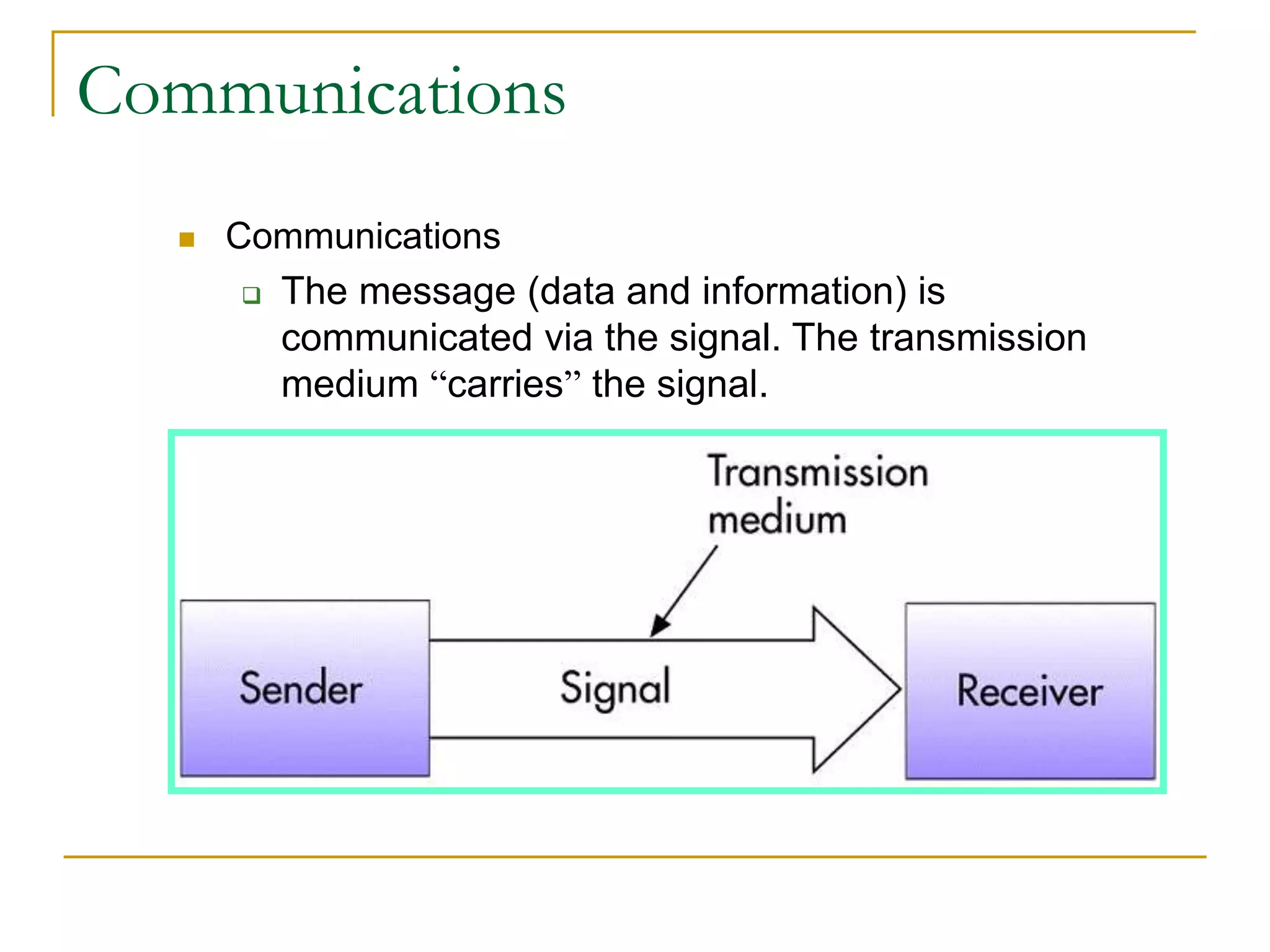
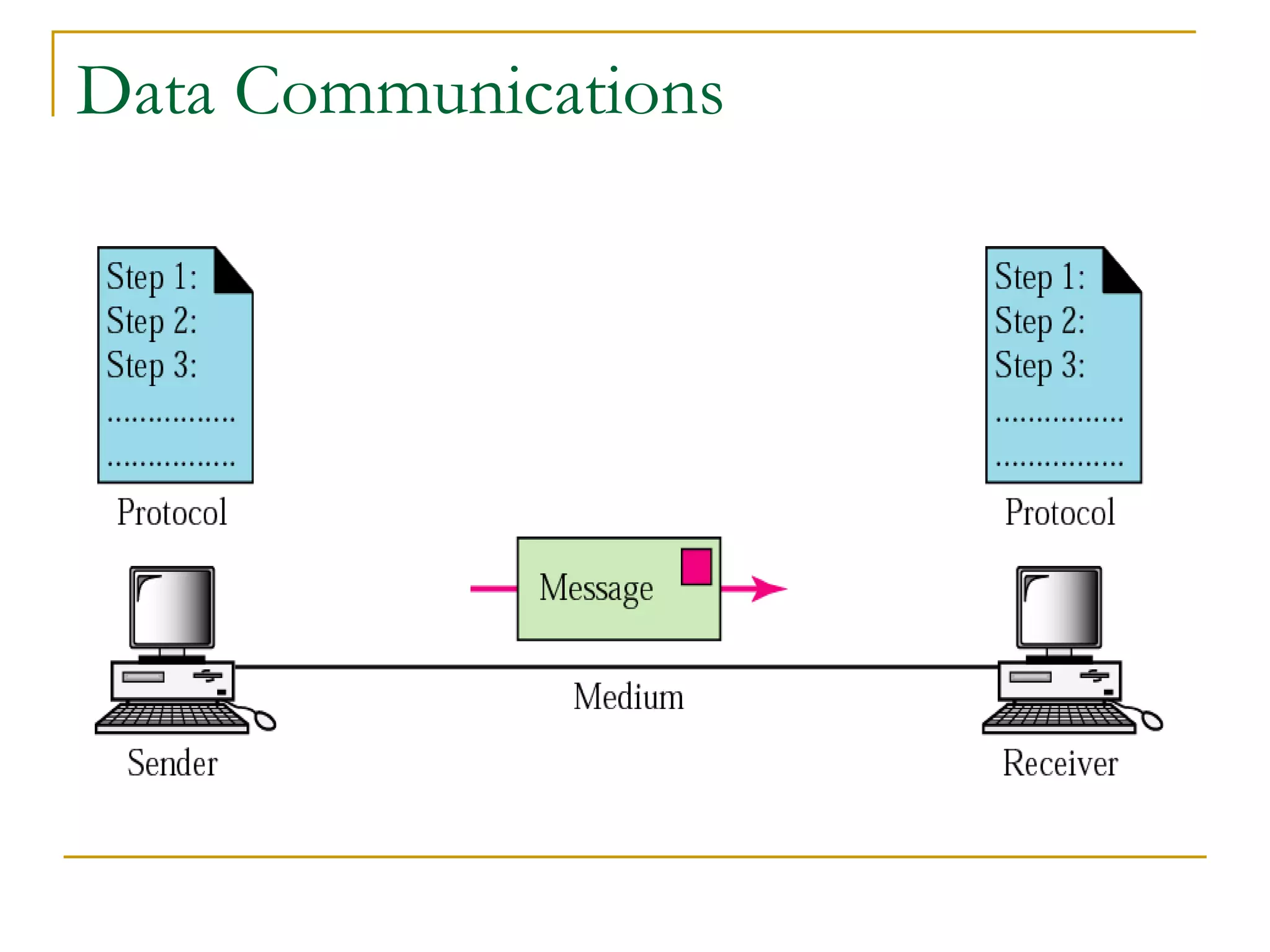
