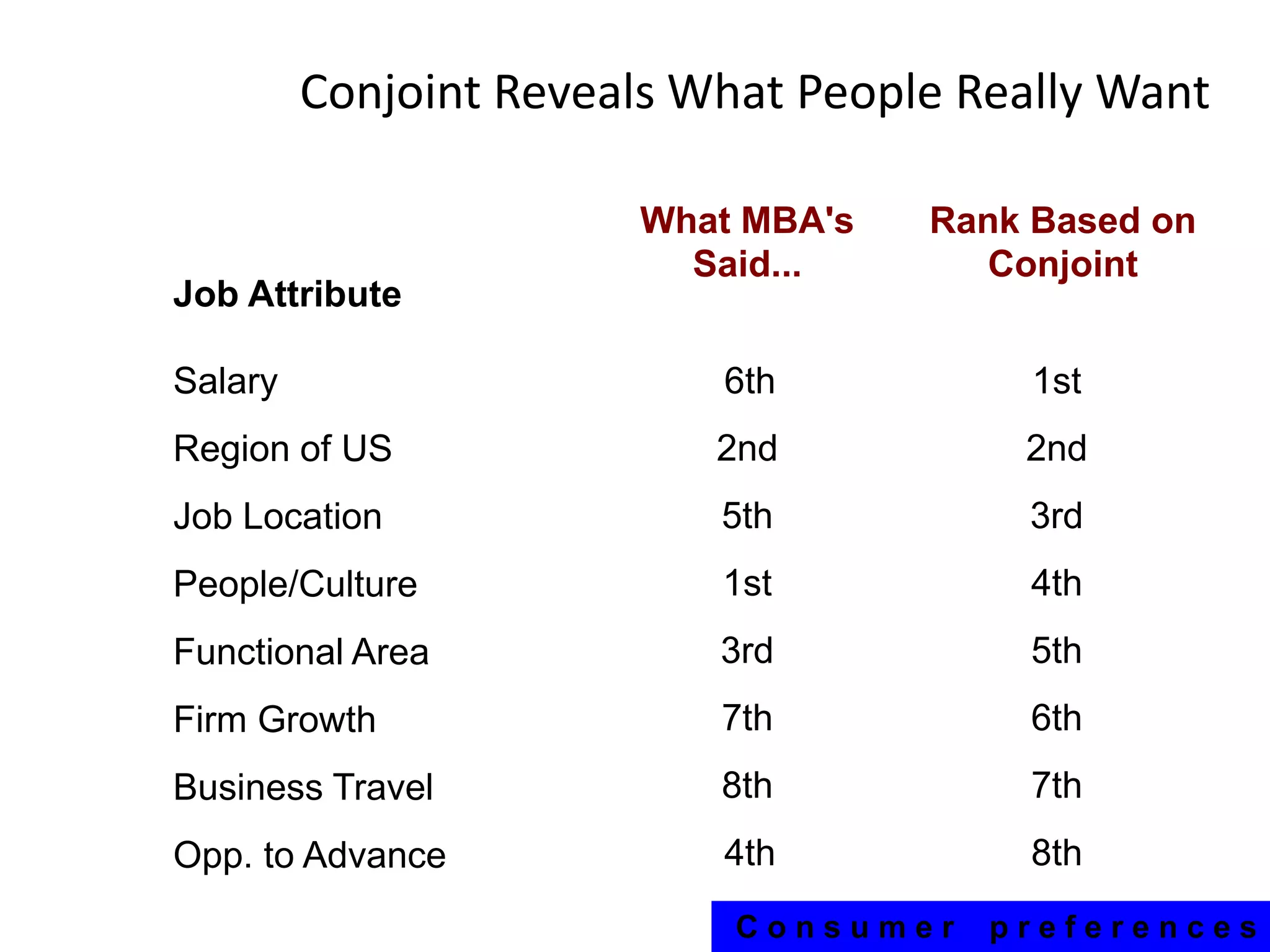
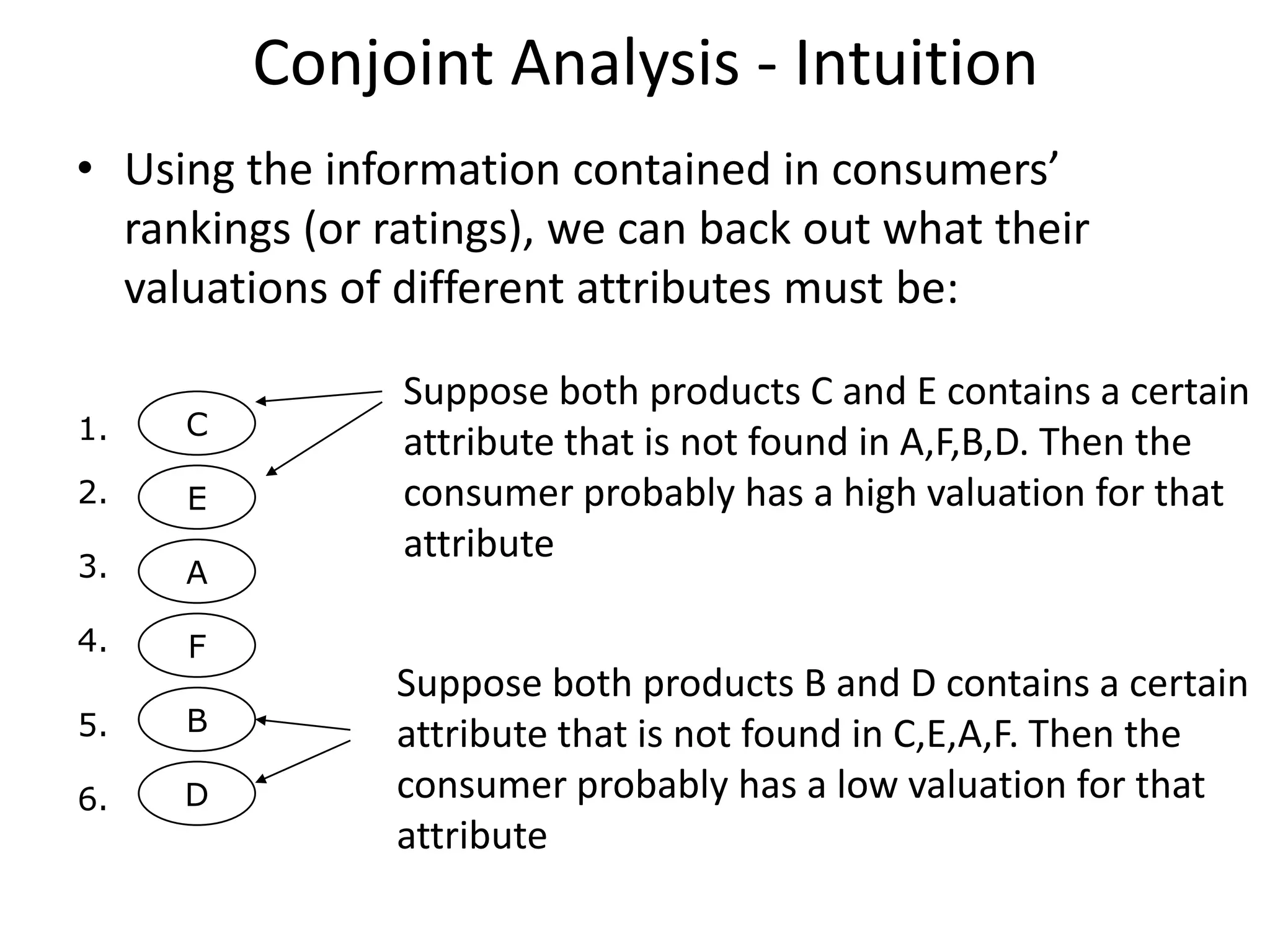
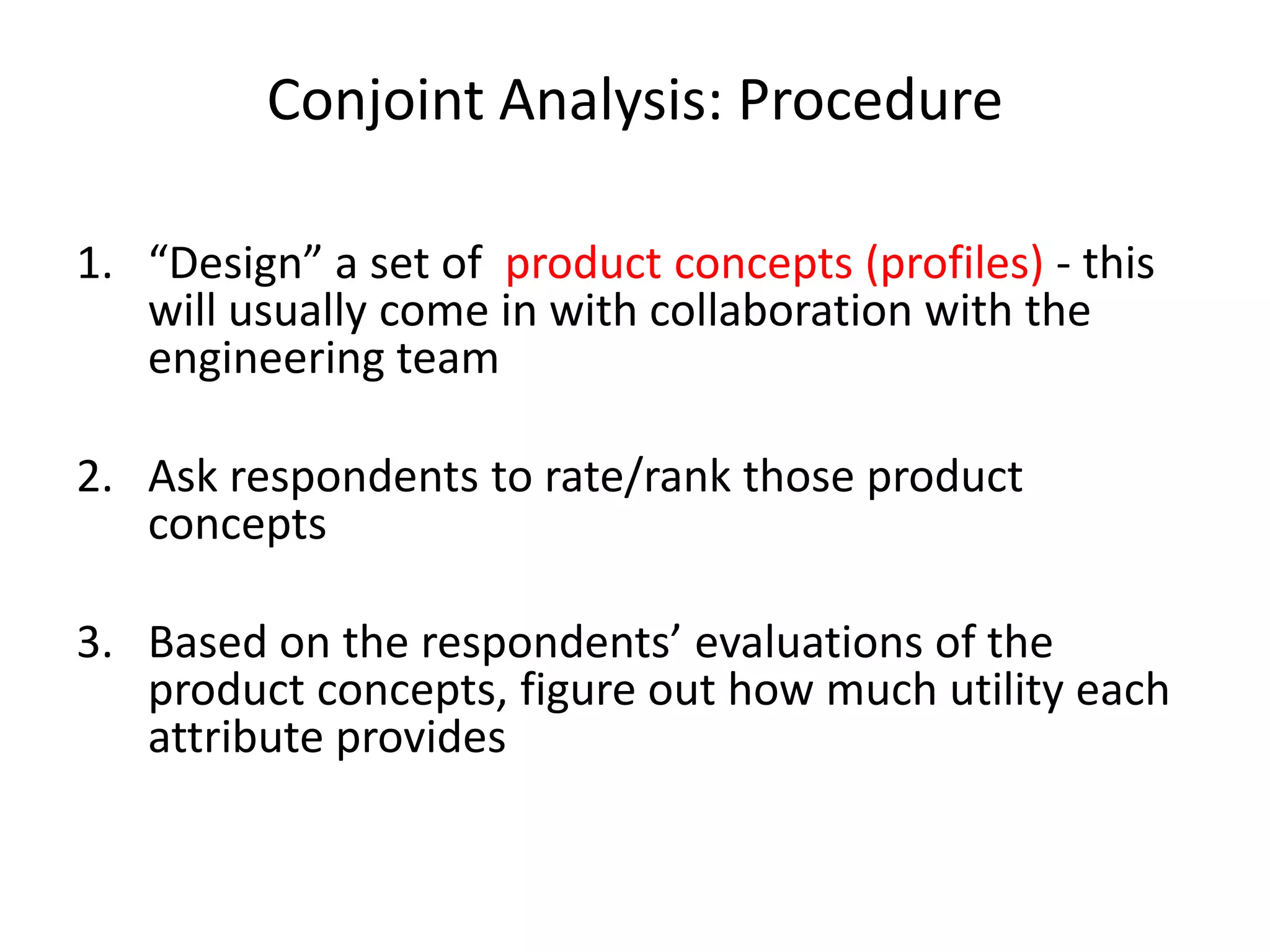
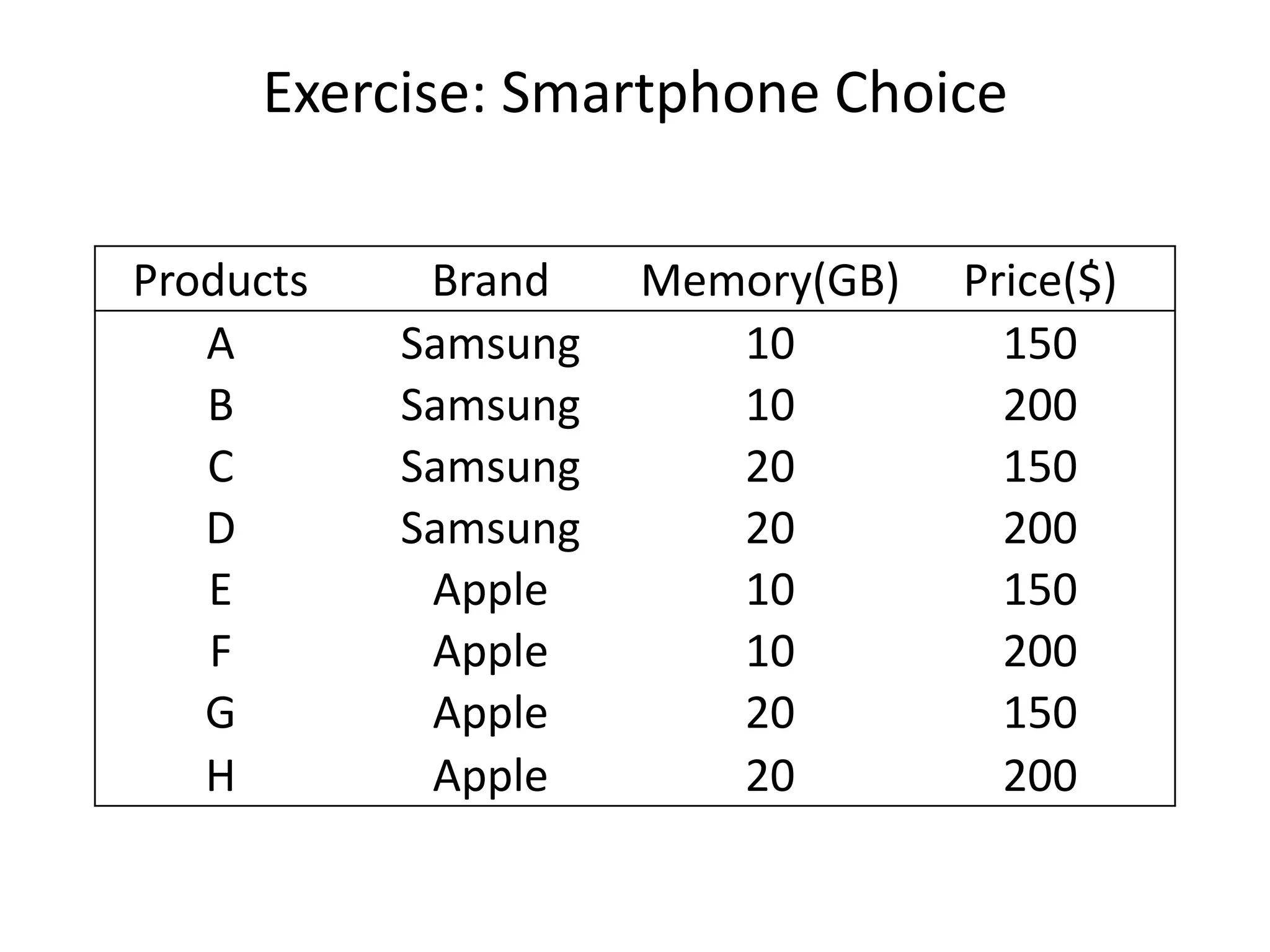
