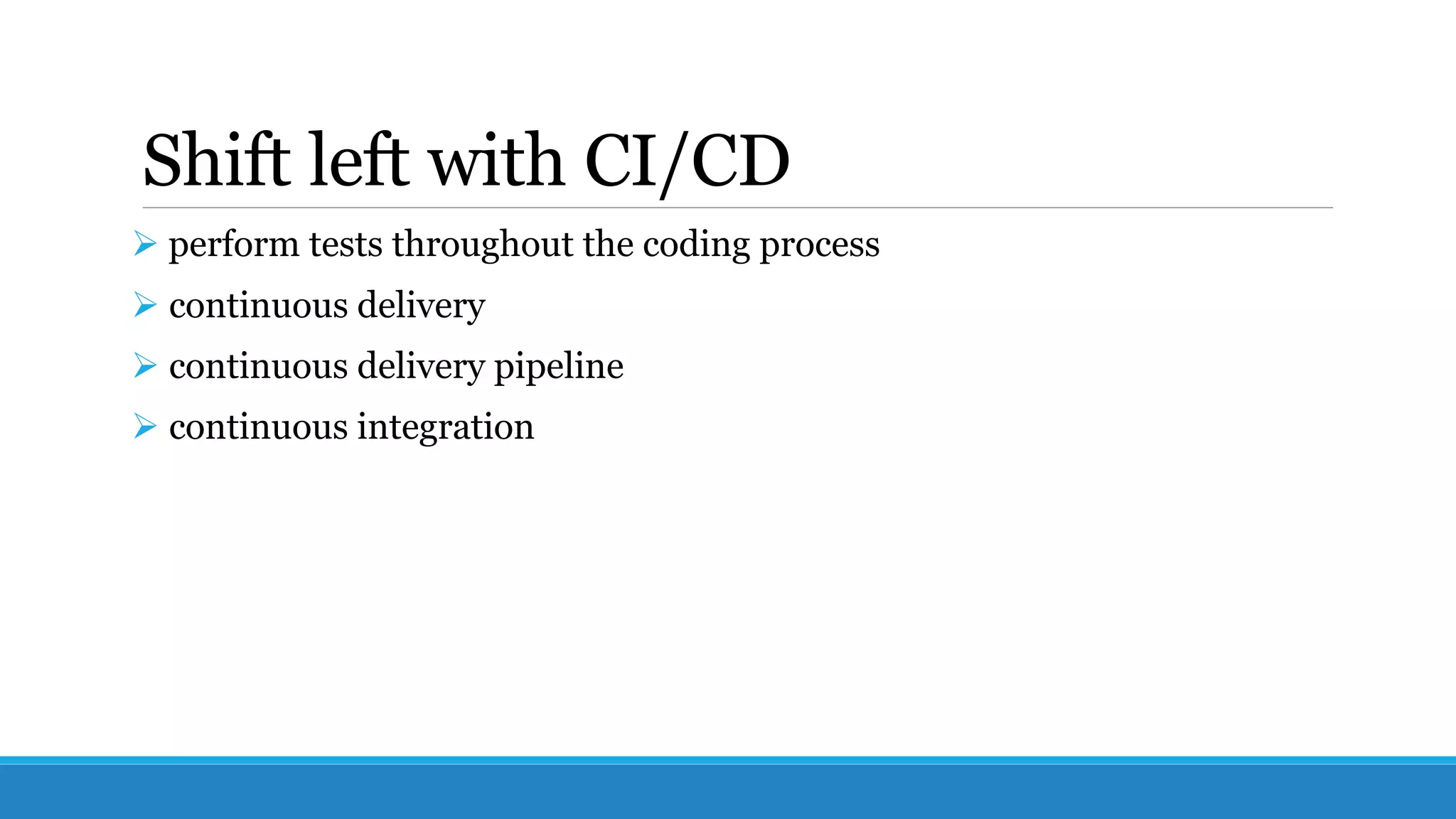
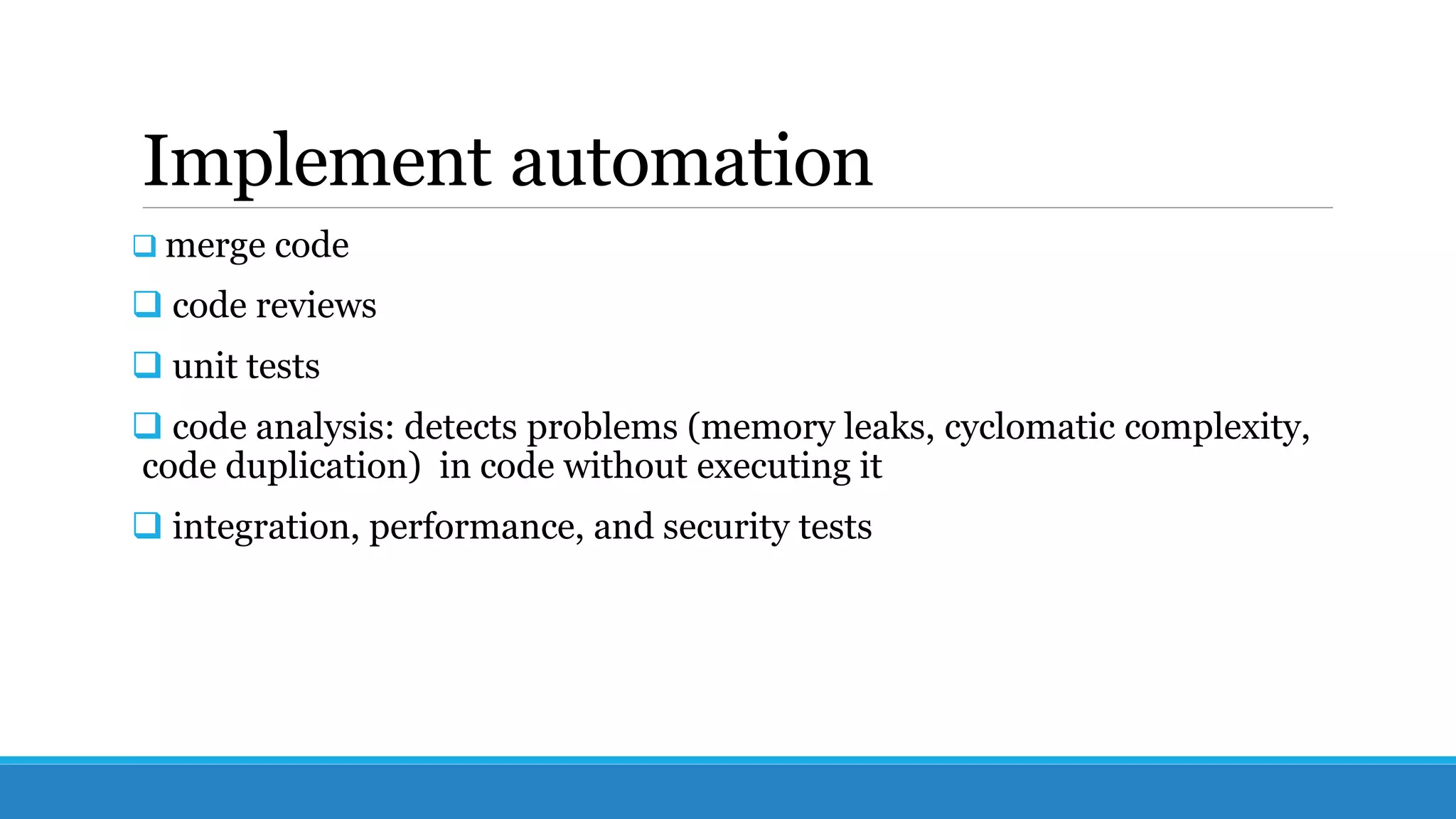
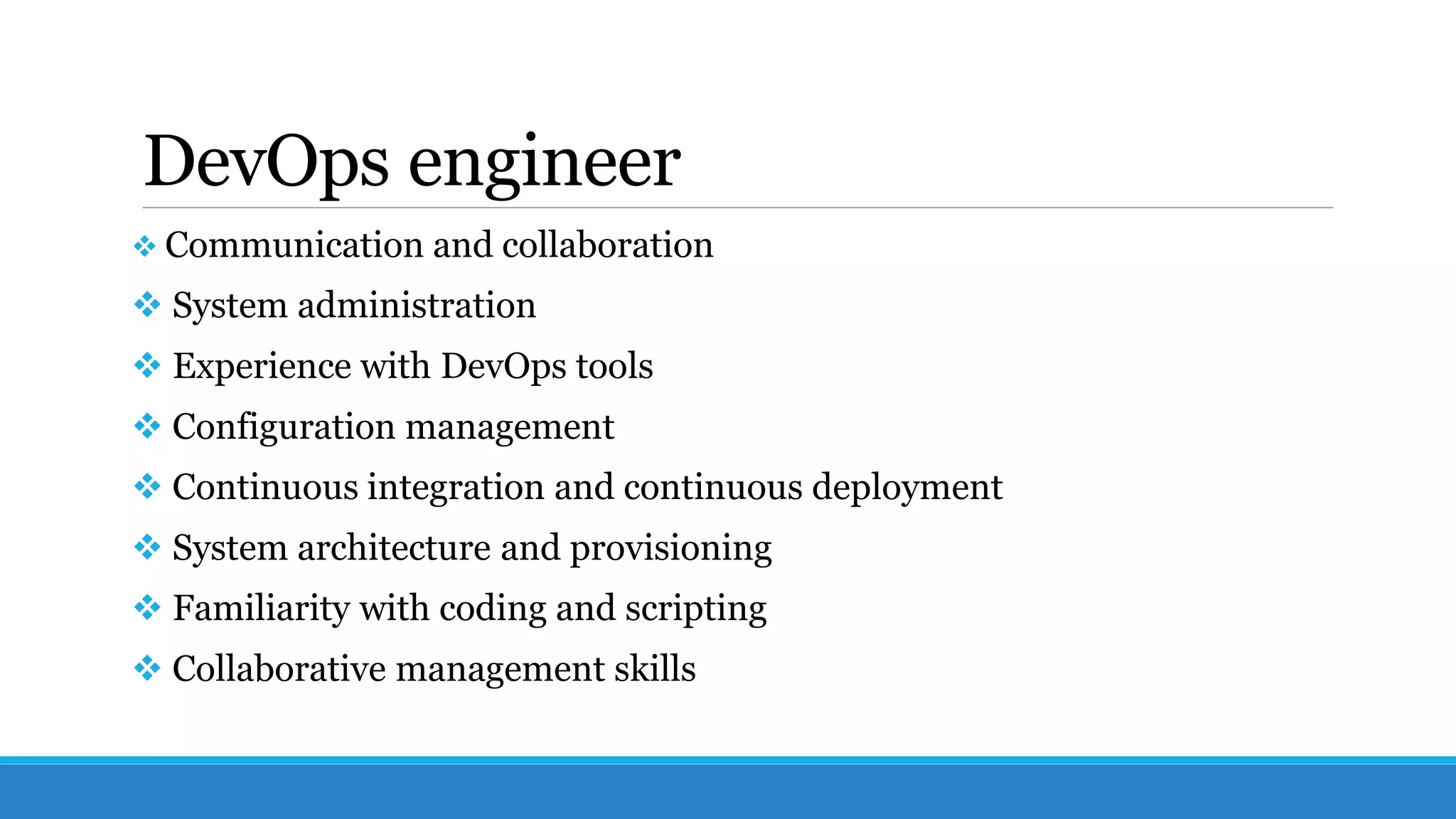
This document discusses DevOps, which aims to bridge the gap between development and operations teams. It involves merging these teams so engineers work across the entire application lifecycle. Key DevOps practices include adopting Agile project management, shifting testing left through continuous integration and delivery, using tools to automate processes, and monitoring applications. DevOps can improve speed, reliability, collaboration and security. Implementing DevOps requires cultural change and using the right tools and practices.