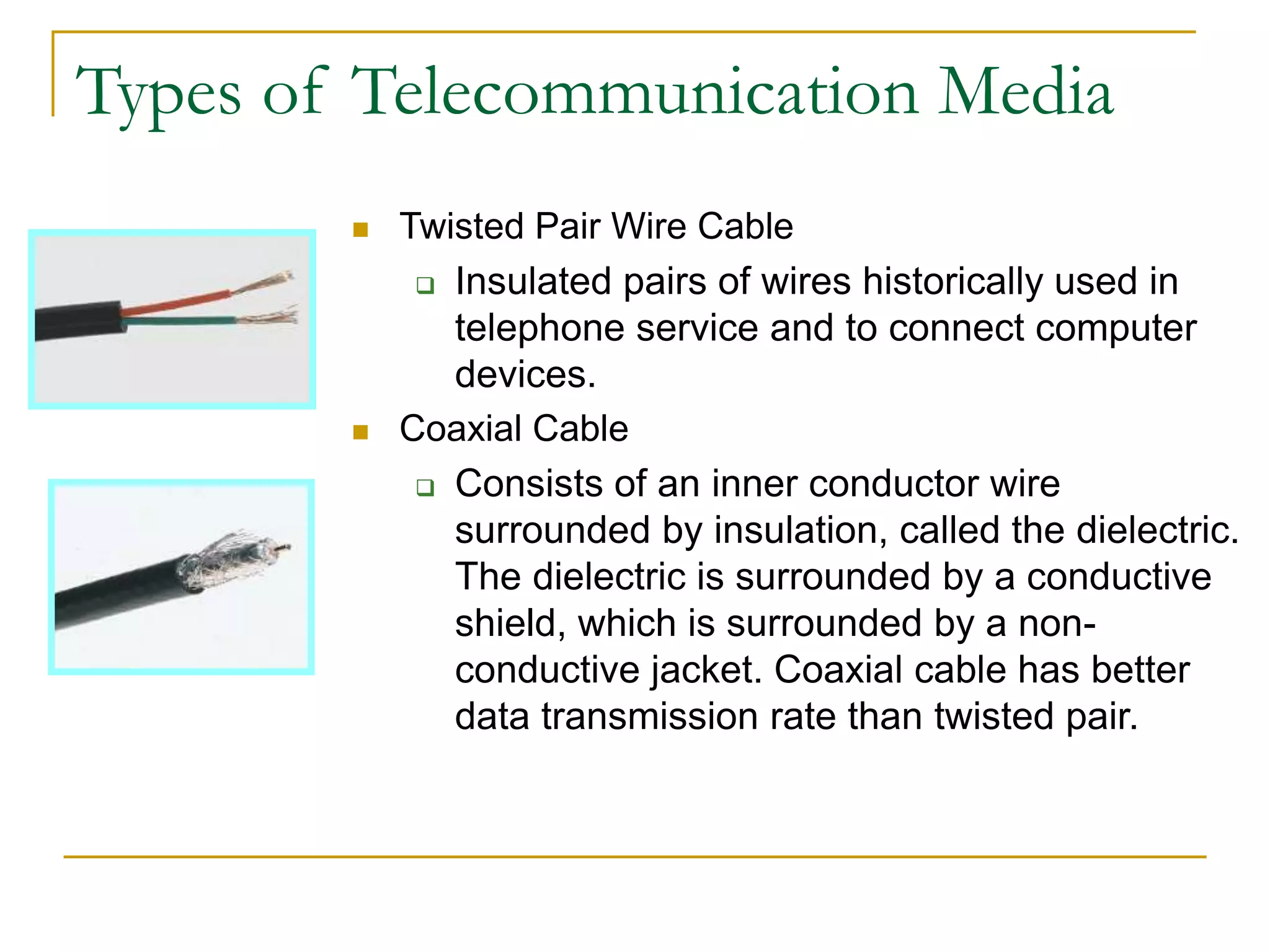
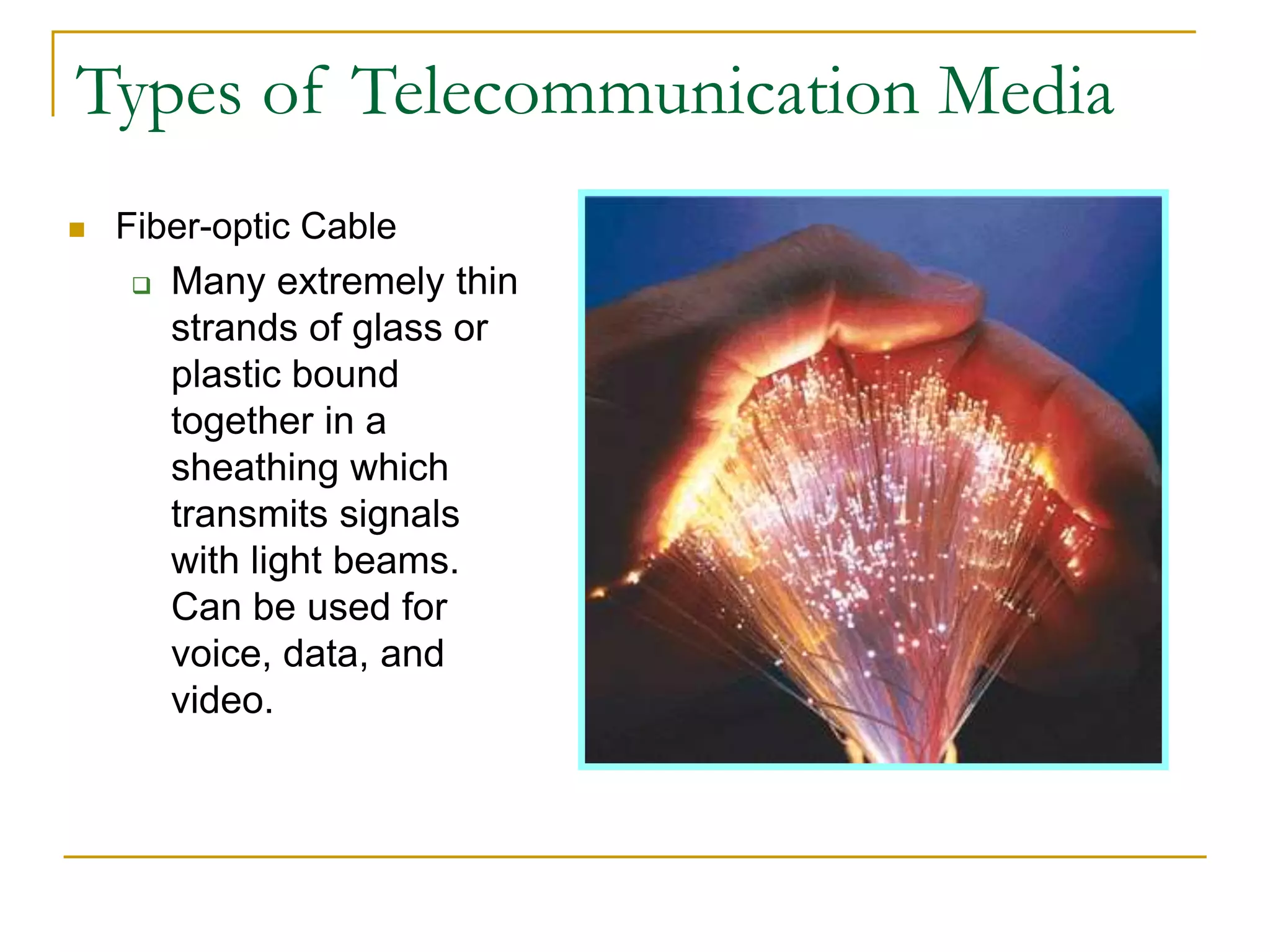