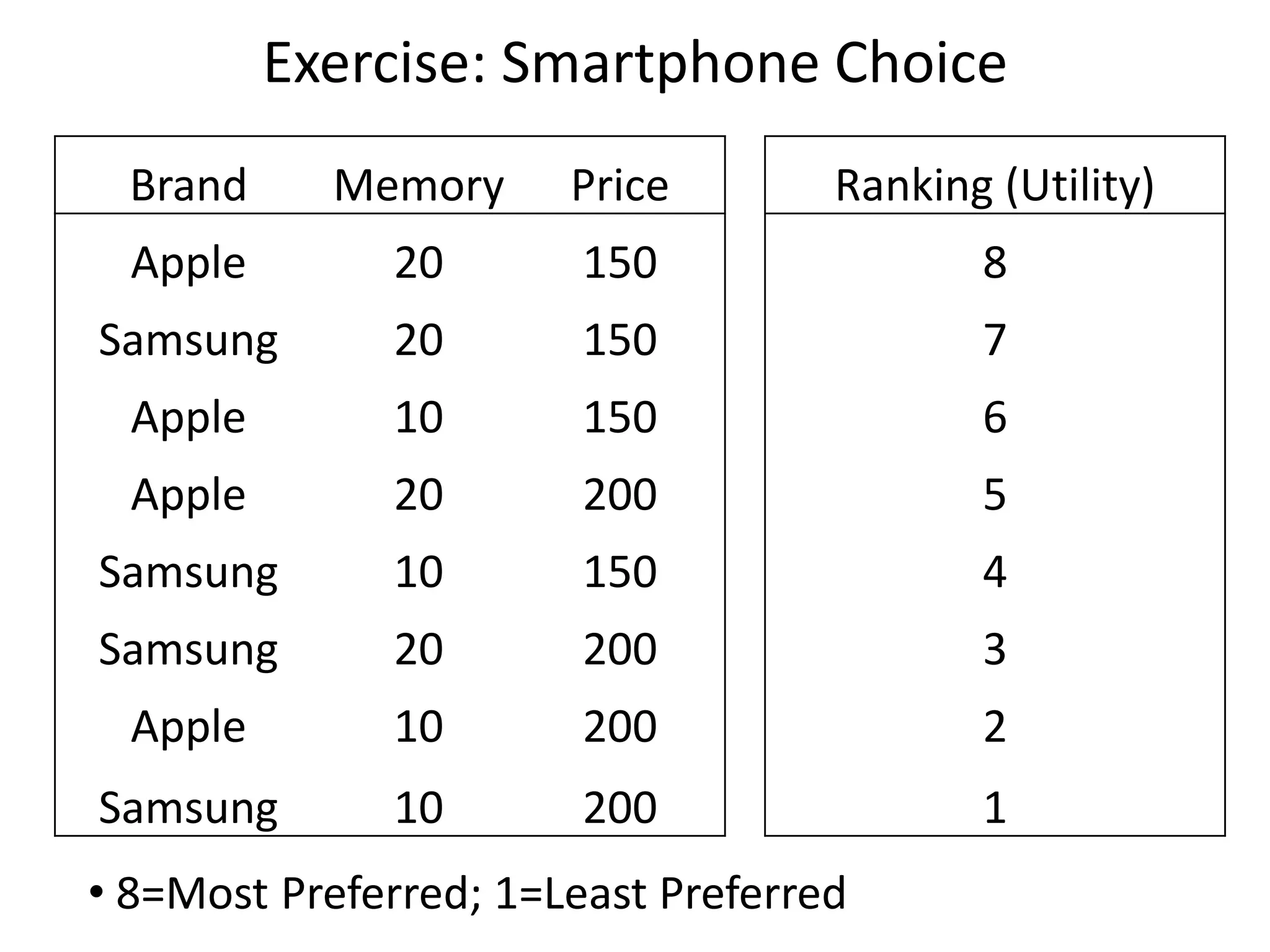
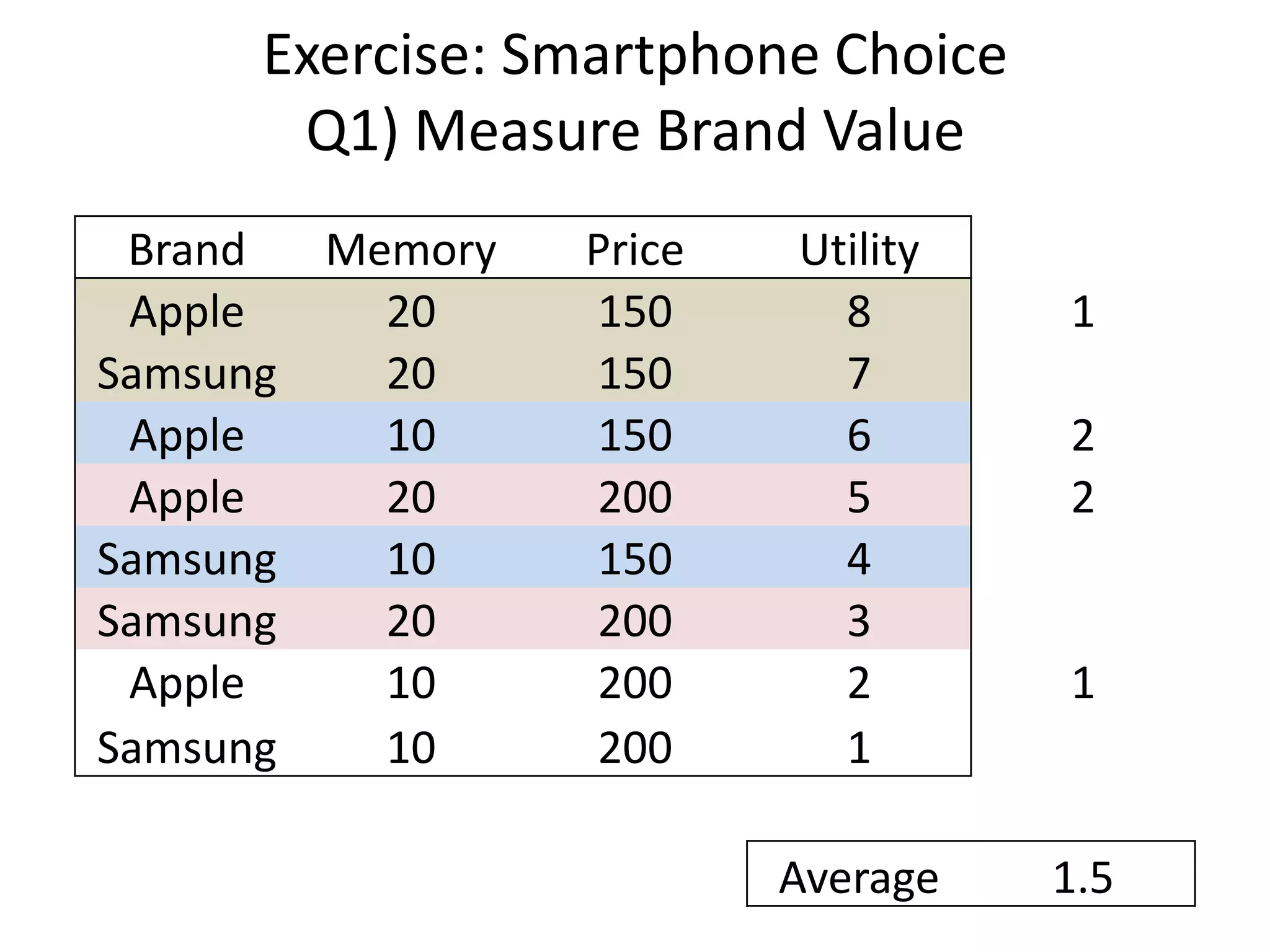
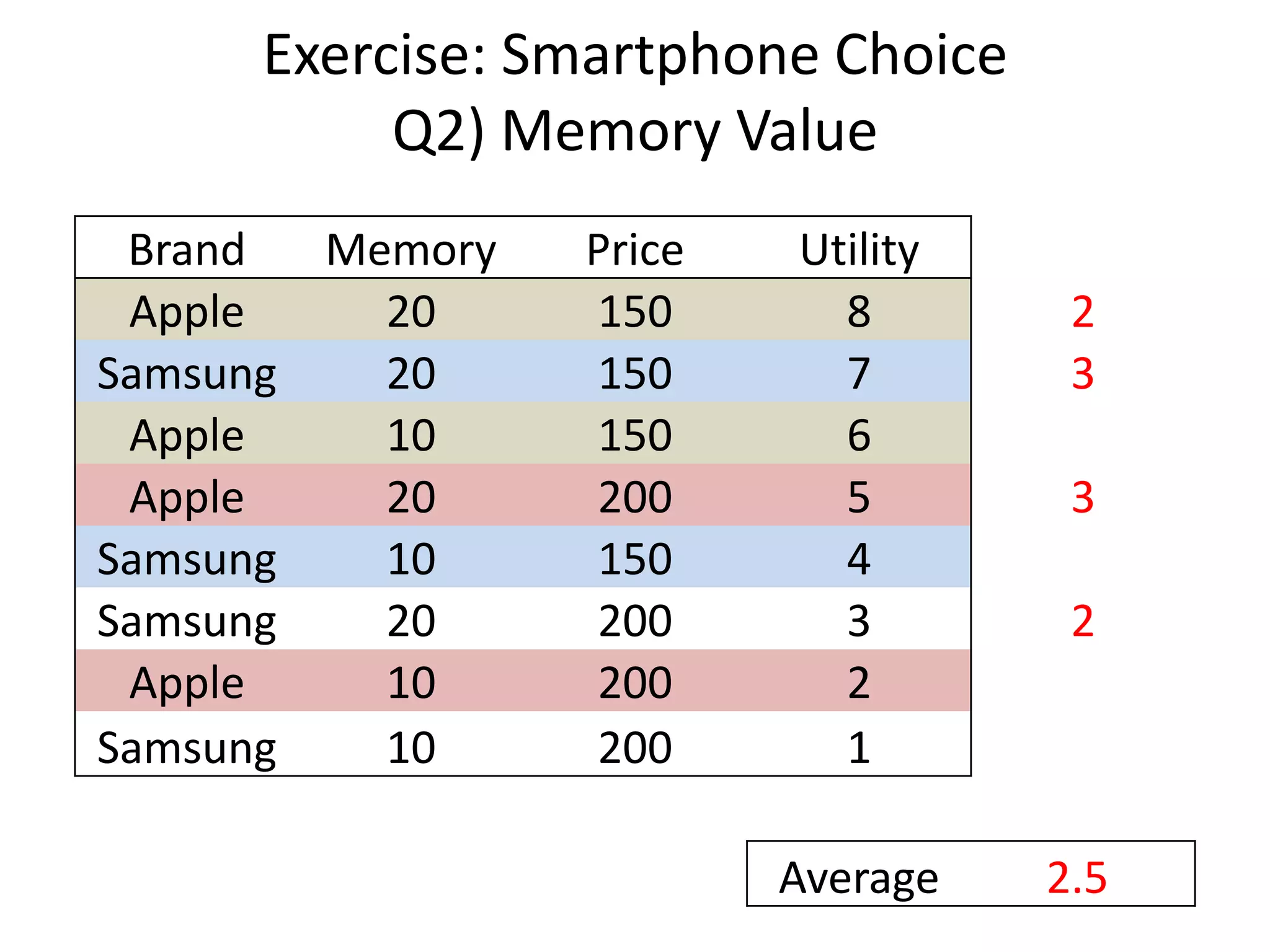
