Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times



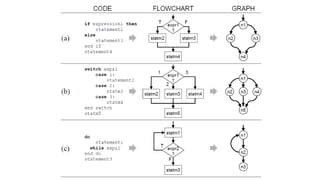

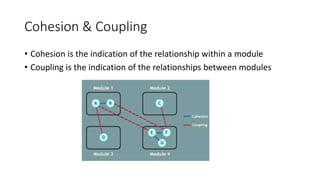


Software measurements can be used to estimate cost and effort and provide feedback to improve quality. Cyclomatic complexity captures the complexity of conditional logic in a program using graph theory and McCabe's metric. It counts linearly independent paths to determine testability and understandability. Cohesion measures relationships within a module while coupling measures relationships between modules.






