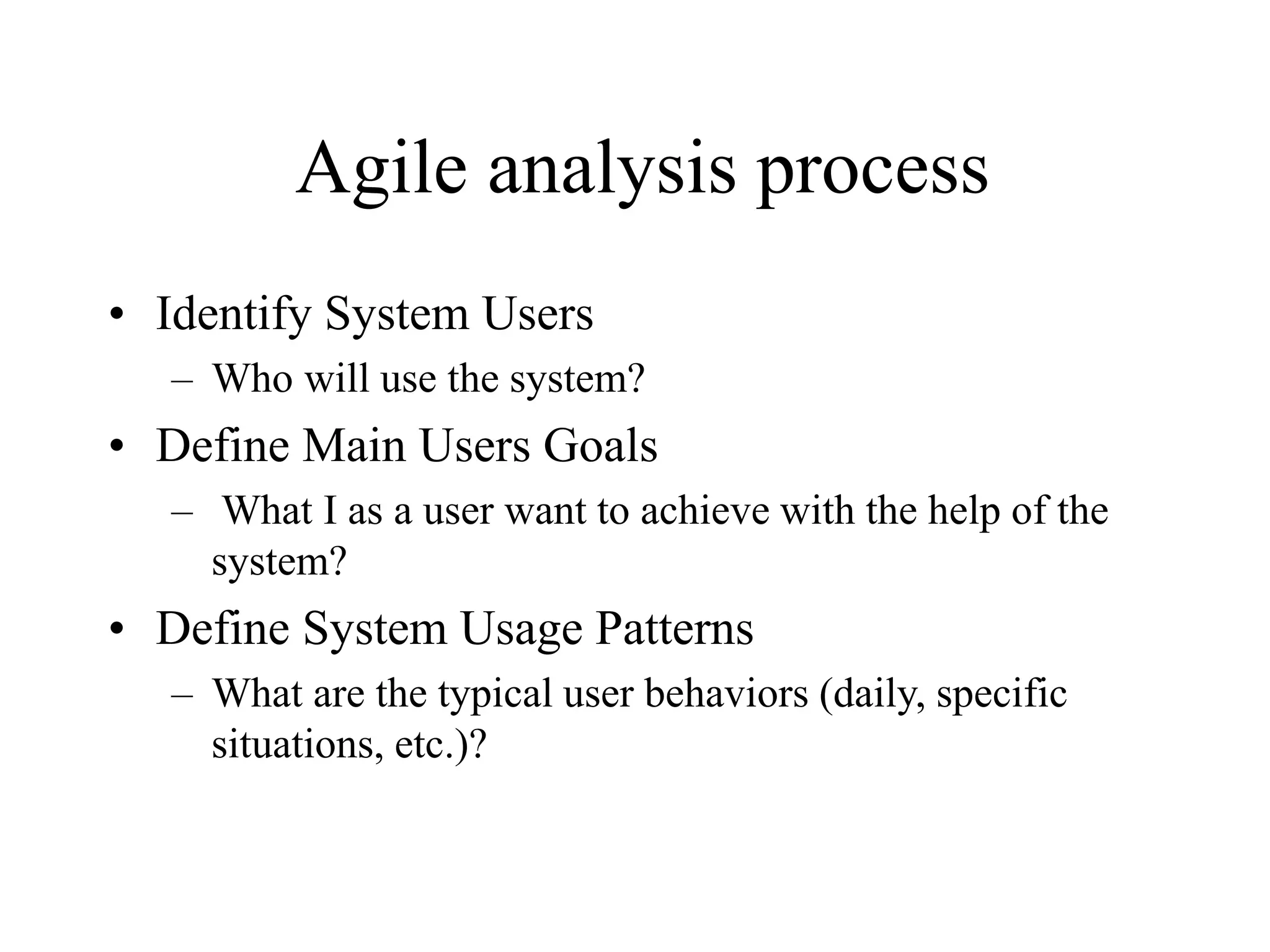
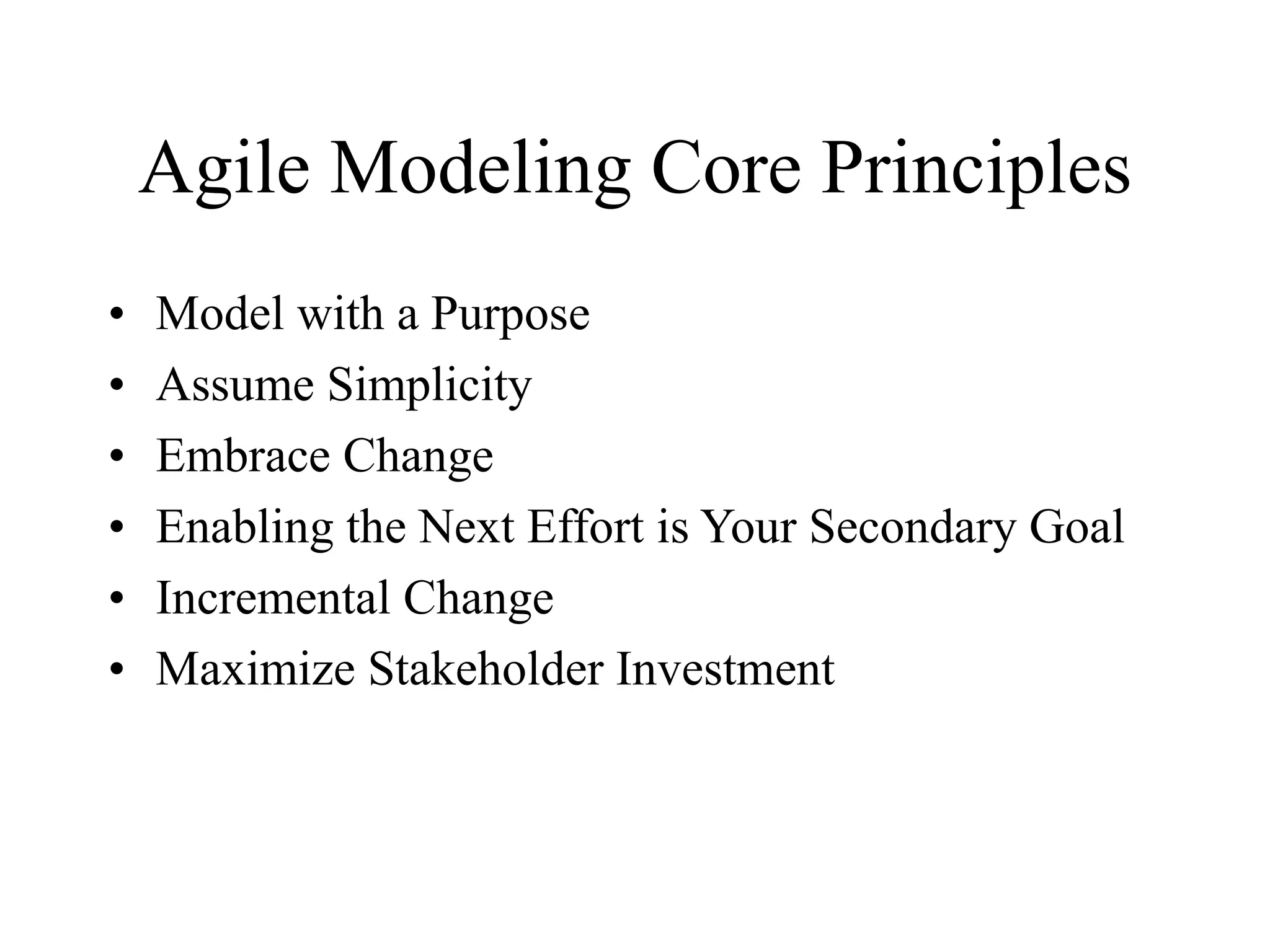
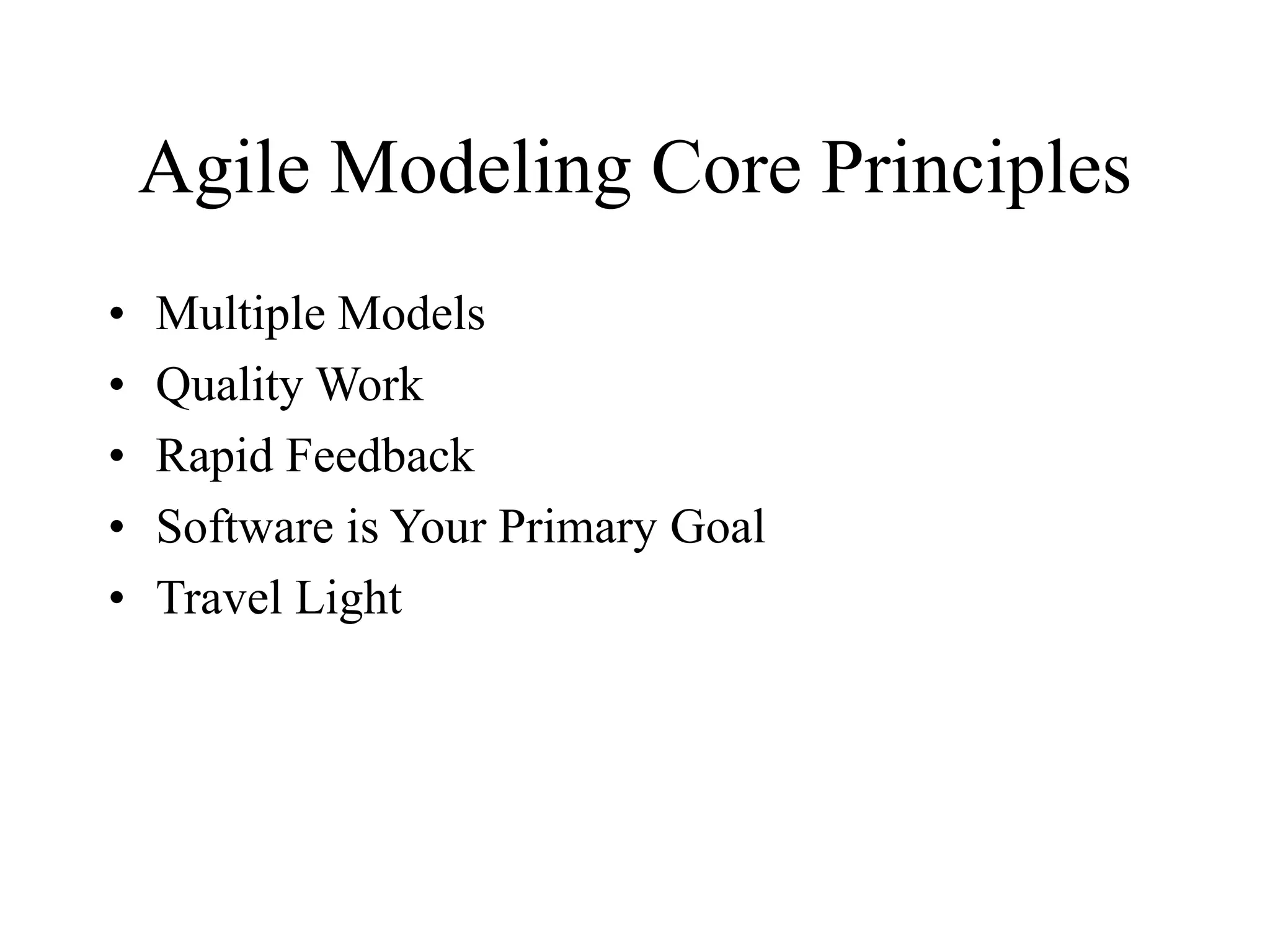