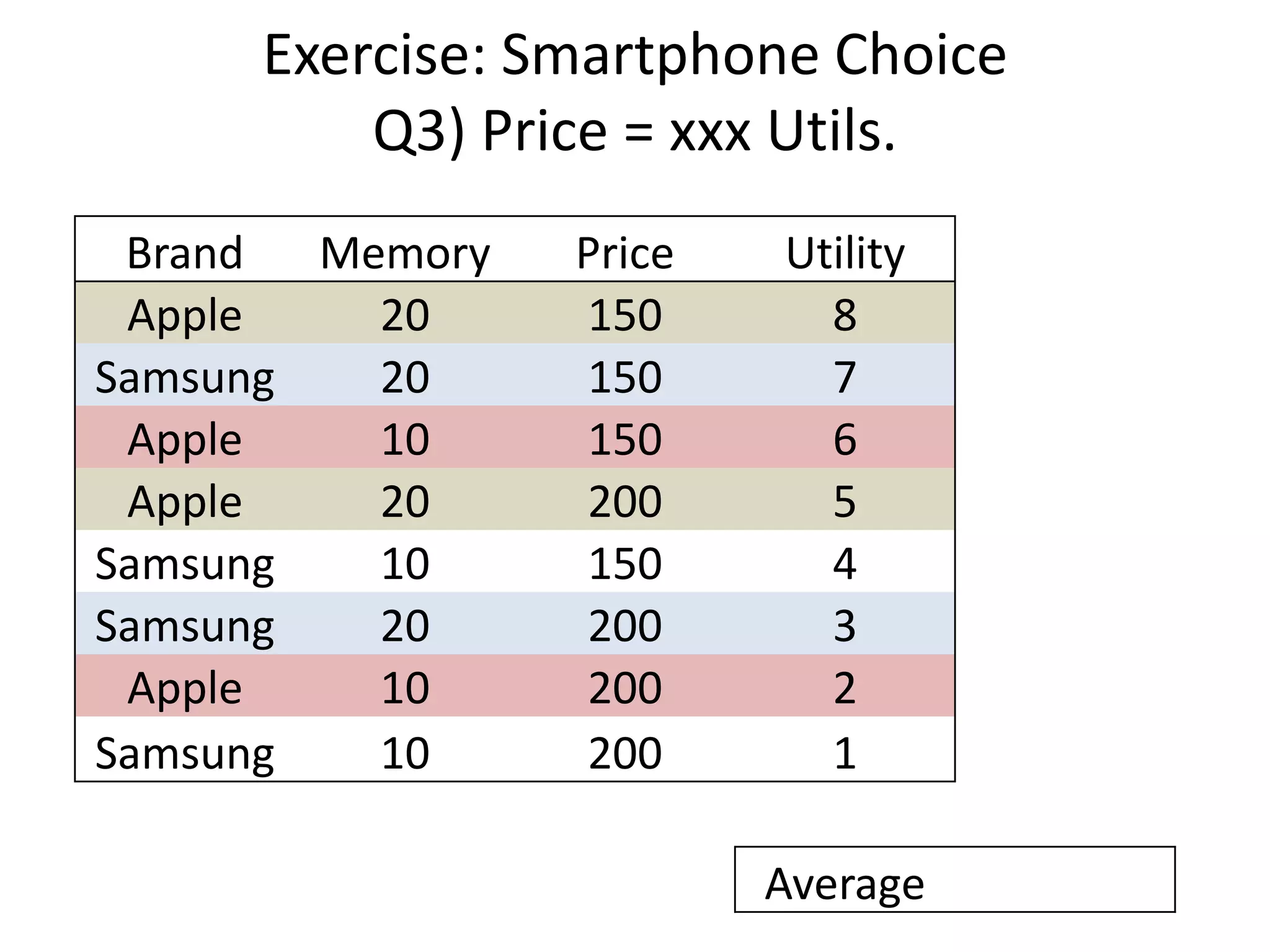
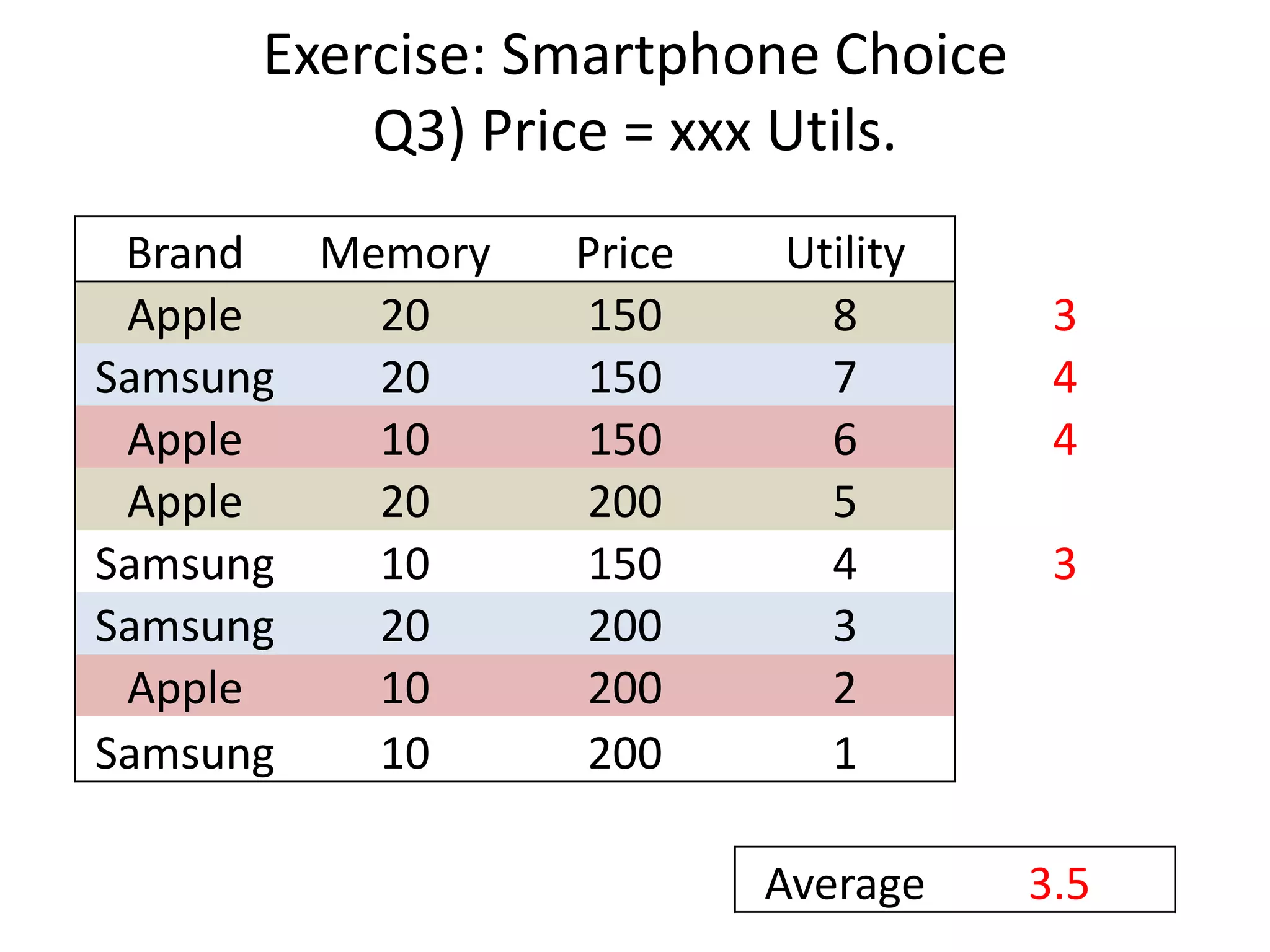
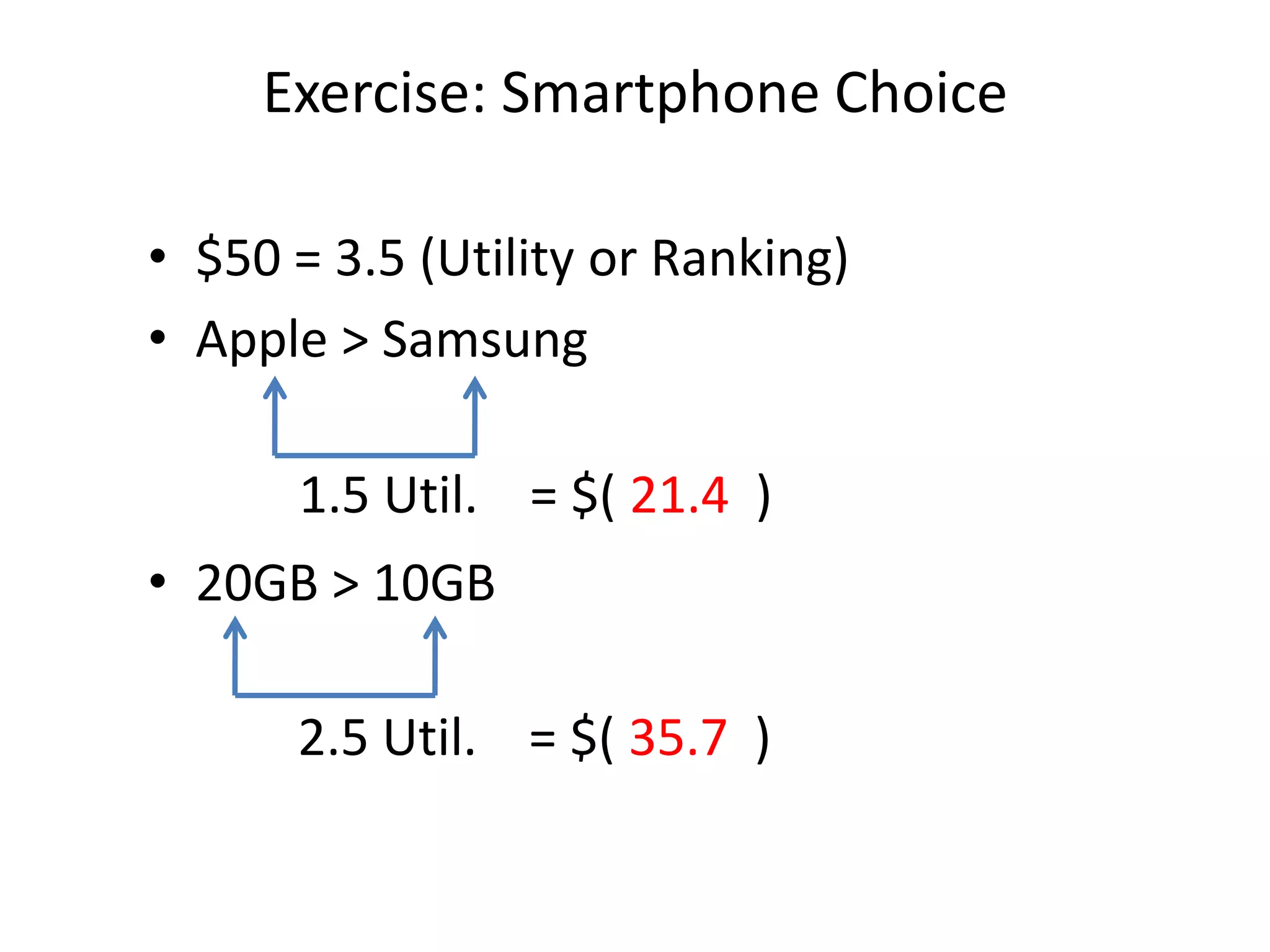
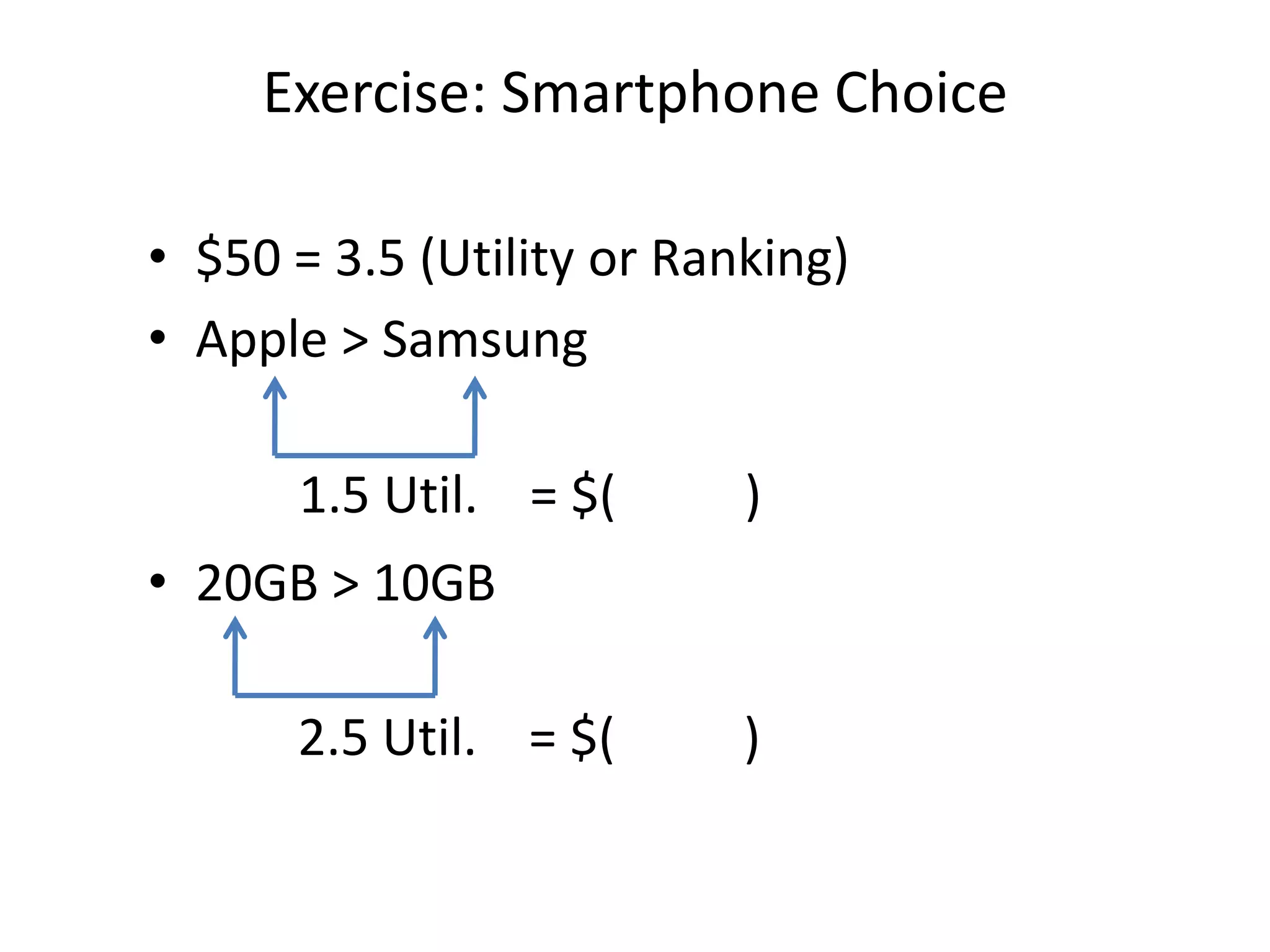
