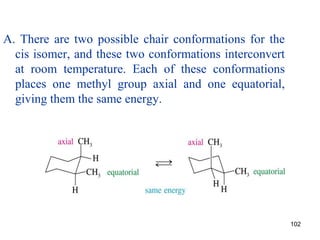
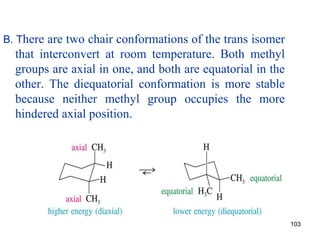
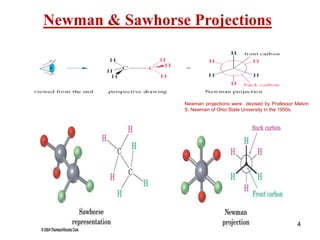
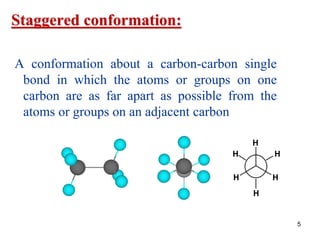
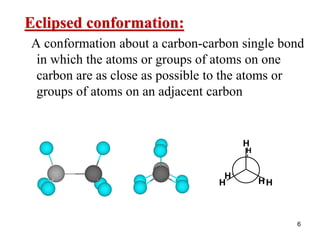
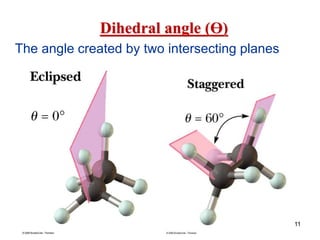
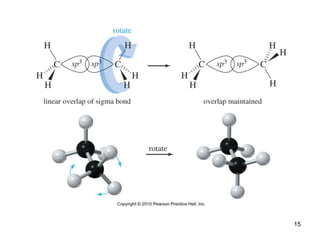
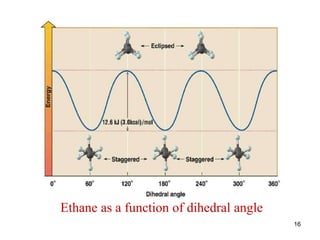
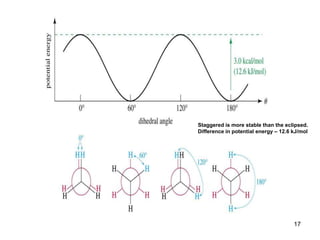
The document discusses conformations and rotational isomers in organic molecules. It begins by defining conformations as different arrangements of atoms or groups in a molecule that can be interconverted by rotation about single bonds. These conformations have different internal dimensions but similar energies, with carbon-carbon single bond rotation barriers typically under 1 kcal/mol.
