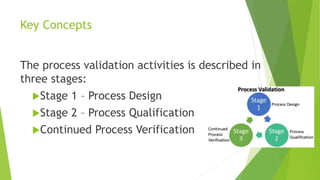
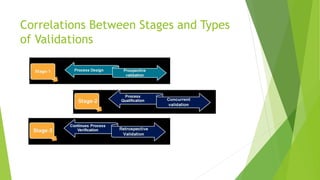
This document discusses computer system validation and process validation. It defines process validation as establishing evidence through all stages of production to consistently deliver quality products according to regulations. The FDA defines process validation as providing high assurance a process consistently meets specifications. Key concepts include three validation stages: process design, process qualification, and continued verification. There are four types of validation: prospective, retrospective, concurrent, and revalidation when changes are made.