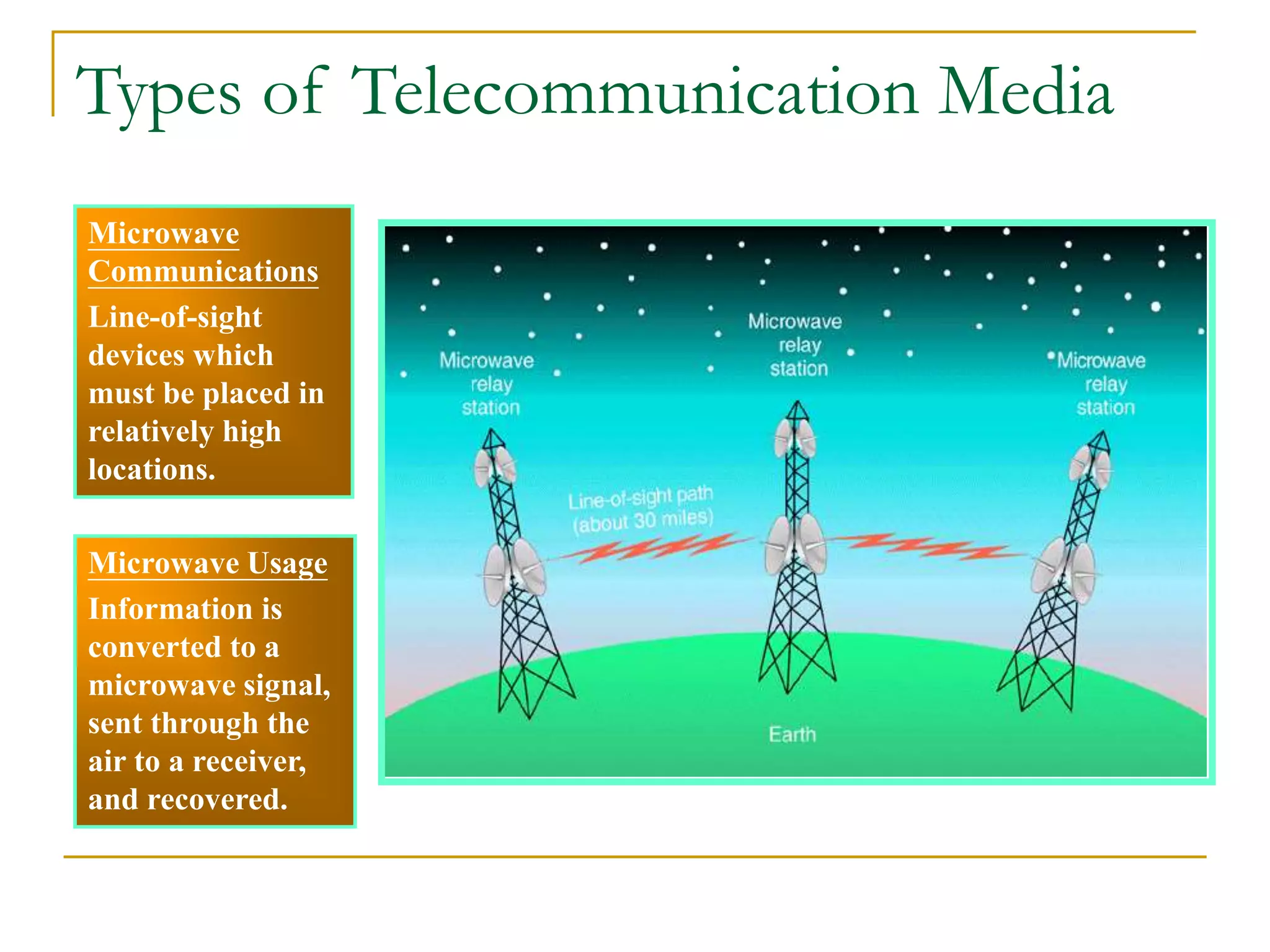
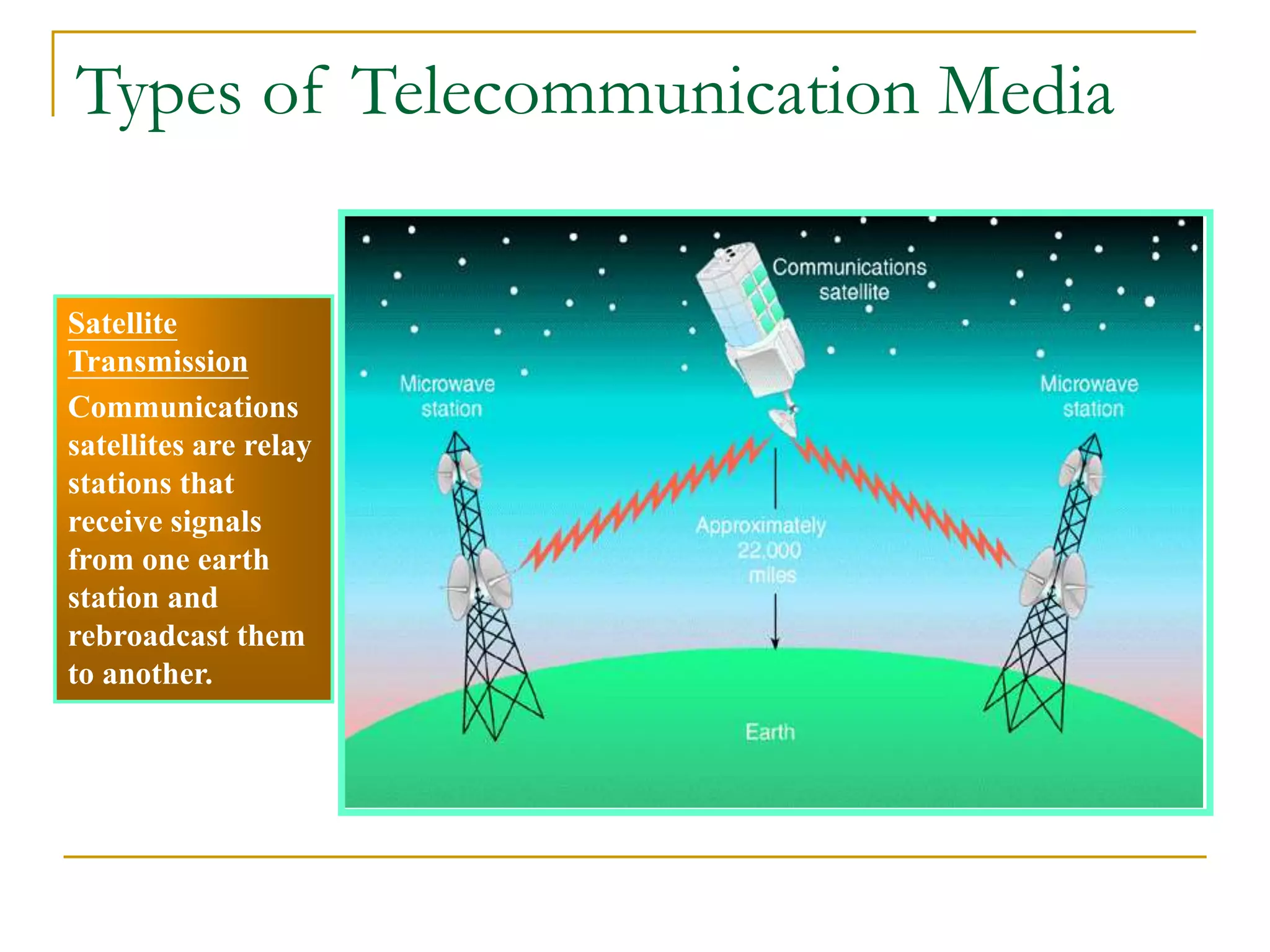