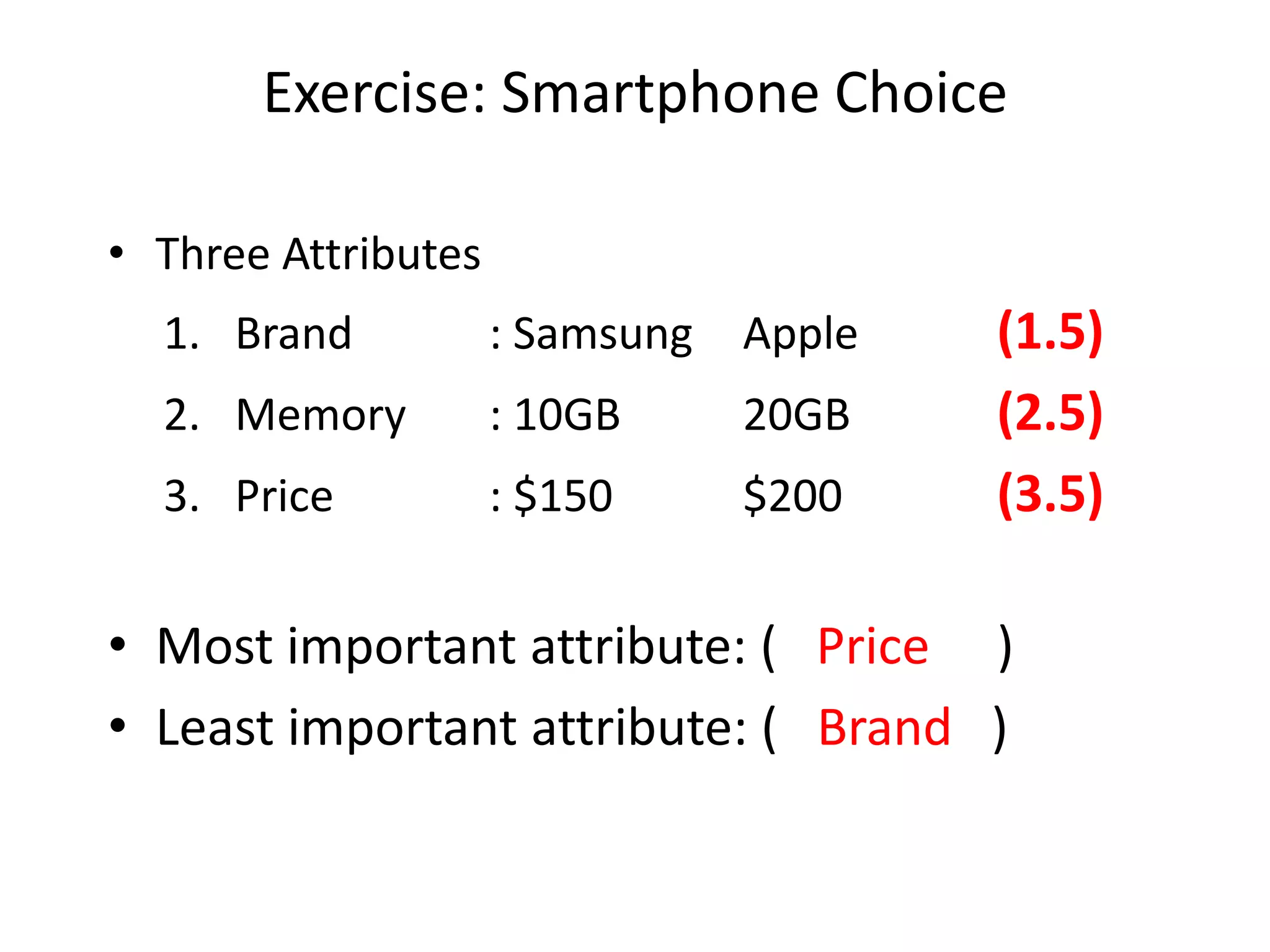
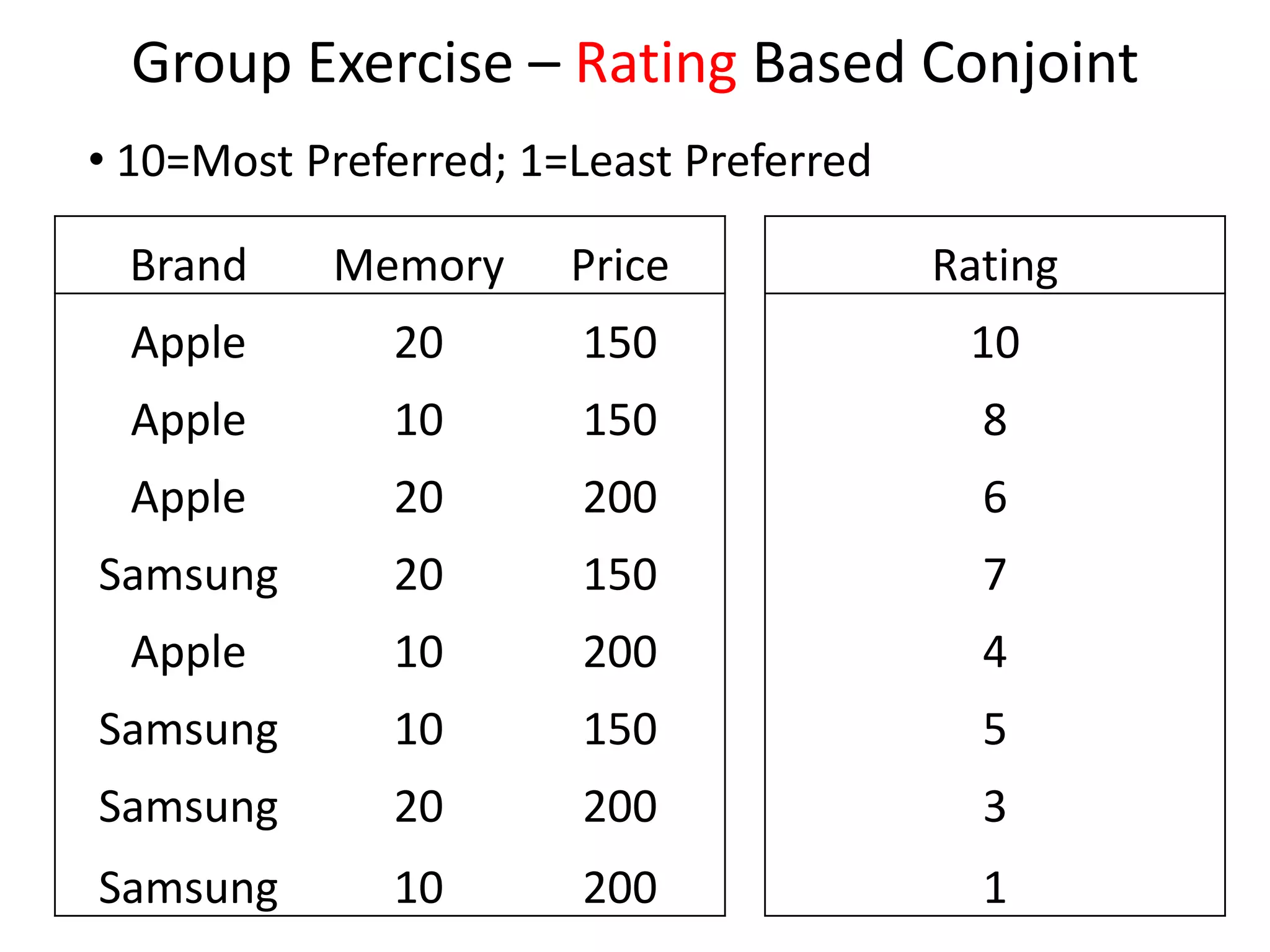
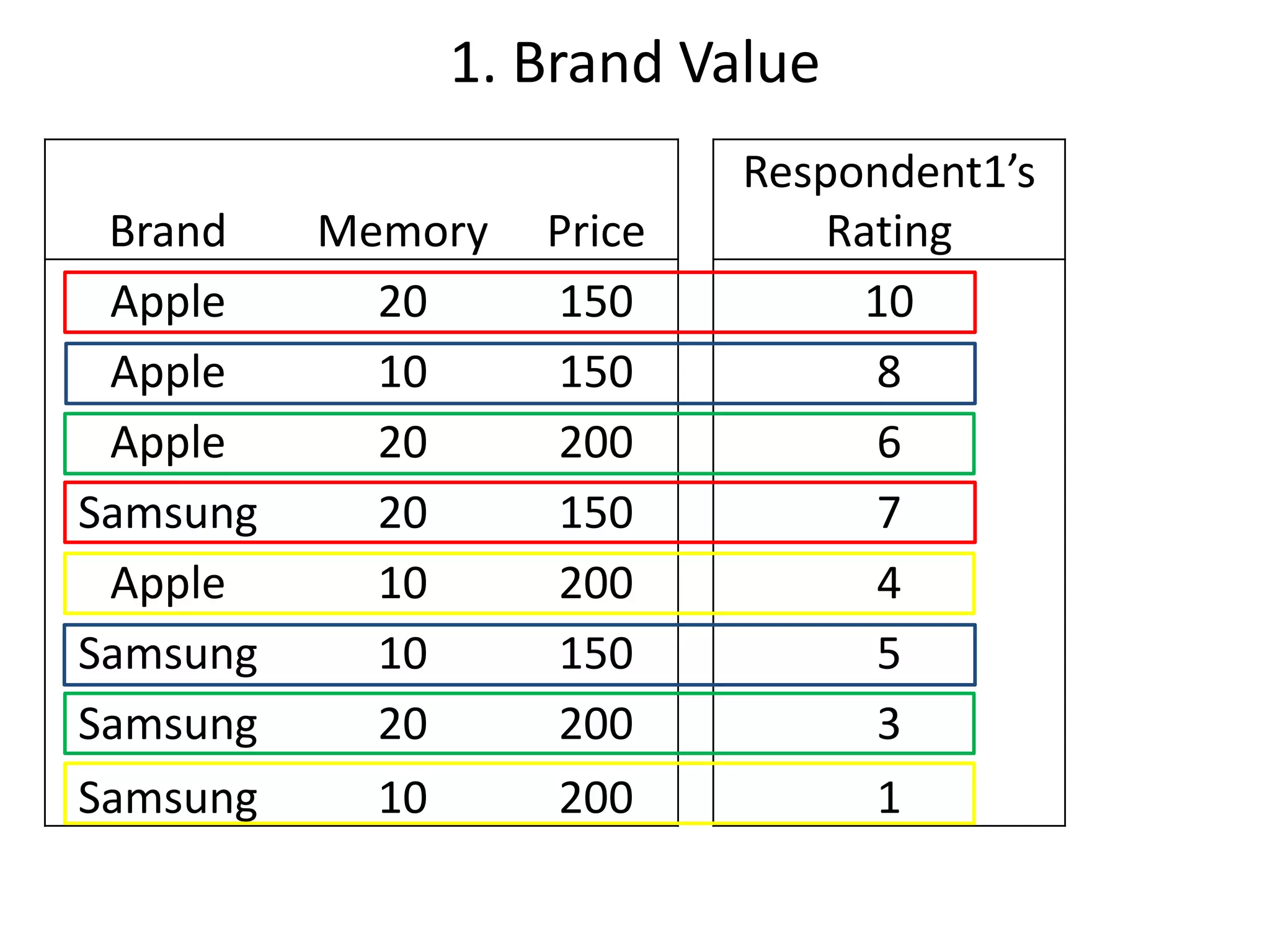
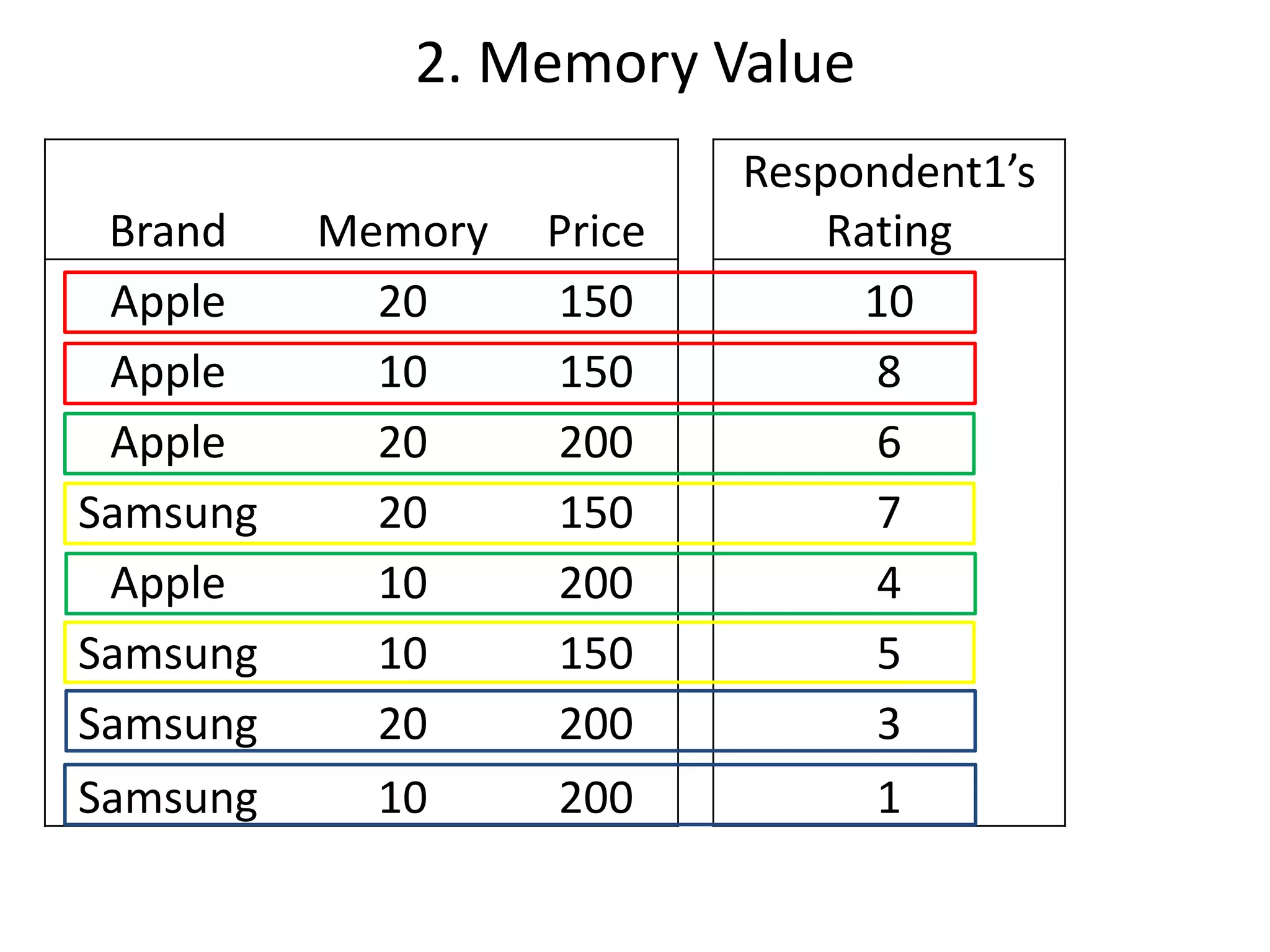
