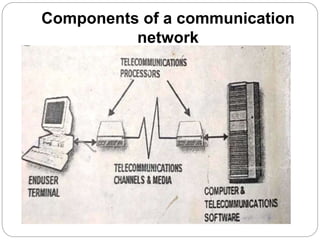
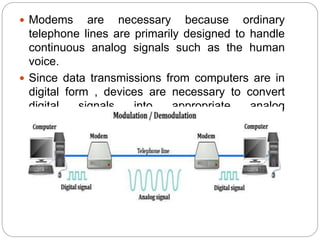
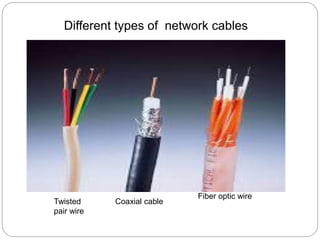
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to computer networks, detailing the essential components such as terminals, telecommunication processors, channels, and software necessary for effective data communication. It discusses various types of communication media, including twisted pair wires, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables, highlighting their functionalities and advantages. Additionally, the text covers the roles of telecommunication software and communication processors in managing network activities, including error detection and security control.