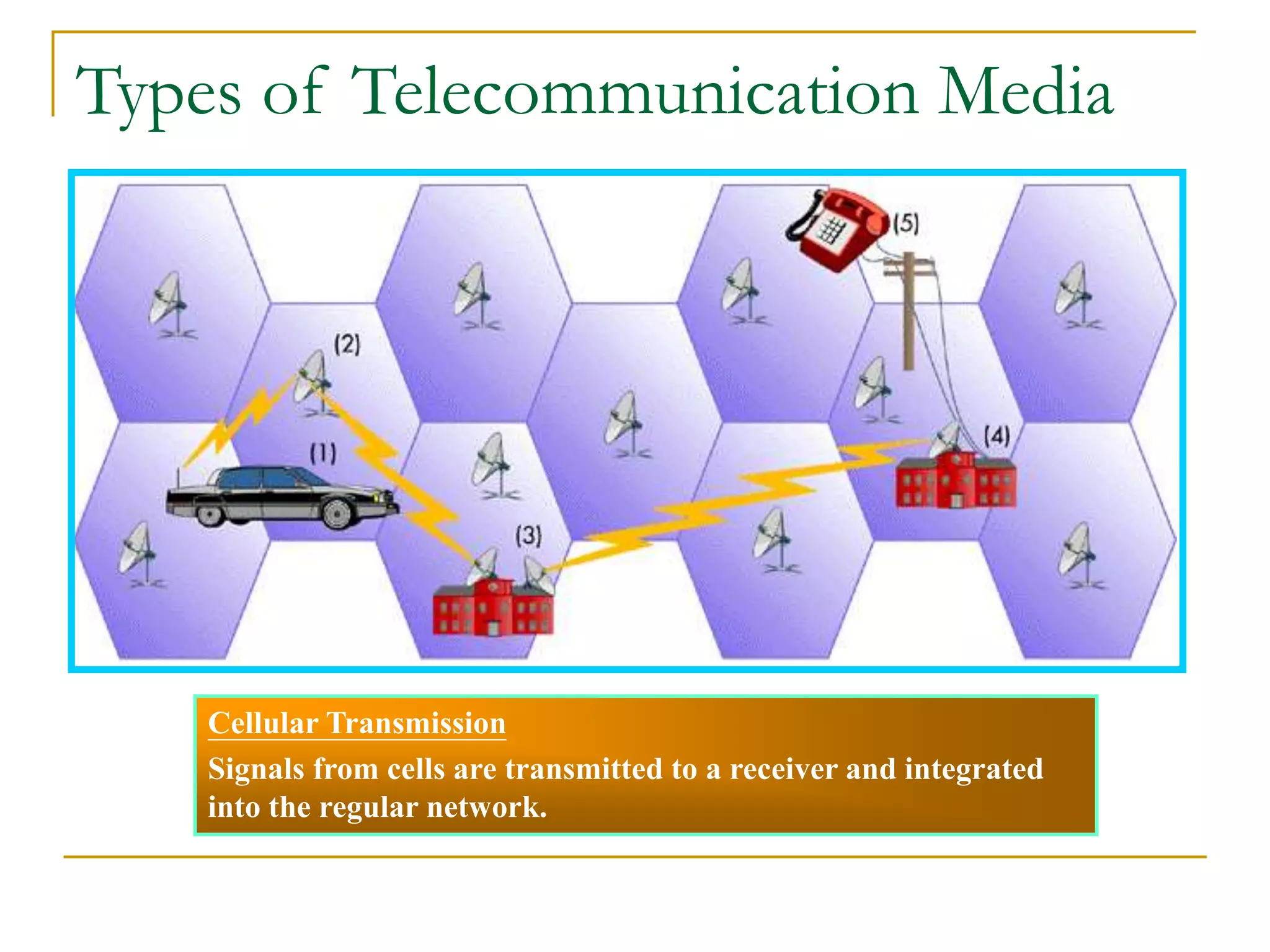
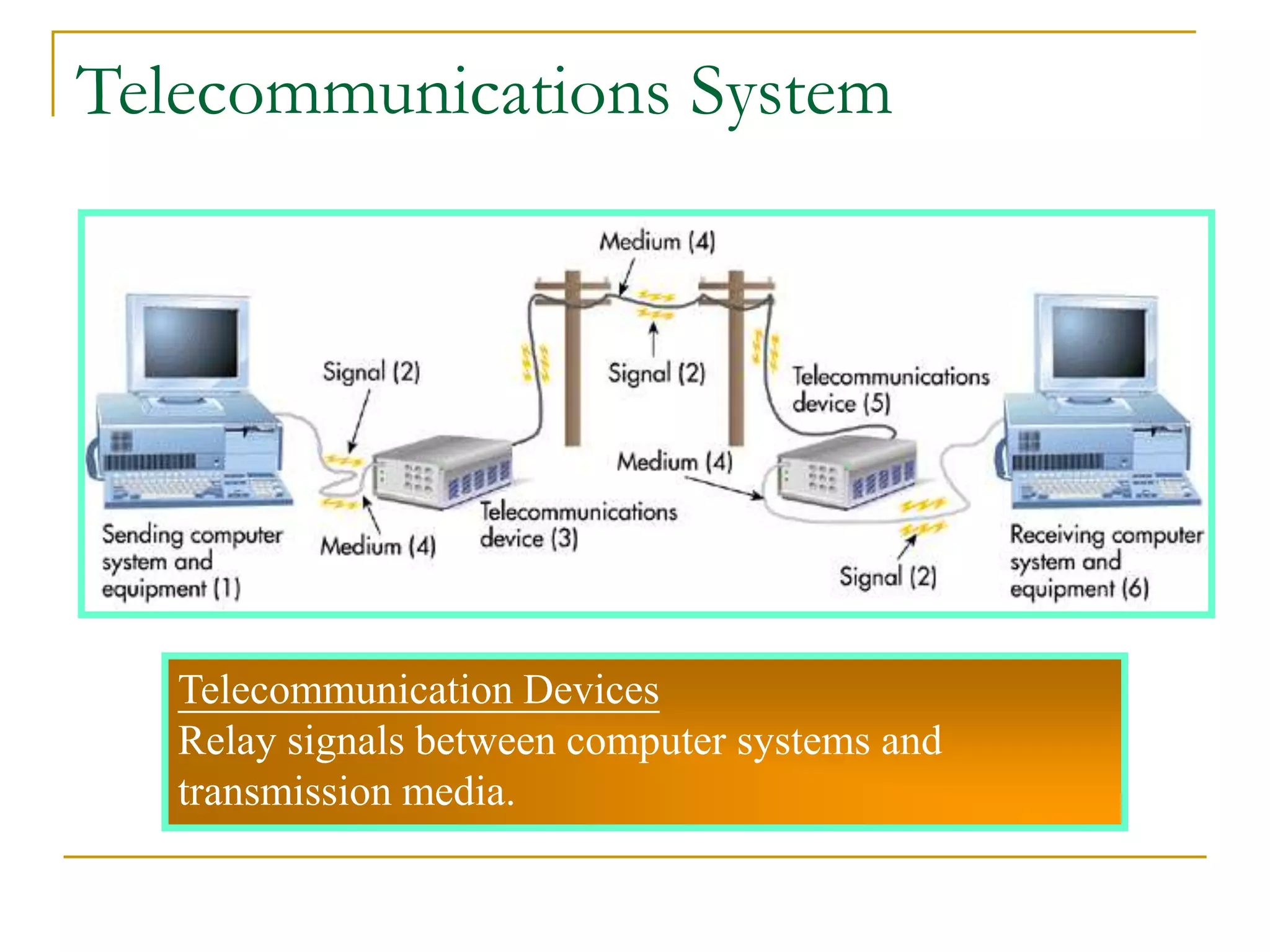
