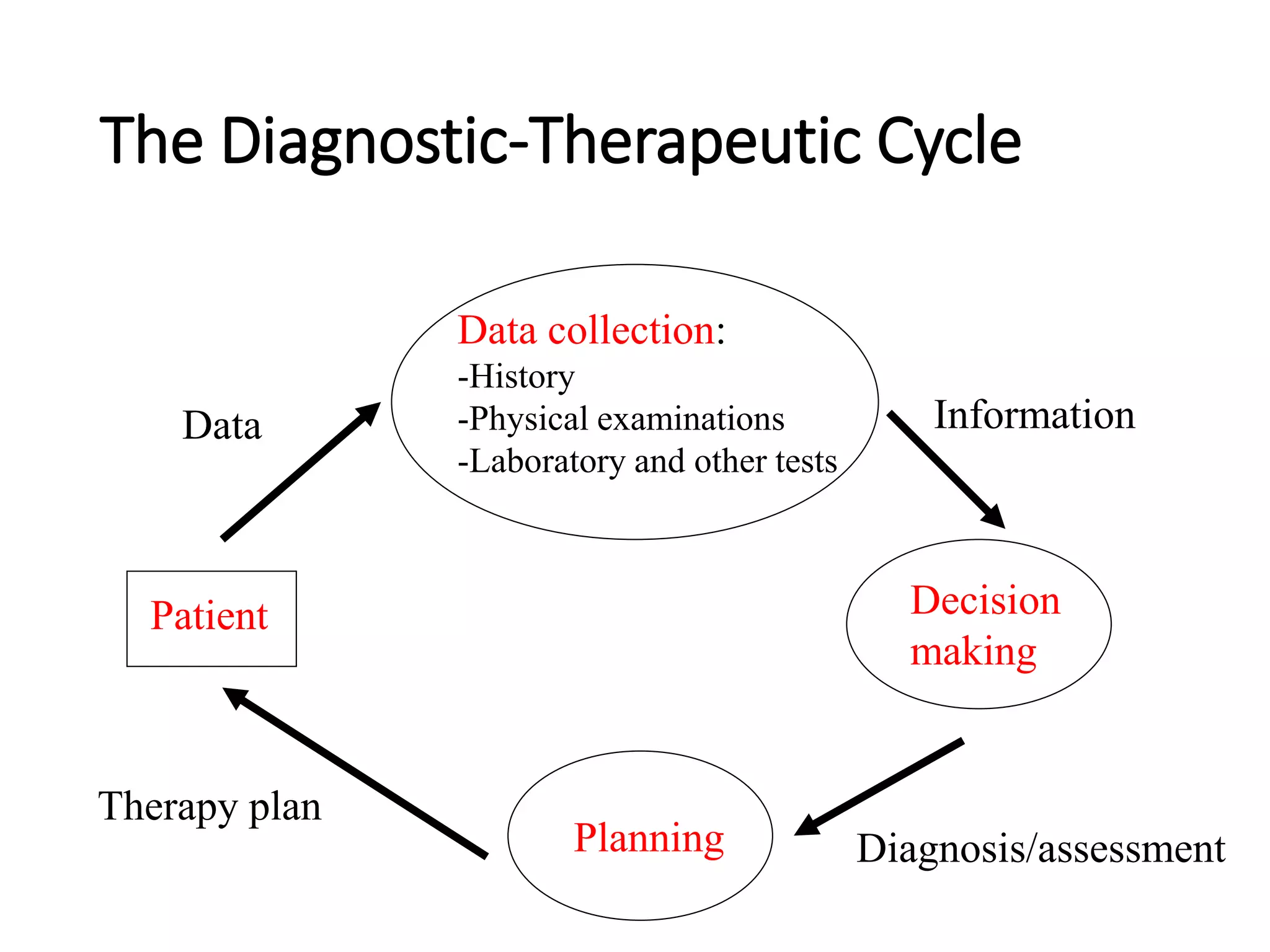
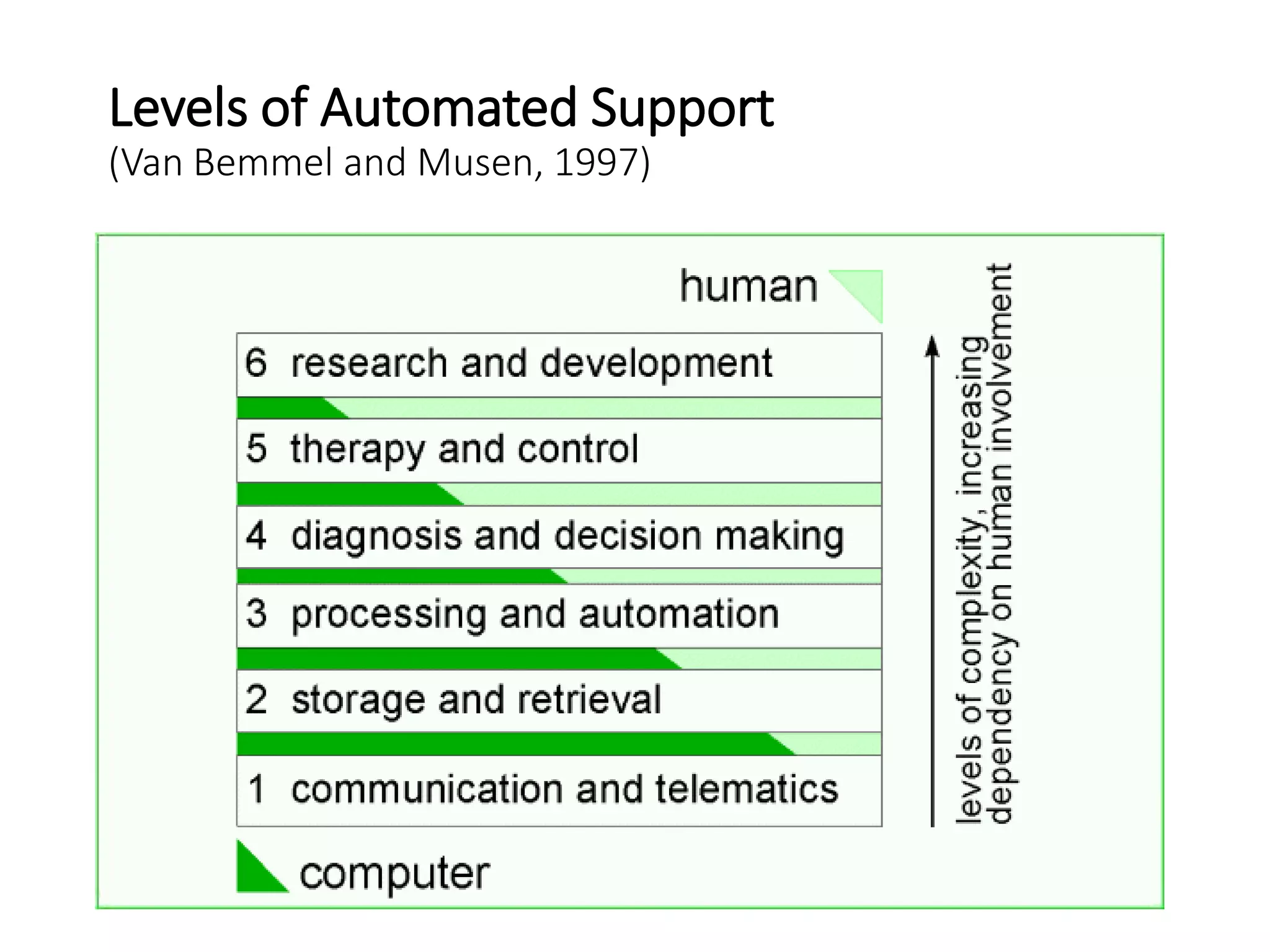
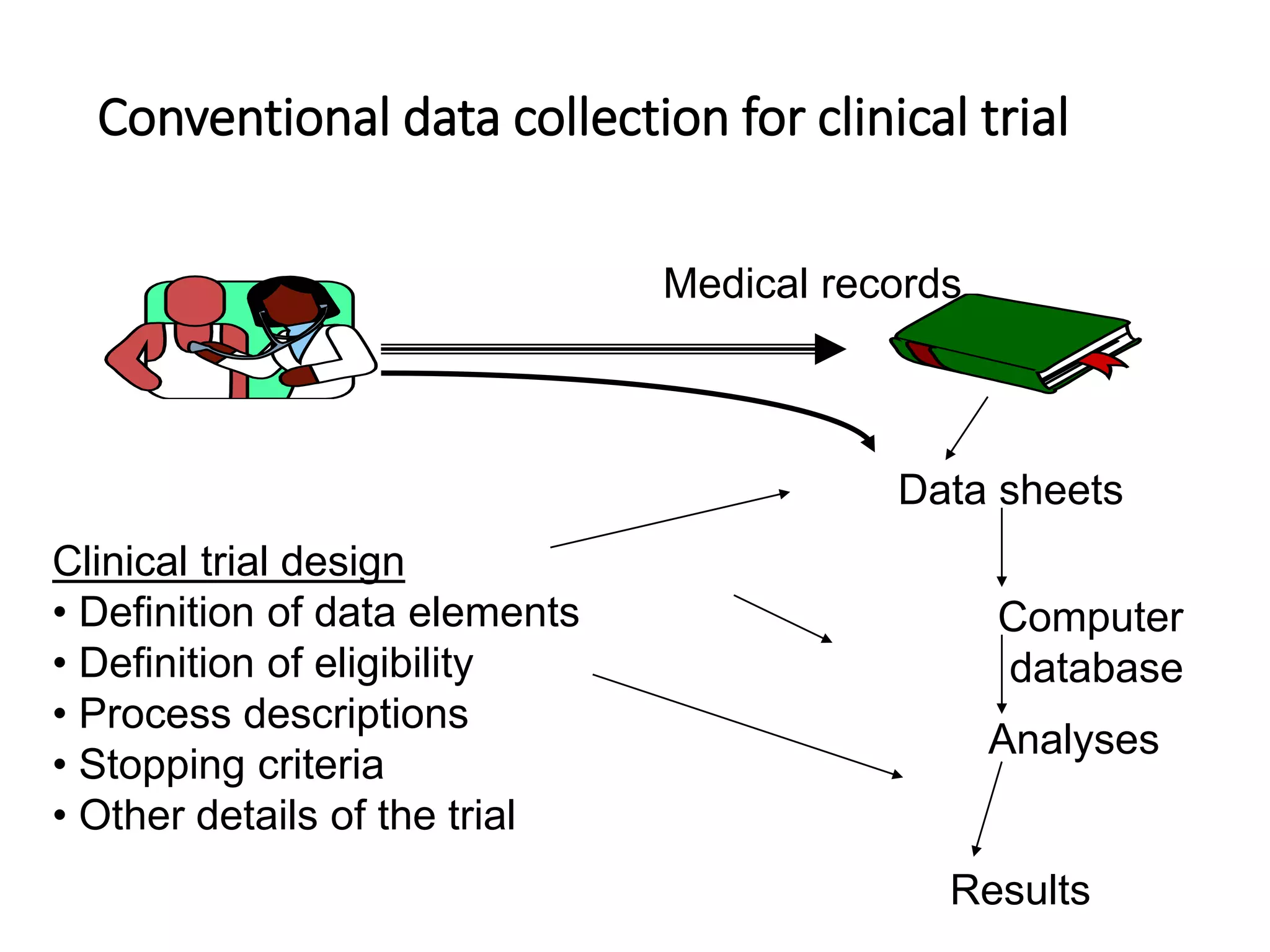
