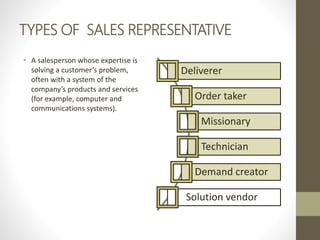
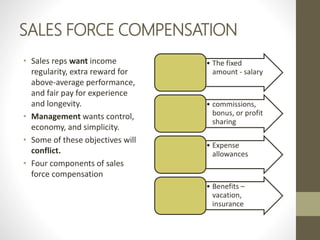
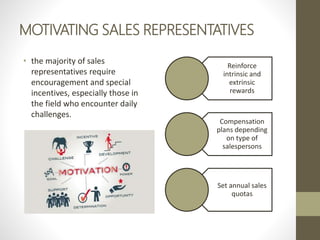
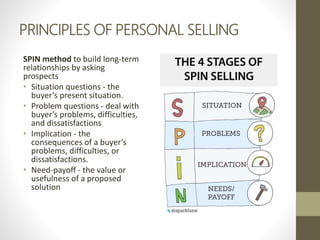
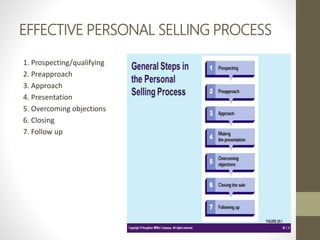
- Direct marketing is an interactive marketing system that uses media to effect a measurable response. It is growing, especially in electronic formats.
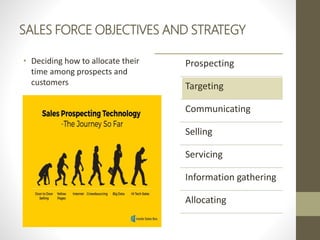
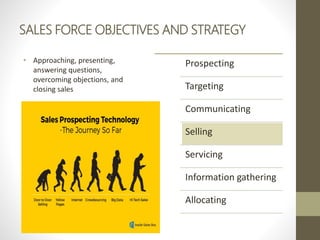
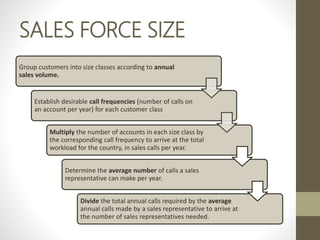
- Direct marketers plan campaigns by deciding objectives, targets, offers and prices, then test and measure success.
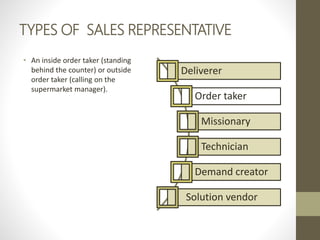
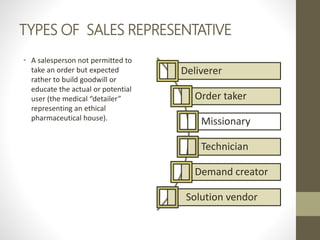
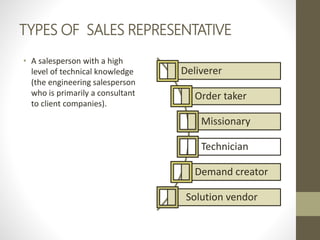
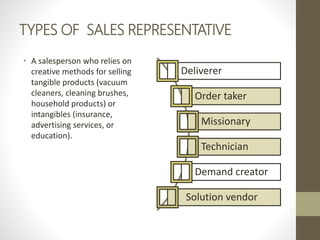
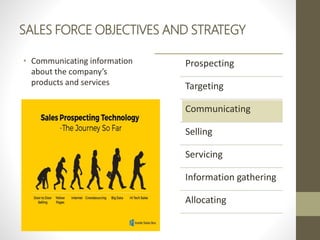
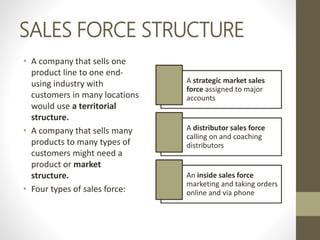
- Major direct marketing channels include face-to-face, direct mail, catalogs, telemarketing, interactive TV, websites and mobile devices.
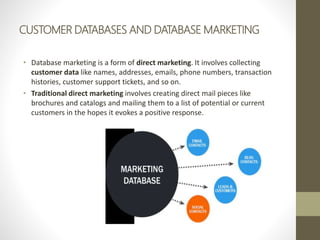
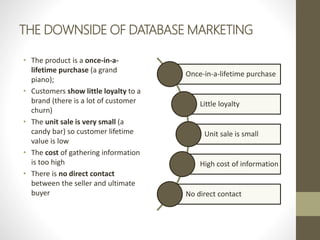
- Customer relationship management often requires building customer databases and data mining to detect trends, segments and needs, with significant risks to consider.