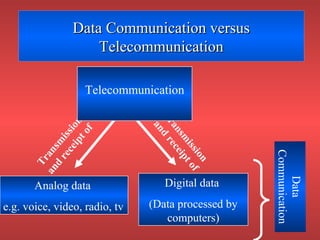
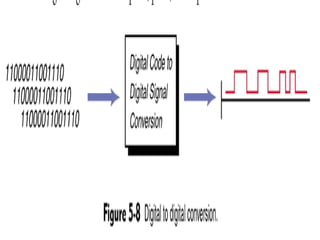
Data communication refers to the transmission of digital data between computers over a medium like telephone lines. Telecommunication includes both digital and analog transmission of data and voice. Data communication is a subset of telecommunication.
A communication network consists of a source that sends messages, a medium like phone lines or fiber optic cables that transmits the data, and a receiver that accepts the messages. Data can be transmitted serially, one bit at a time over a single line, or in parallel, with all bits sent simultaneously over multiple lines.