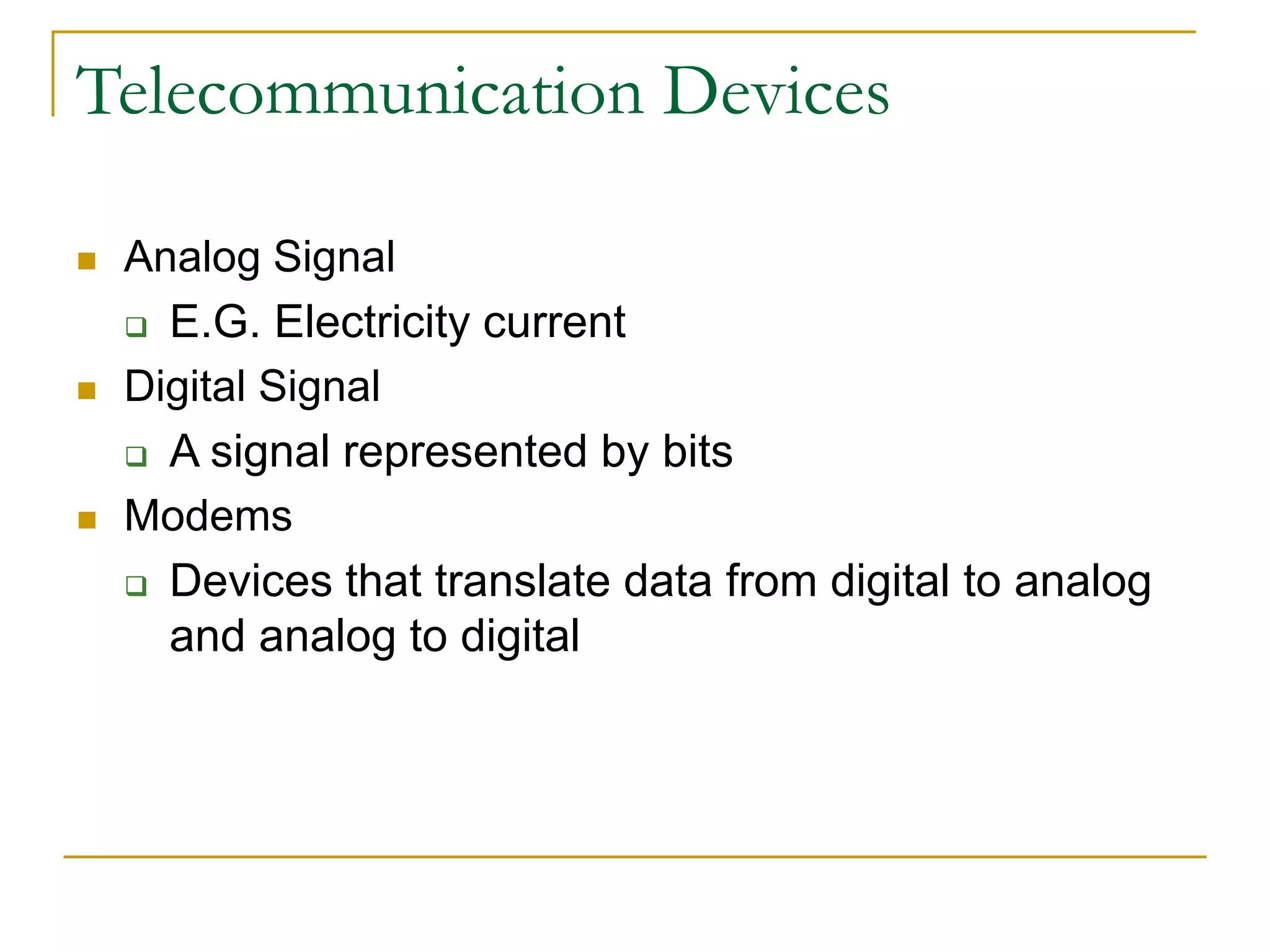
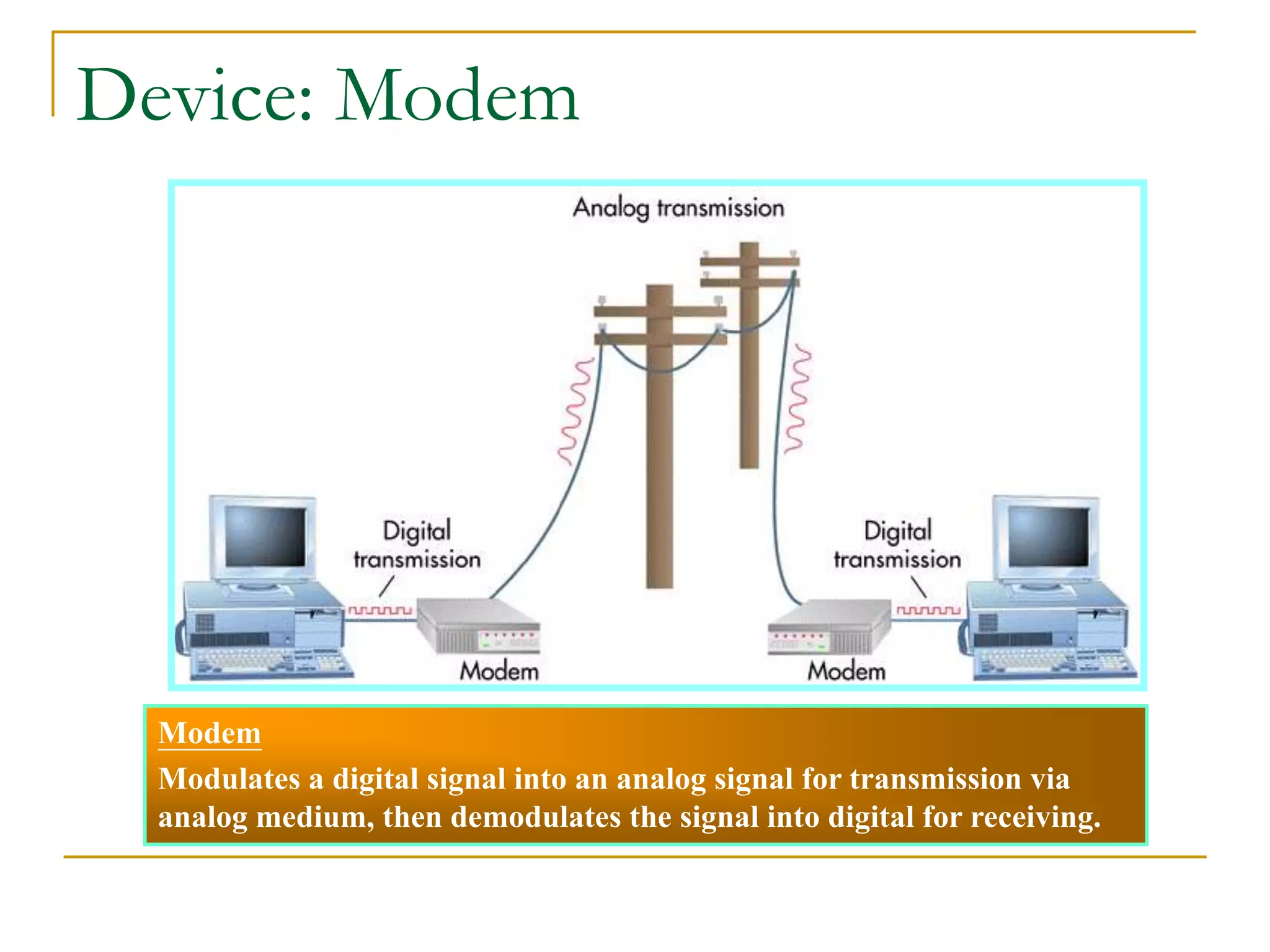