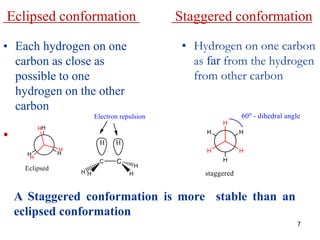
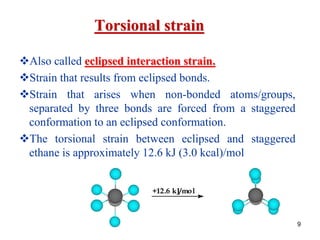
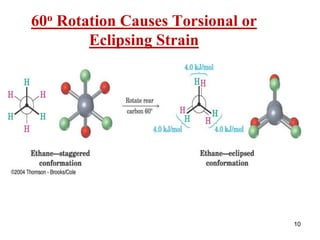
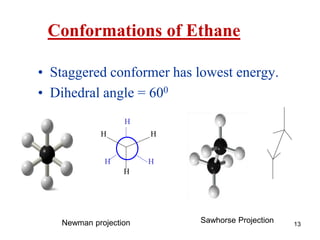
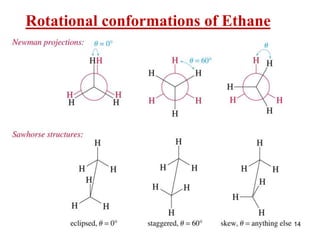
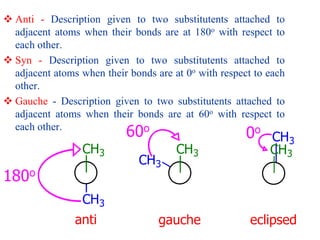
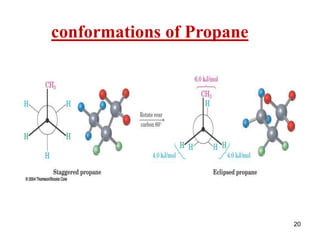
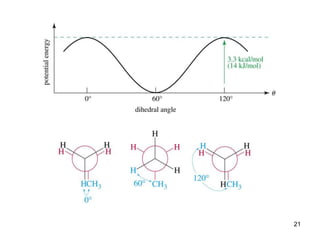
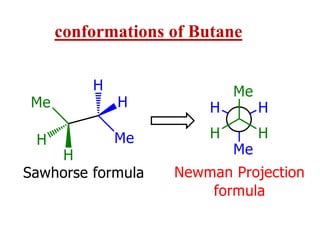
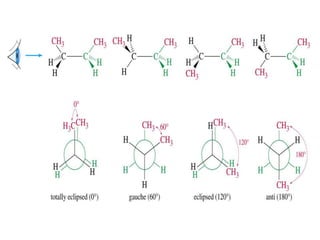
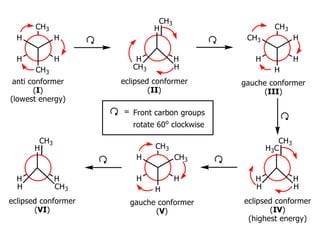
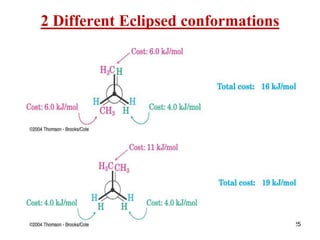
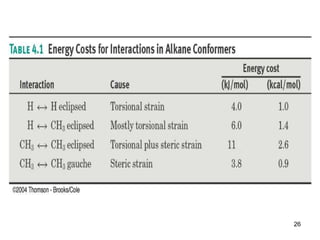
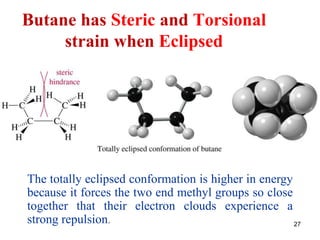
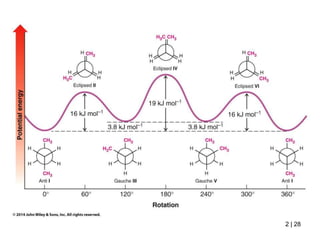
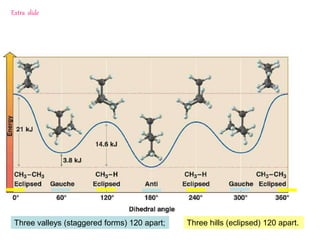
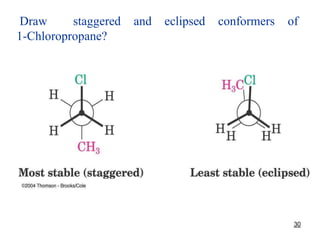
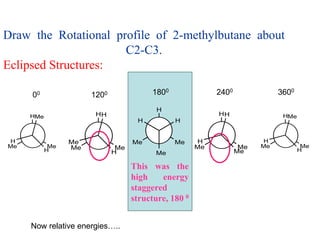
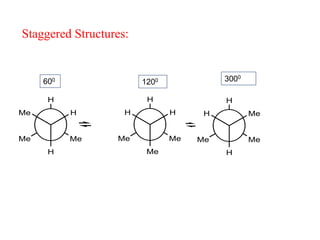
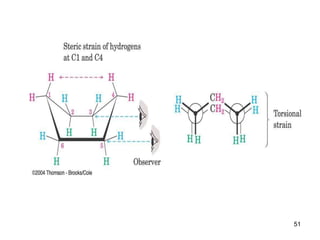
It then discusses specific examples like ethane, propane, and butane conformations. Ethane prefers the staggered conformation to avoid eclipsed hydrogen interactions. Butane experiences both steric and torsional strain in the eclipsed conformation.