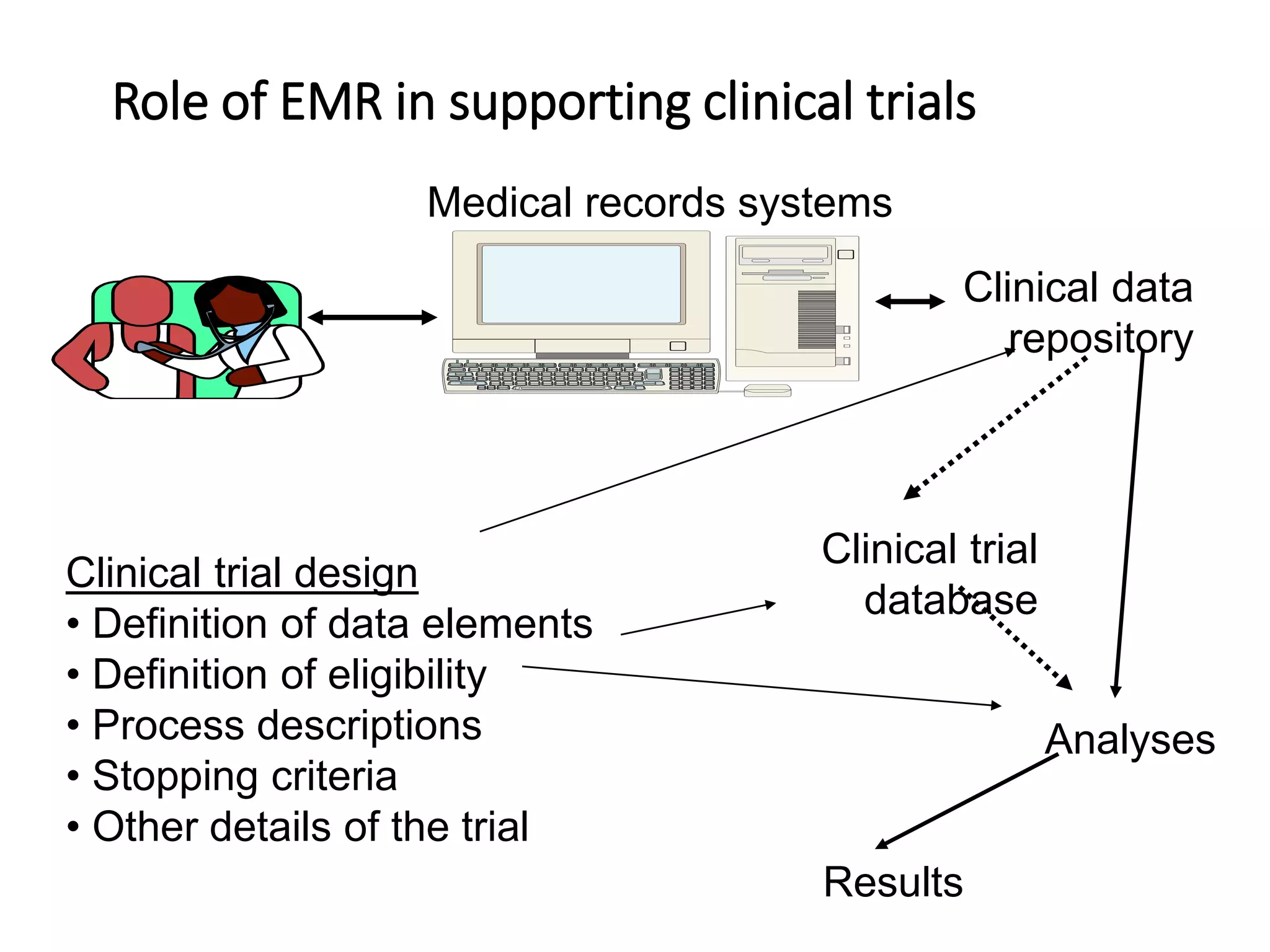
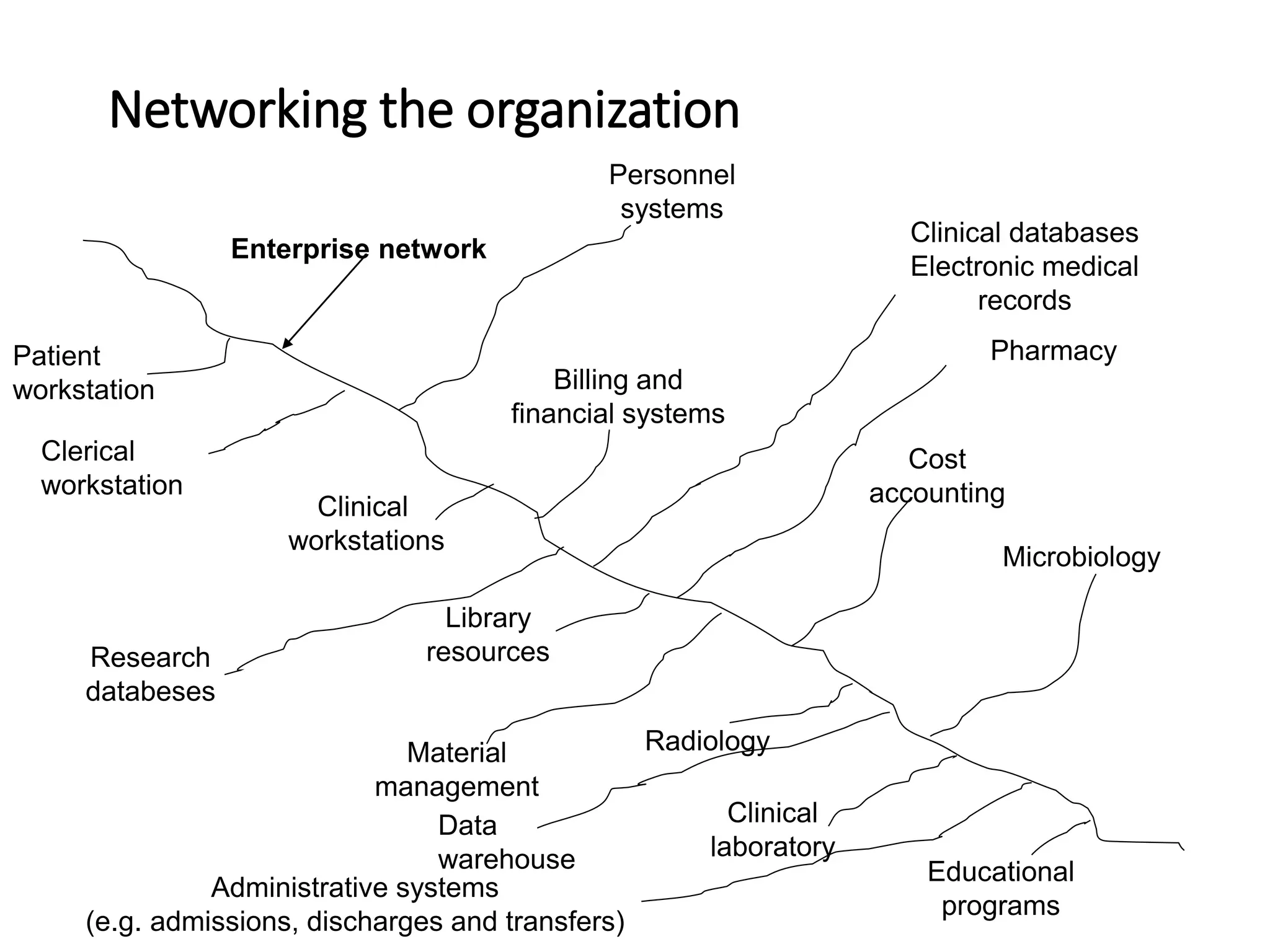
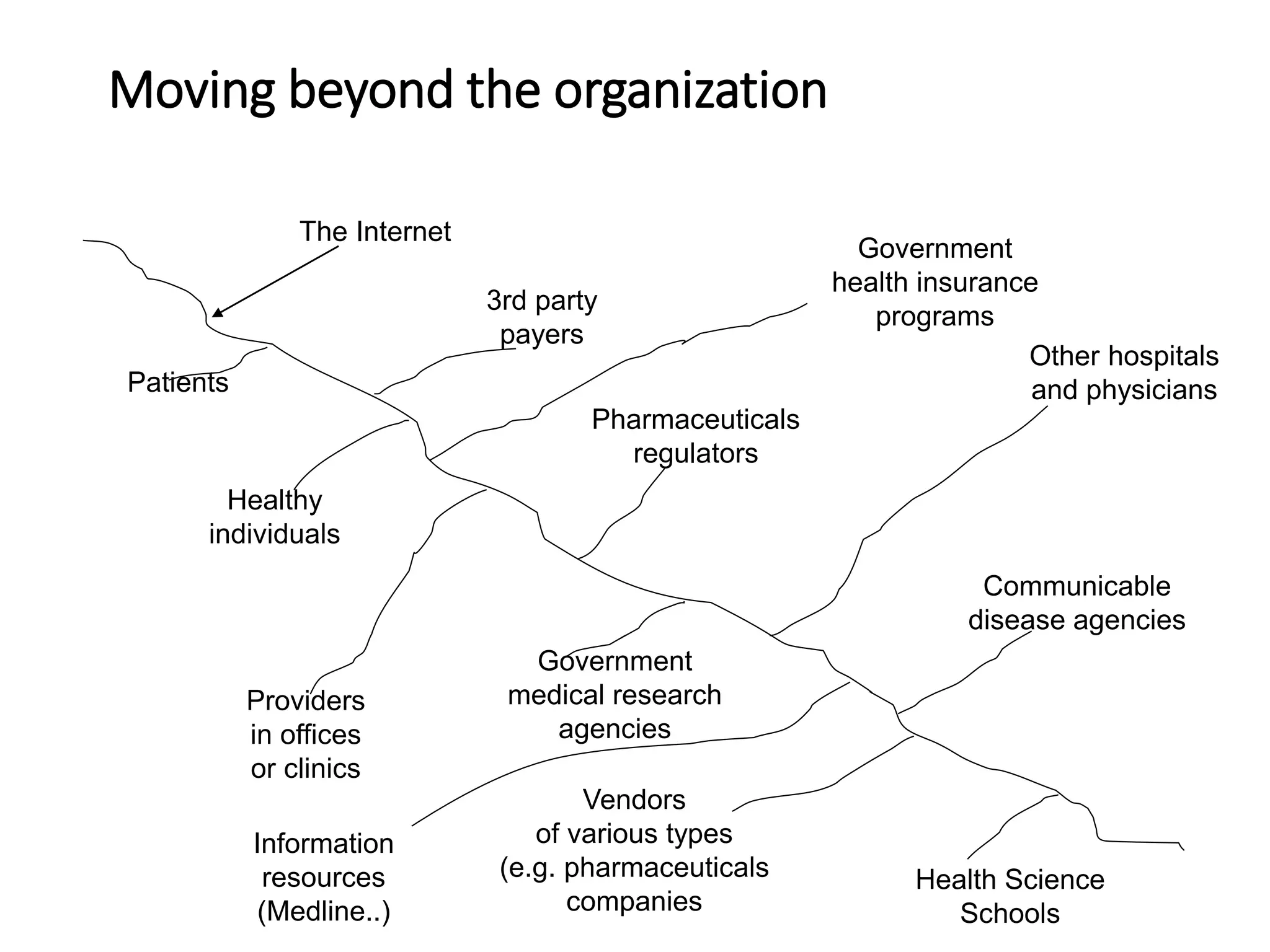
This document discusses the field of medical informatics, which deals with optimizing the storage, retrieval, and management of biomedical information. It defines medical informatics and related fields like medical decision making, computing, and decision support. It outlines key areas that medical informatics impacts like education, clinical decision support, and imaging. It also examines the role of informatics in clinical settings and clinical trials.