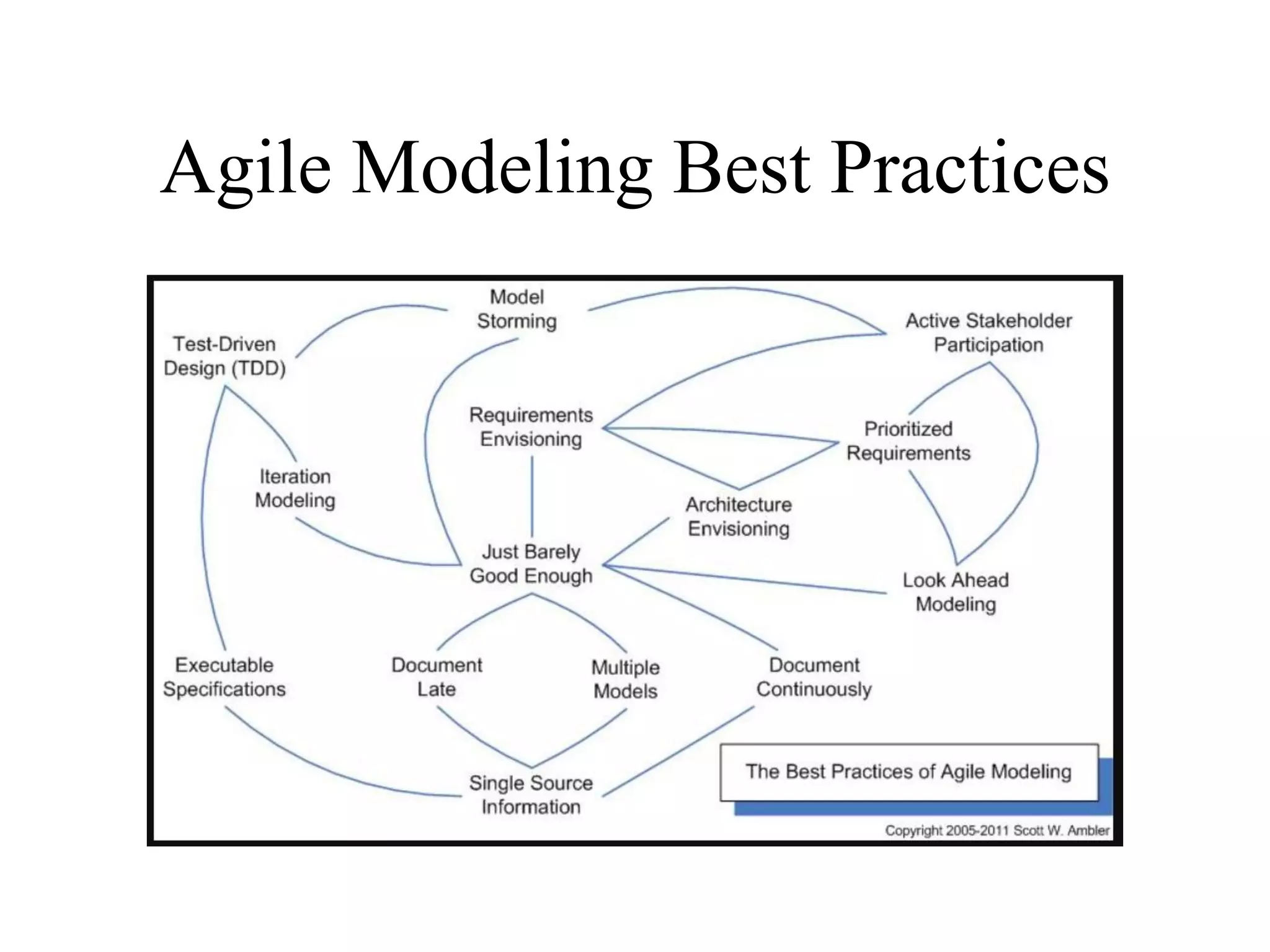
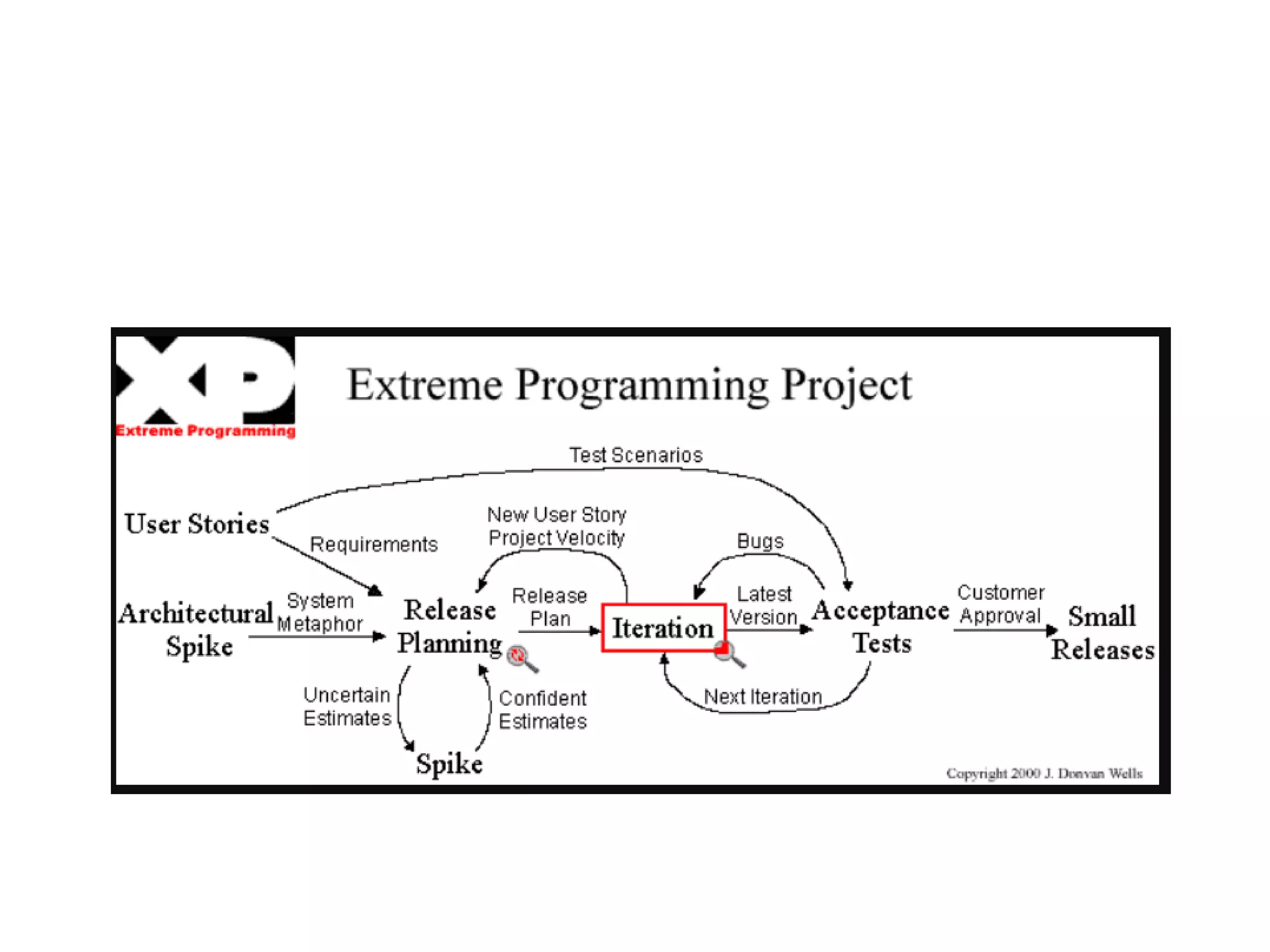
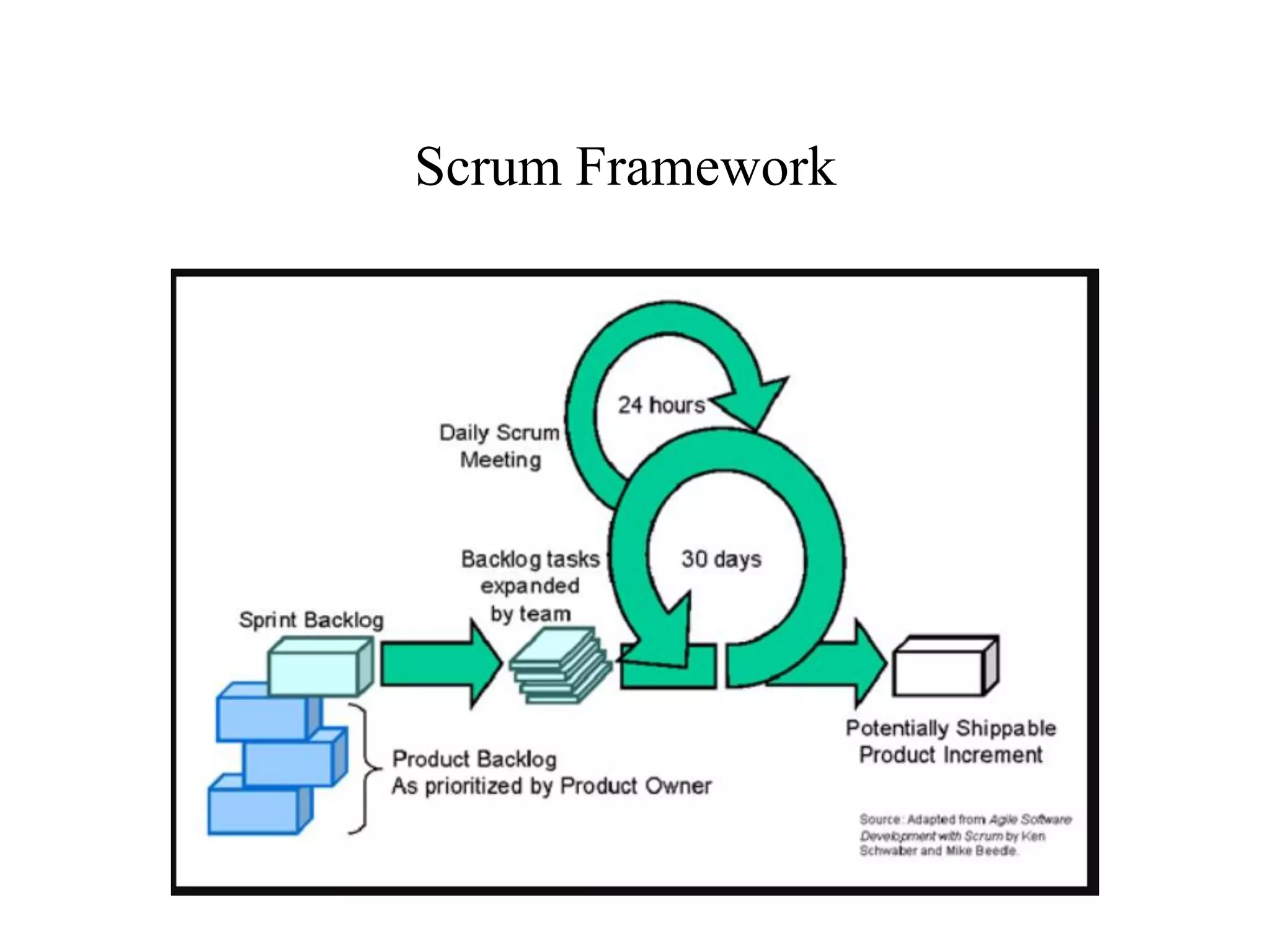
This document discusses agile analysis and modeling processes and methodologies. It describes the core principles of the Agile Manifesto which emphasize individuals, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change. It then outlines the agile analysis process of identifying users and goals, defining usage patterns and solutions. It also discusses the core principles and practices of extreme programming and scrum, including events, roles, and artifacts. It notes some limitations of agile methodologies in terms of dependence on user involvement and small team sizes.