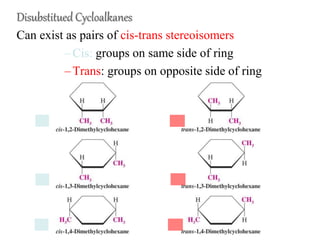
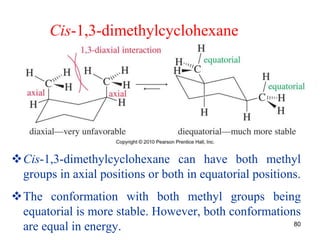
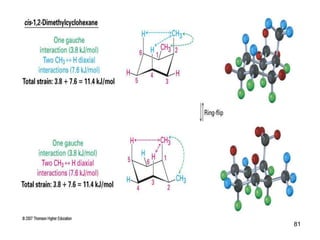
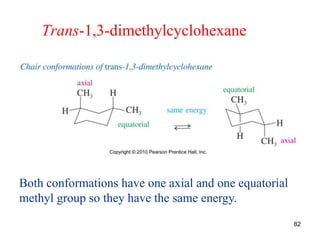
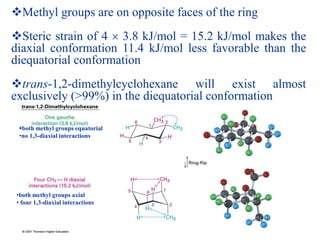
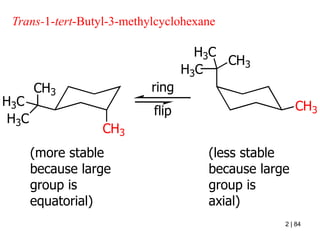
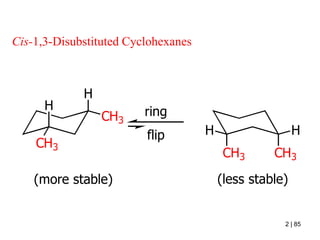
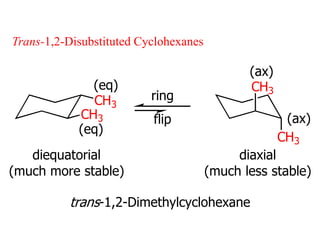
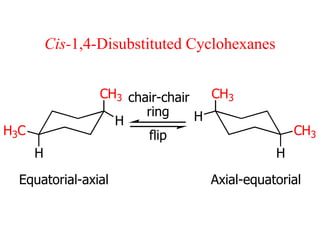
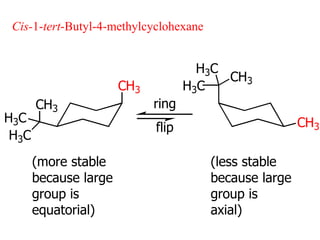
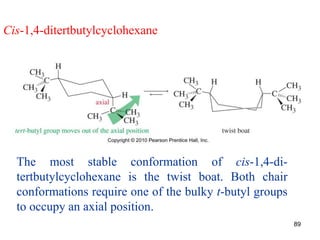
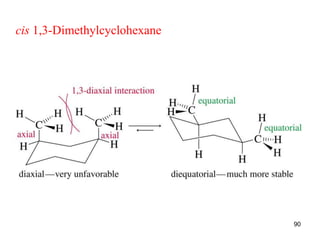
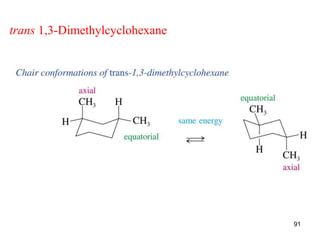
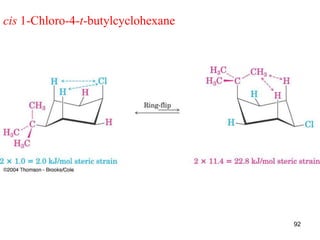
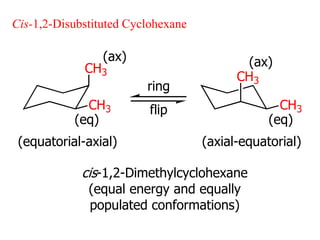
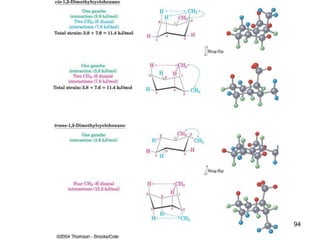
