This document discusses different types of discrete probability distributions:
- The uniform distribution where all outcomes are equally likely. Rolling a fair die is given as an example.
- The Bernoulli distribution which has only two possible outcomes (success/failure) with probabilities p and q=1-p.
- The binomial distribution which models experiments with a fixed number of trials, two possible outcomes per trial (success/failure), and where trials are independent.

![
)]
(
2
)
(
2 x
P
x
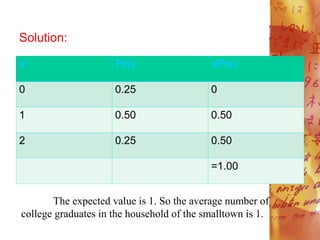
The mean or expected value of a
discrete random variable X is compted
using the following formula:
where: X= discrete random variable
x= outcome or the value of
random variable
P(x)= probability of the outcome x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicswithawesomeexample-240201063351-8ade9dd9/85/Mathematics-with-awesome-example-pdf-2-320.jpg)



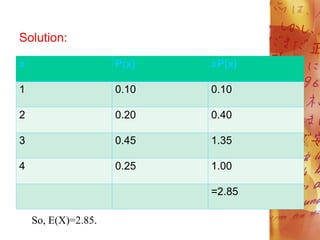
![Variance and Standard Deviation of a Discrete
Random Variable
The variance of a random variable X is
denoted by o2. It can likewise be written as Var
(X). The variance of a random variable is the
expected value of the square of the difference
between the assumed value of random variable
and the mean. The variance of X is:
)]
(
2
)
(
2 x
P
x
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicswithawesomeexample-240201063351-8ade9dd9/85/Mathematics-with-awesome-example-pdf-8-320.jpg)


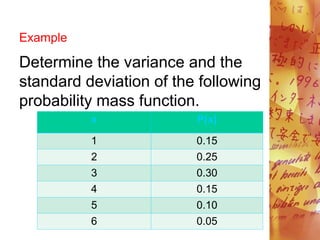

![E(X)= 2. 95
=1.8475 or 1.85
Therefore, the standard deviation
is 1.85.
)]
(
2
)
(
2 x
P
x
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicswithawesomeexample-240201063351-8ade9dd9/85/Mathematics-with-awesome-example-pdf-14-320.jpg)





![SOLUTION:
x P(x) xP(x)
0 0.995 0
5000 0.005 25
=25
The expected gain is P25.00.
)]
(
[ x
xP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicswithawesomeexample-240201063351-8ade9dd9/85/Mathematics-with-awesome-example-pdf-20-320.jpg)

![SOLUTION:
x P(x) xP(x) X2P(x)
0 0.99375 0 0
3000 0.00625 18.75 56,250
=18.75 =56,250
)]
(
[ x
xP )]
(
2
[ x
P
x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicswithawesomeexample-240201063351-8ade9dd9/85/Mathematics-with-awesome-example-pdf-22-320.jpg)
![a. E(X)= [xP(x)]
=18.75
b. = [x2P(x) - ([xP(x)])2
= 56,250 - (18.75)2
= 56,250 - 351.5625
= 55,898.44
2
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicswithawesomeexample-240201063351-8ade9dd9/85/Mathematics-with-awesome-example-pdf-23-320.jpg)


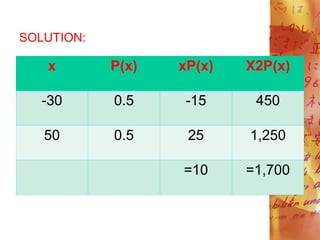
![a. E(X)= [xP(x)]
=10
b. =[x2P(x) - ([xP(x)])2
= 1,700 - (10)2
= 1,700 - 100
= 1,600](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicswithawesomeexample-240201063351-8ade9dd9/85/Mathematics-with-awesome-example-pdf-27-320.jpg)