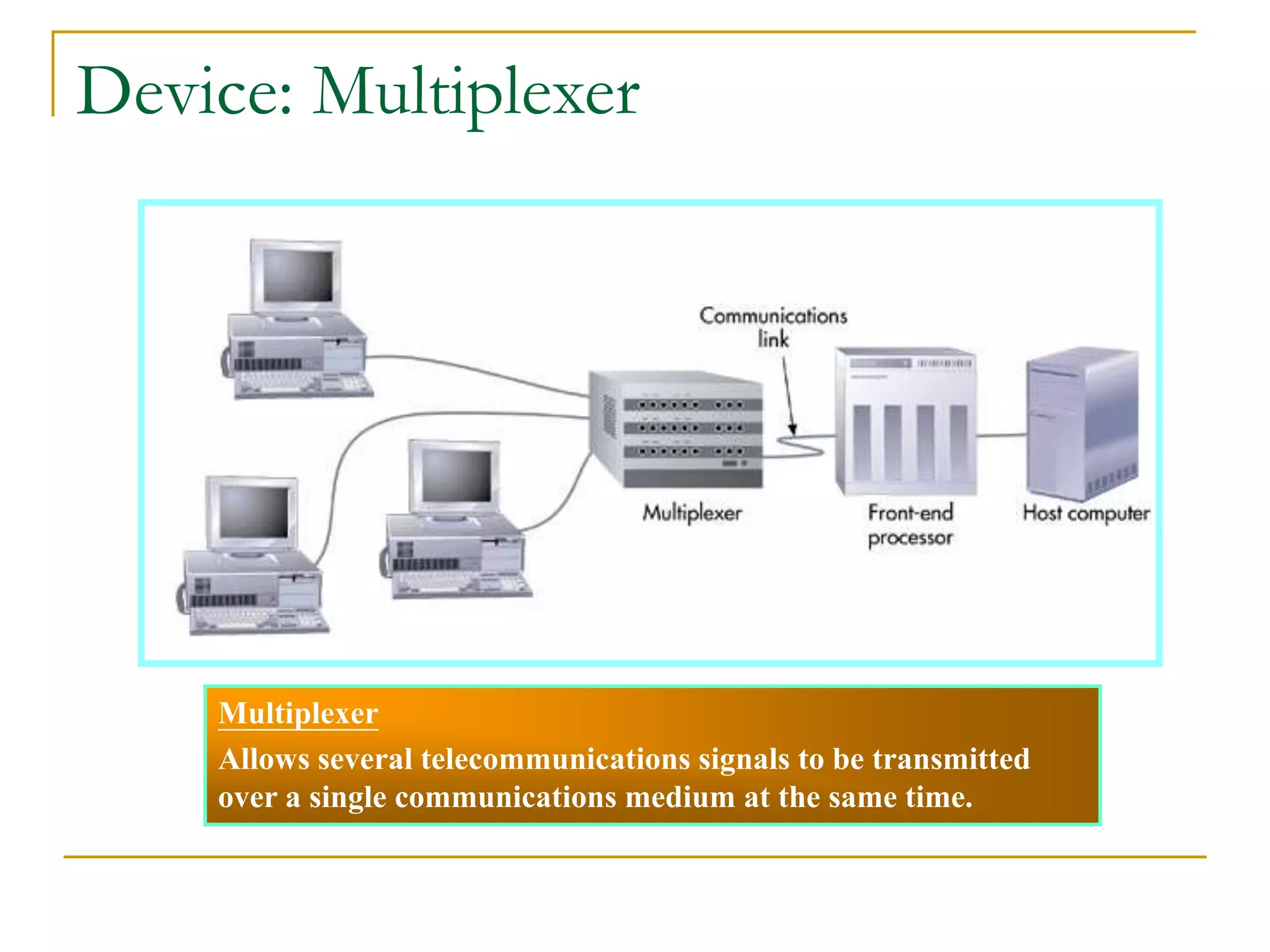
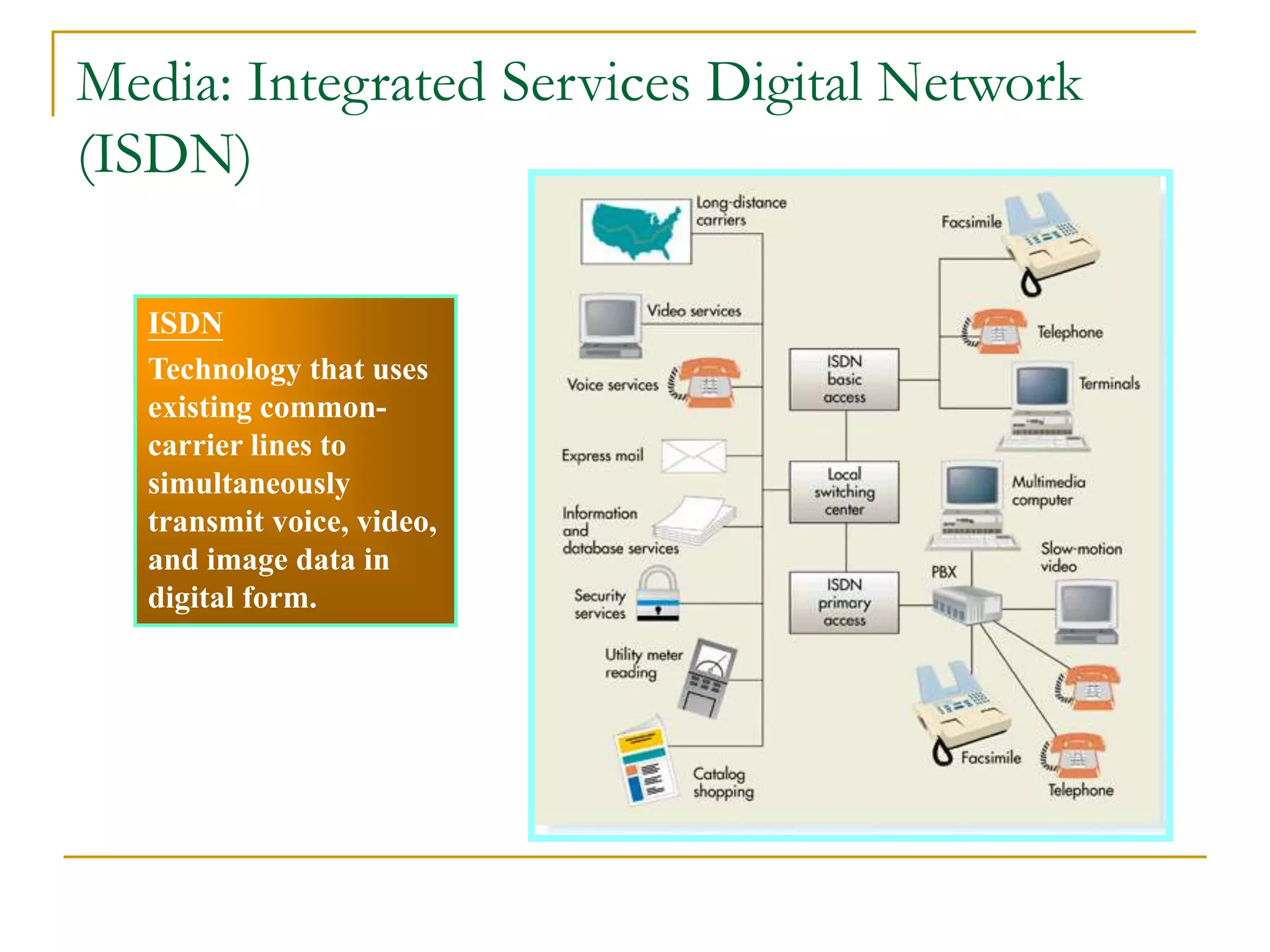
