1) The document discusses the determination of the time to reach maximum drug concentration (tmax) after oral administration of a drug.
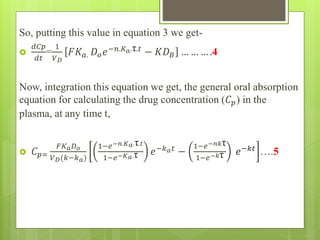
2) It presents equations that model the absorption and elimination rates of drugs in the body over time and how these rates impact the drug concentration in plasma.
3) It derives an equation that shows tmax is independent of dose and depends only on the absorption and elimination rate constants (ka and k). The tmax occurs when the rates of drug absorption and elimination are equal, making the rate of concentration change equal zero.