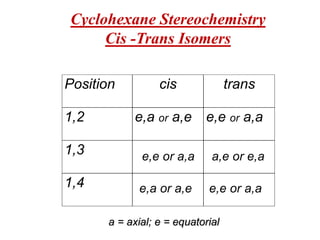
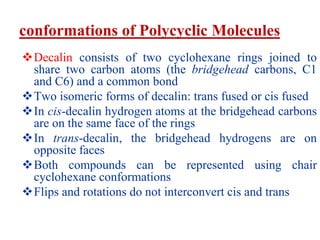
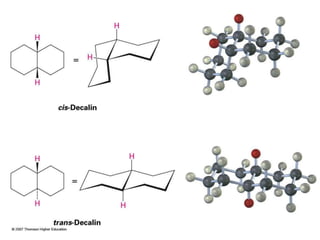
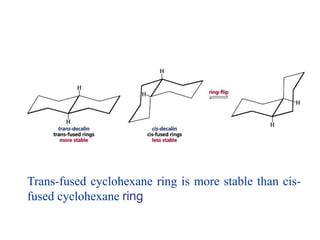
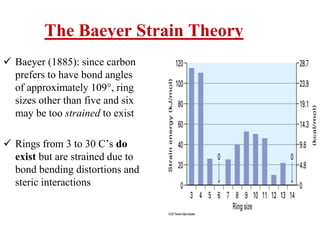
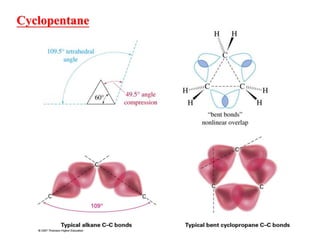
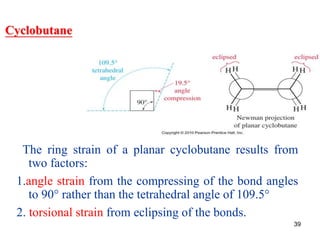
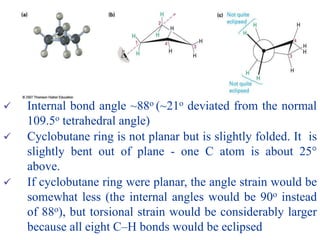
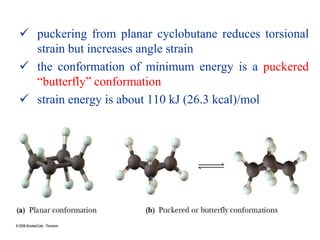
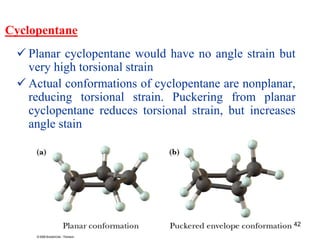
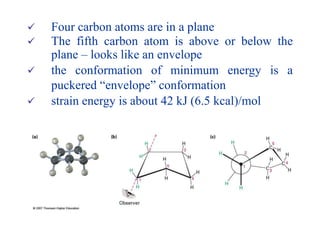
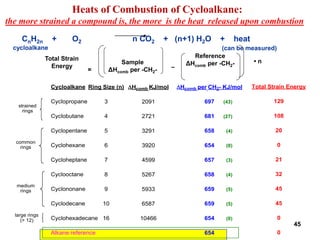
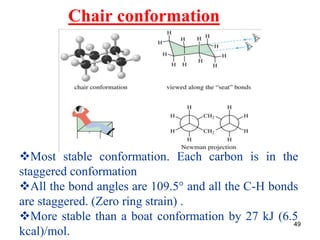
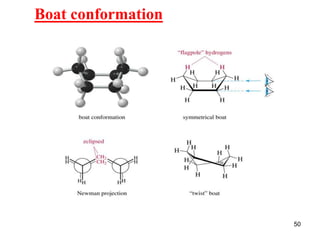
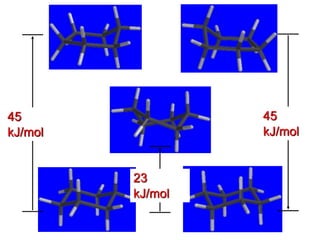
