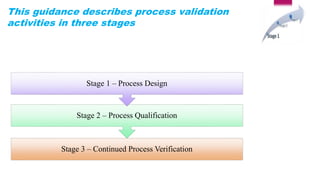
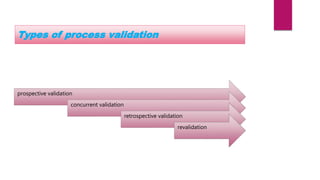
This document discusses process validation, which involves proving that manufacturing processes will consistently produce products meeting specifications. It describes the three stages of process validation: process design, process qualification, and continued process verification. The types of process validation covered are prospective, concurrent, and retrospective validation, as well as revalidation. The advantages of process validation include increased process knowledge, repeatability, production fluency, and decreased risks and expenses.