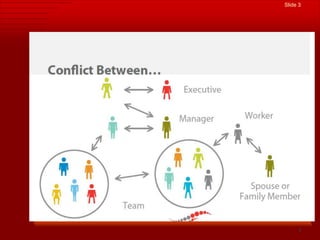
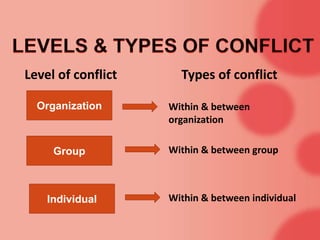
This document discusses organizational conflict and its causes. It defines conflict as occurring between two groups that perceive some incompatibility and interact in a way that one group feels negatively affected by the other. Common causes of conflict in organizations include misunderstandings, personality clashes, competition over resources, disagreements over authority or methods. The document also describes functional conflict as furthering organizational goals, while dysfunctional conflict blocks goals. It outlines different levels and types of conflict within and between individuals, groups, and organizations. Finally, it discusses five approaches to managing conflict: avoidance, competition, accommodation, compromise, and collaboration.