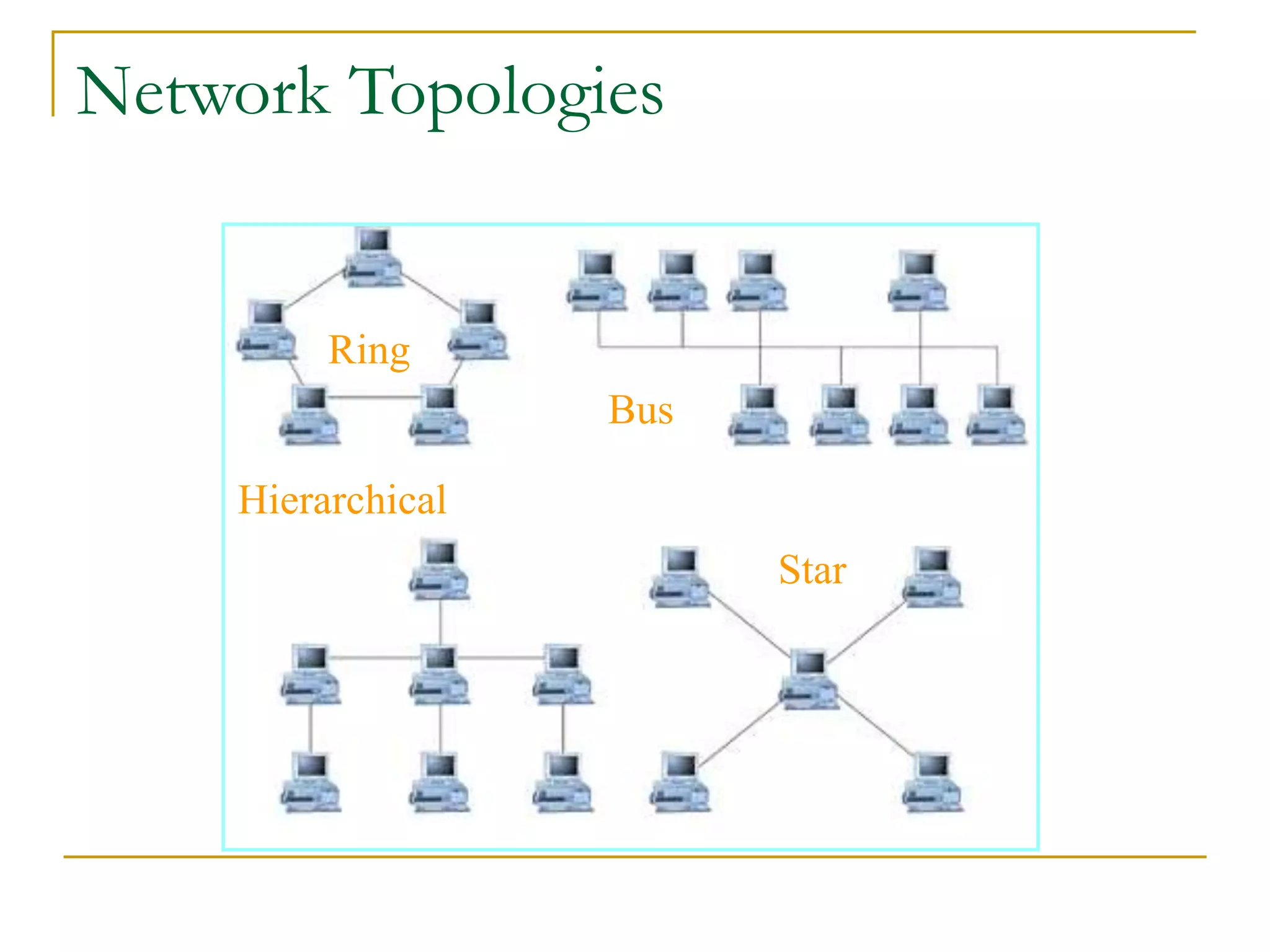
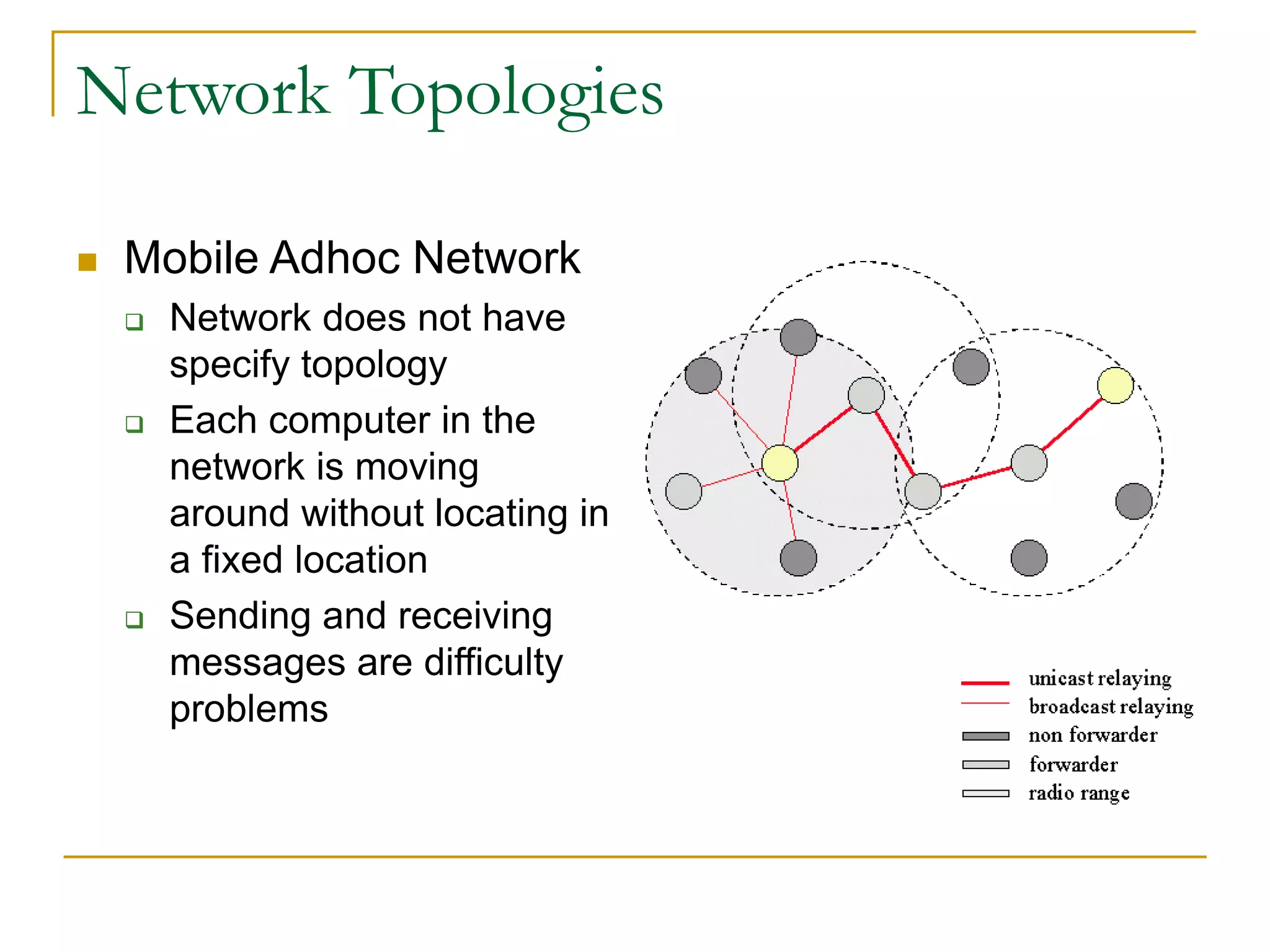