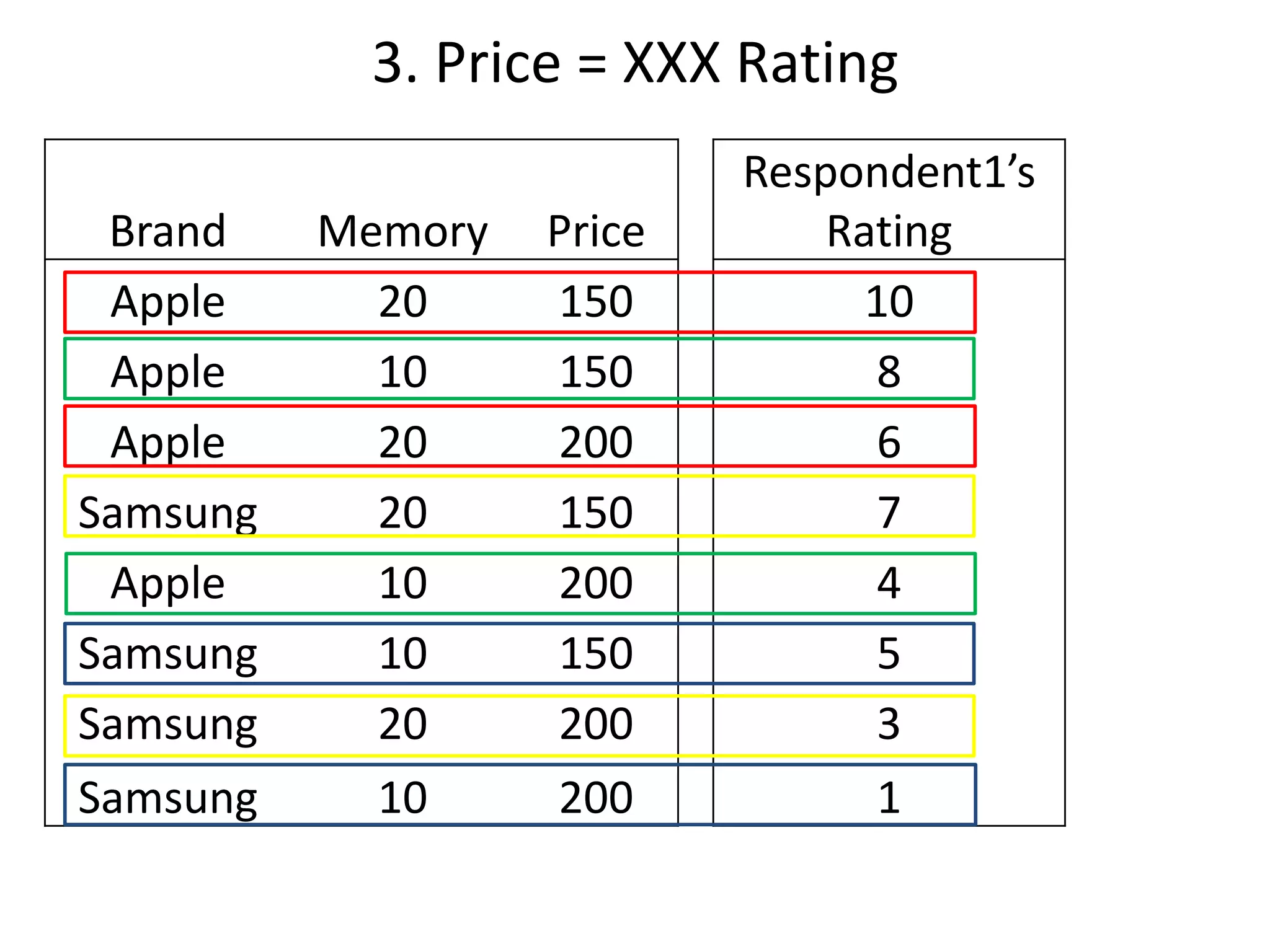
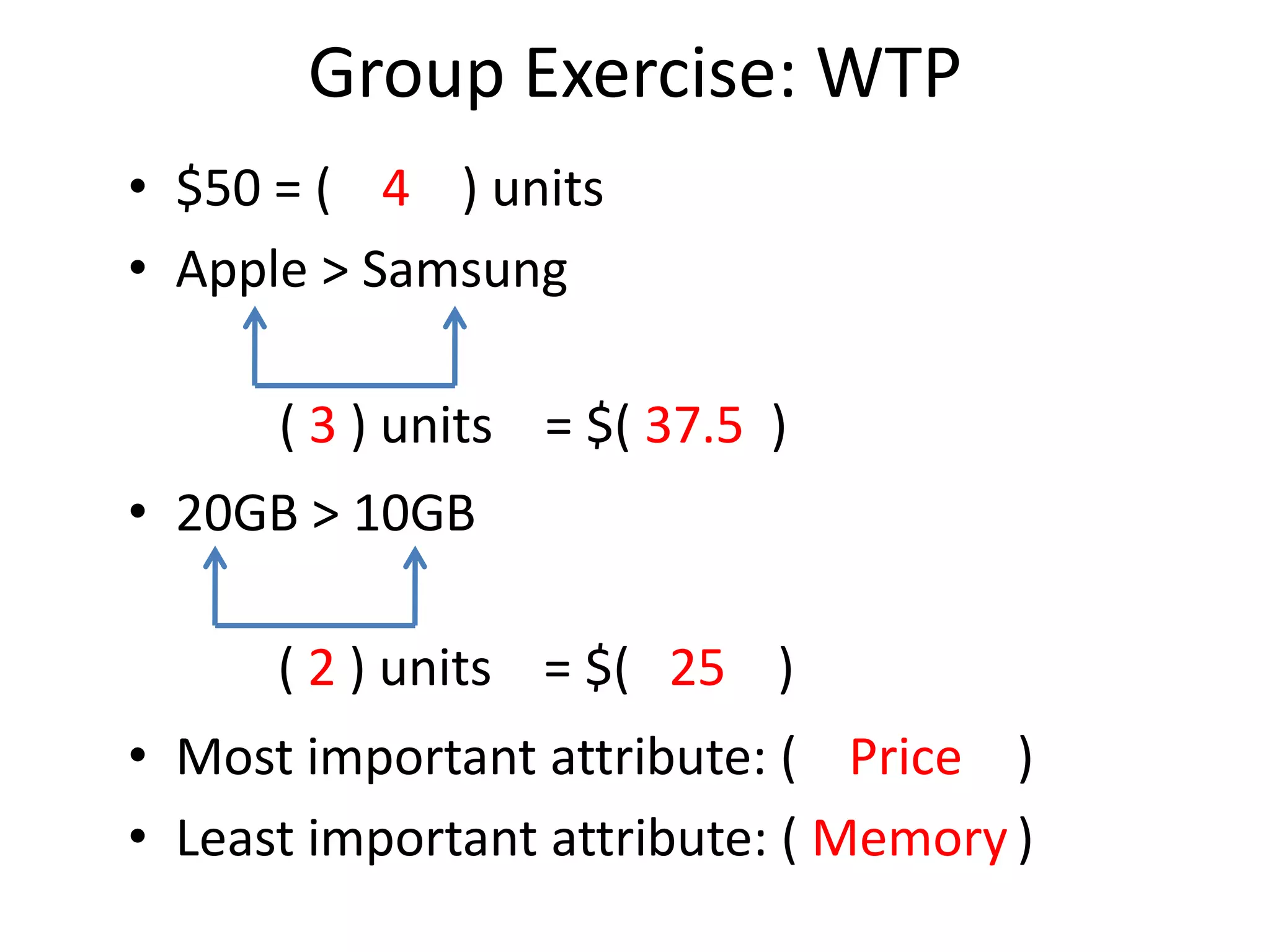
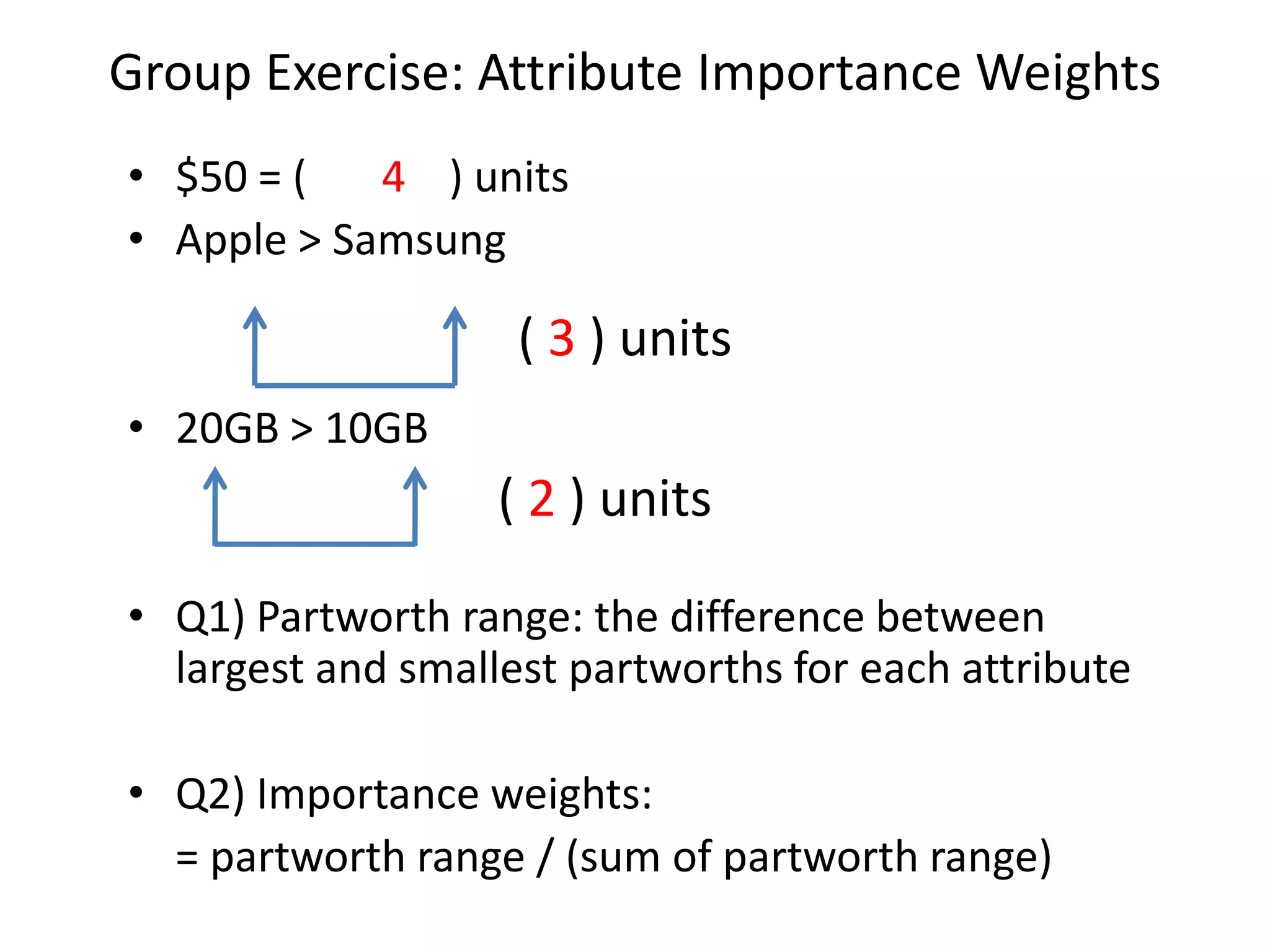
The document discusses different methods for measuring consumer preferences, including direct questioning, stated preferences, and revealed preferences such as purchase data. It notes problems with directly asking consumers about their preferences and intentions to buy. The document then introduces conjoint analysis as a technique that can provide more useful insights into how consumers make tradeoffs between product attributes and their relative attribute importance.