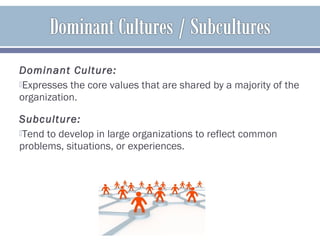
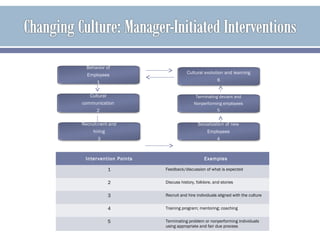
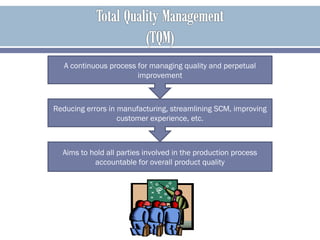
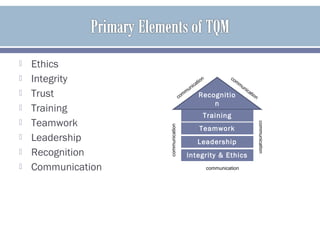
The document discusses organizational culture and how it guides employee behavior through shared beliefs and values. A strong culture facilitates goal alignment and motivation while a weak culture has high turnover. Culture is expressed through symbols, stories, heroes, and rituals. The document also discusses dominant and sub cultures, different types of cultures, and how culture impacts employees and can be shaped through socialization, hiring, training, feedback, and terminating deviant employees. It provides examples of quality improvement techniques for building a strong culture focused on continuous improvement, accountability and developing trust between all parties.