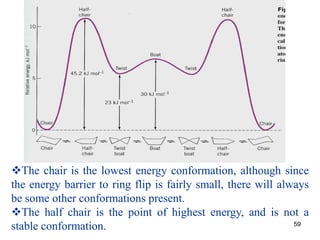
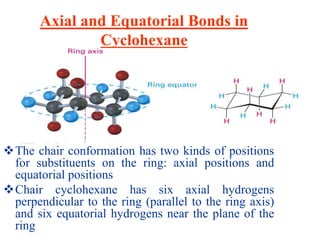
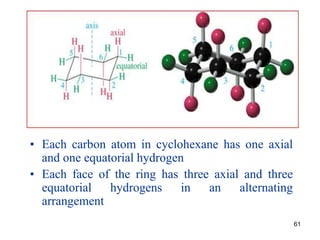
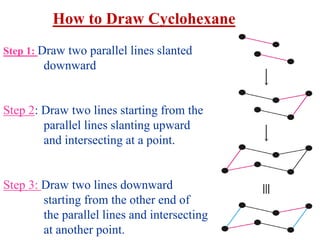
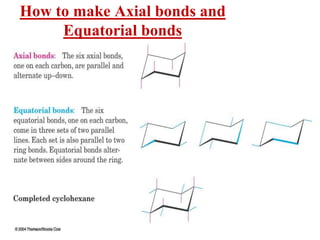
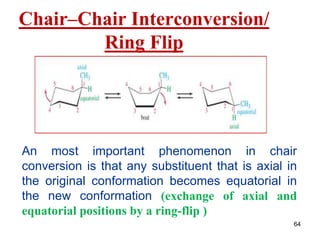
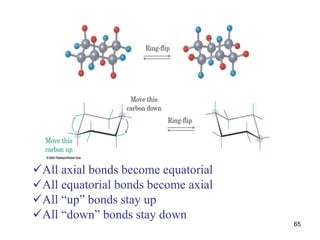
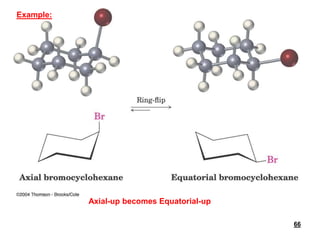
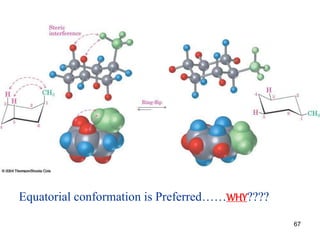
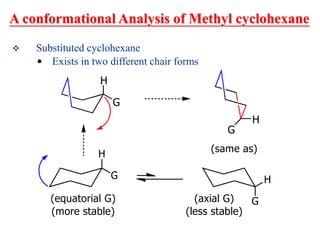
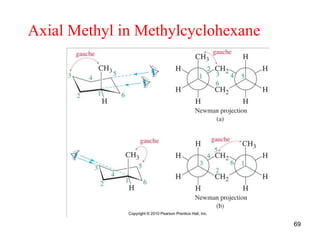
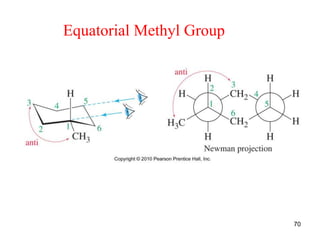
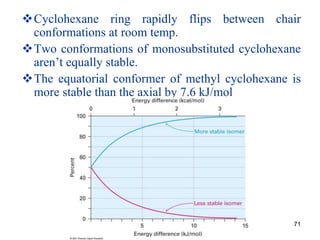
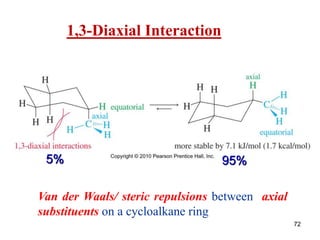
The document also covers cycloalkane conformations, ring strain effects, and the preferred chair conformation of cyclohex















