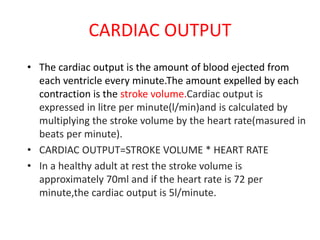
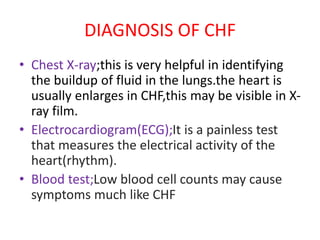
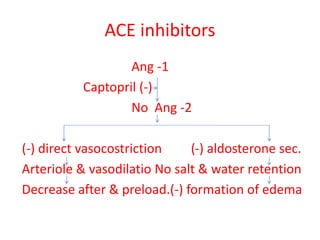
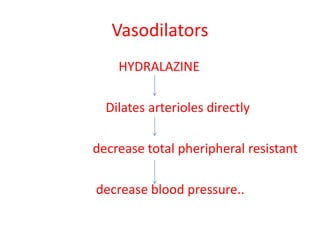
Congestive heart failure occurs when the heart fails to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It results from the heart's inability to contract sufficiently. Diagnosis involves tests like chest X-rays, ECGs, blood tests, and cardiac catheterization. Treatment includes diuretics to reduce preload, nitrates to reduce afterload, ACE inhibitors to reduce both, and cardiotonics like digoxin to increase contractility and cardiac output. The goal of treatment is to increase stroke volume and cardiac output in order to correct symptoms and heart enlargement caused by heart failure.