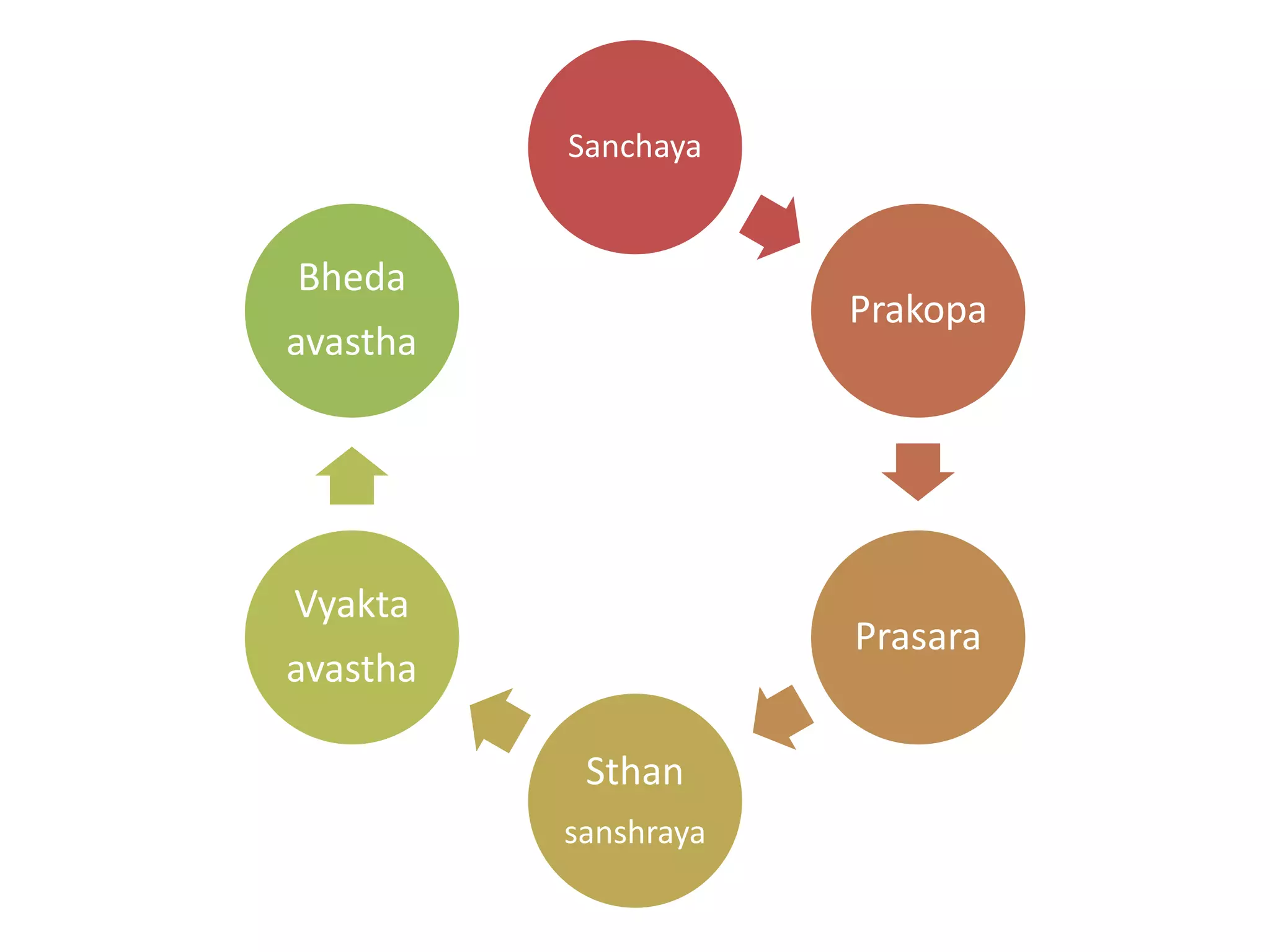
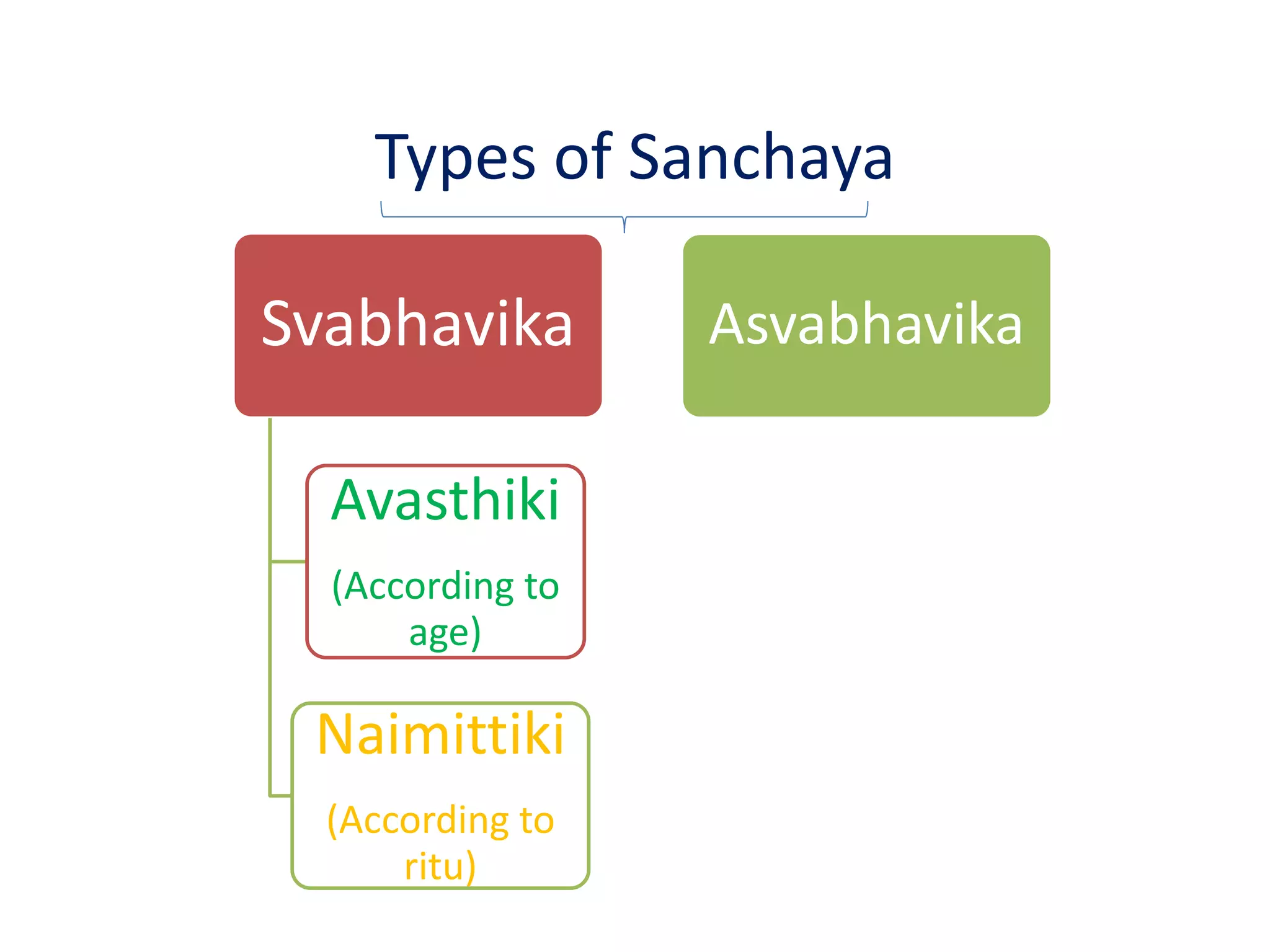
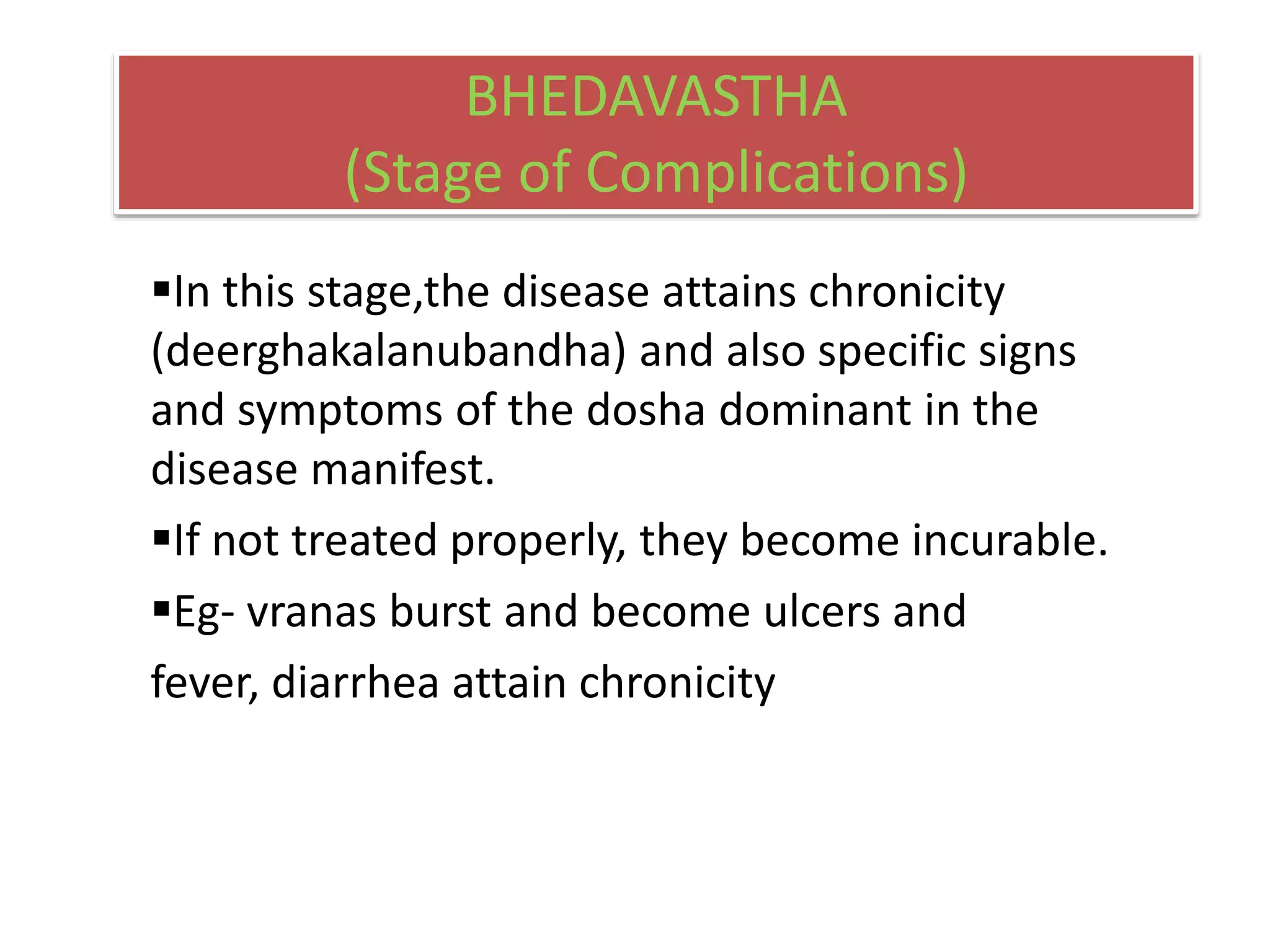
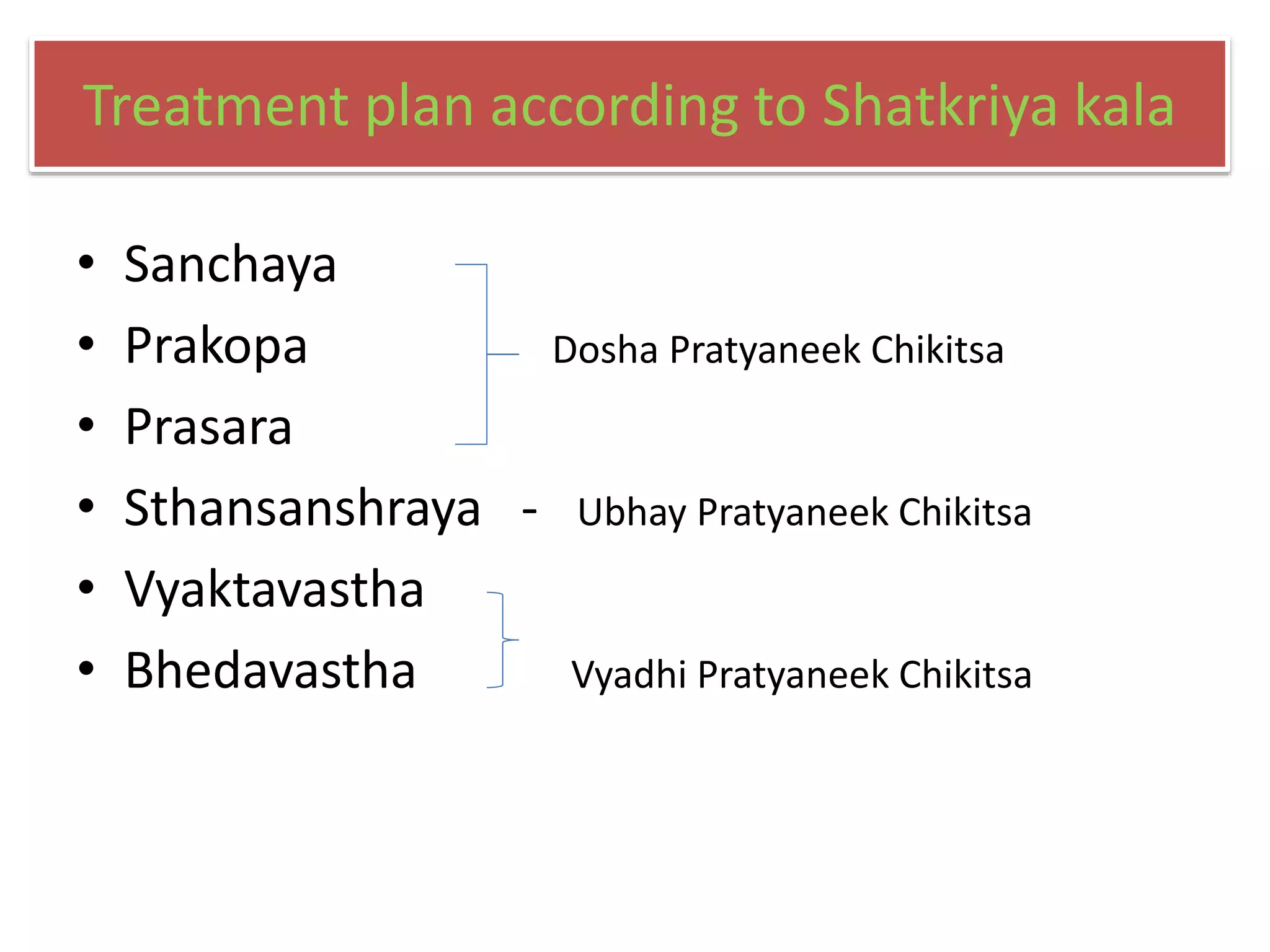
Shatkriya kala refers to the six stages of disease progression - sanchaya, prakopa, prasara, sthansanshraya, vyaktavastha, and bhedavastha. In sanchaya, doshas accumulate in their sites without changes in quality. Prakopa is the stage of aggravation where doshas increase in quantity and quality. Prasara is when aggravated doshas spread from their sites. In sthansanshraya doshas localize in tissues. Vyaktavastha is manifestation of clear symptoms. Bhedavastha is the stage of complications when disease becomes chronic if untreated. Understanding shatkriya kala