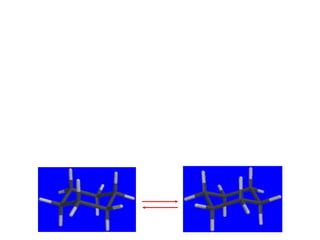
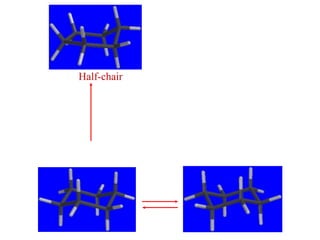
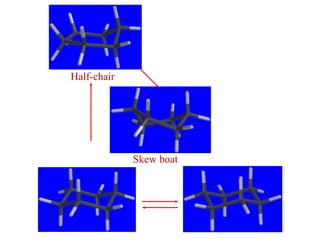
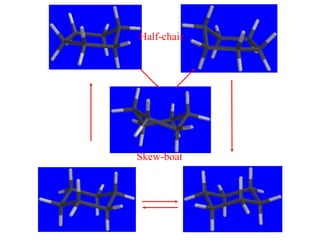

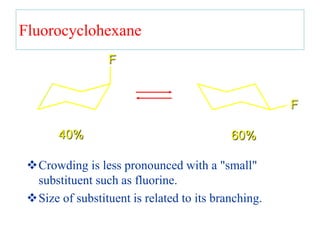
![Keq = [equatorial conformer]/[axial conformer]
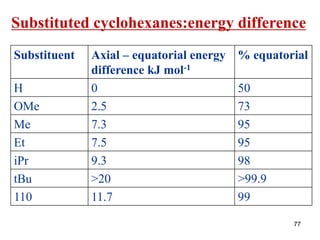
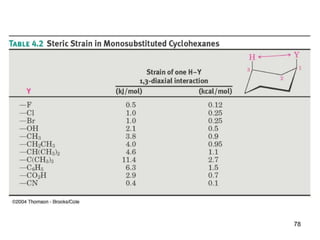
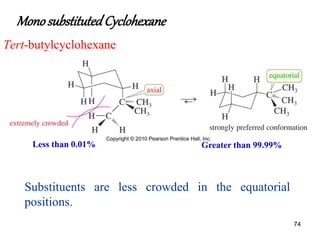
• The larger the substituent on a cyclohexane ring, the
more the equatorial substituted conformer will be
favored](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msconformation-200420075154/85/conformation-76-320.jpg)