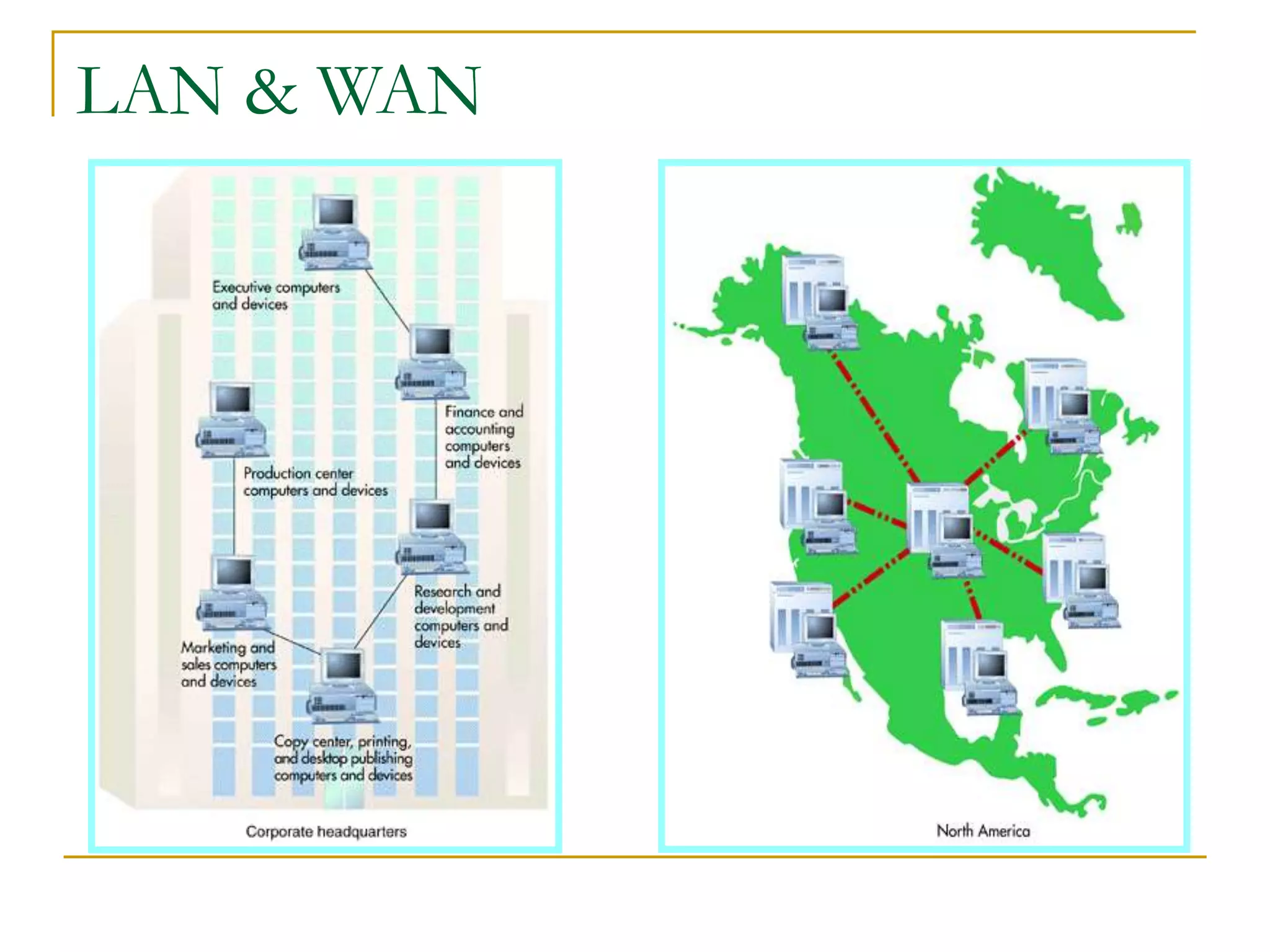
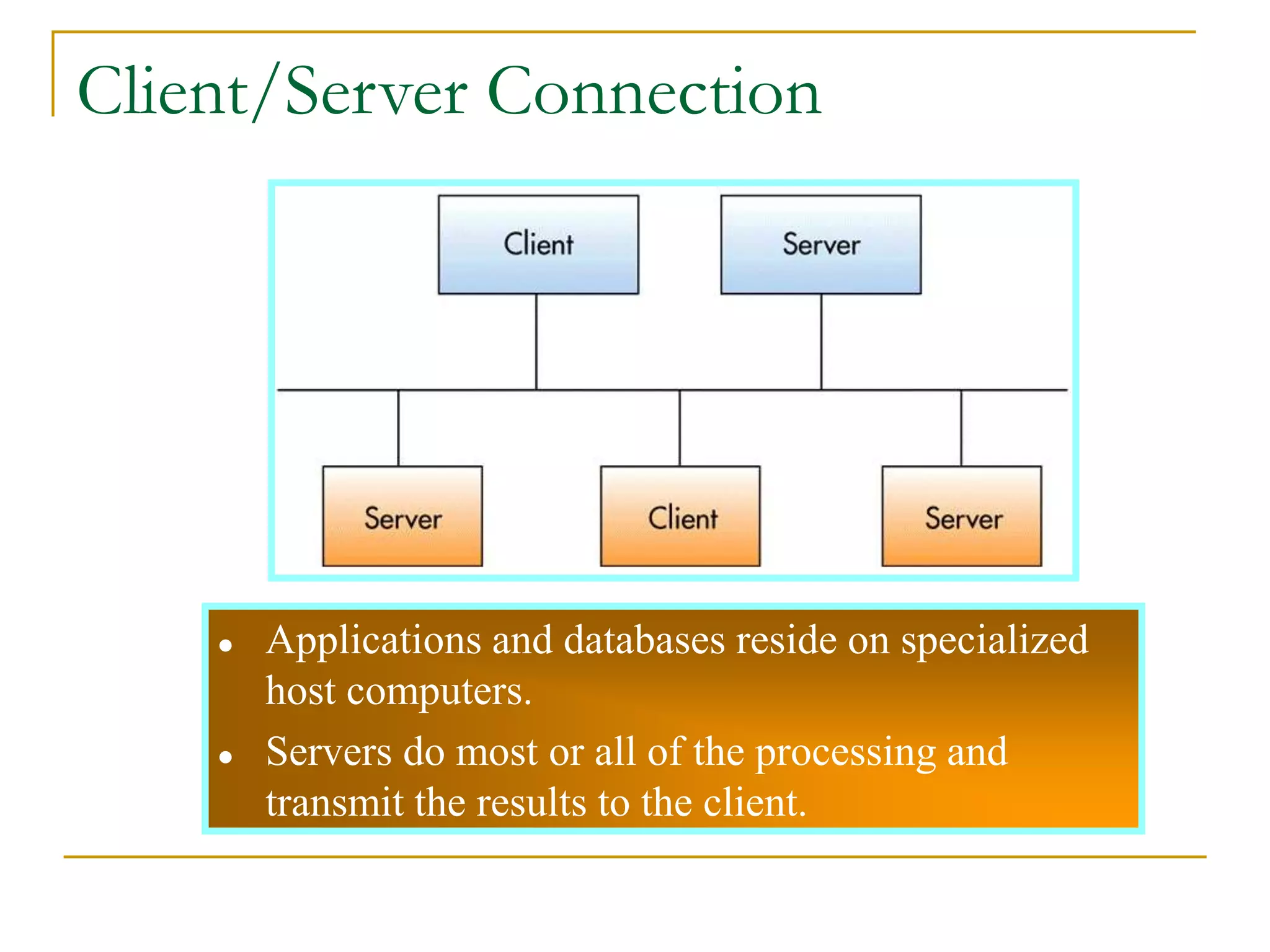
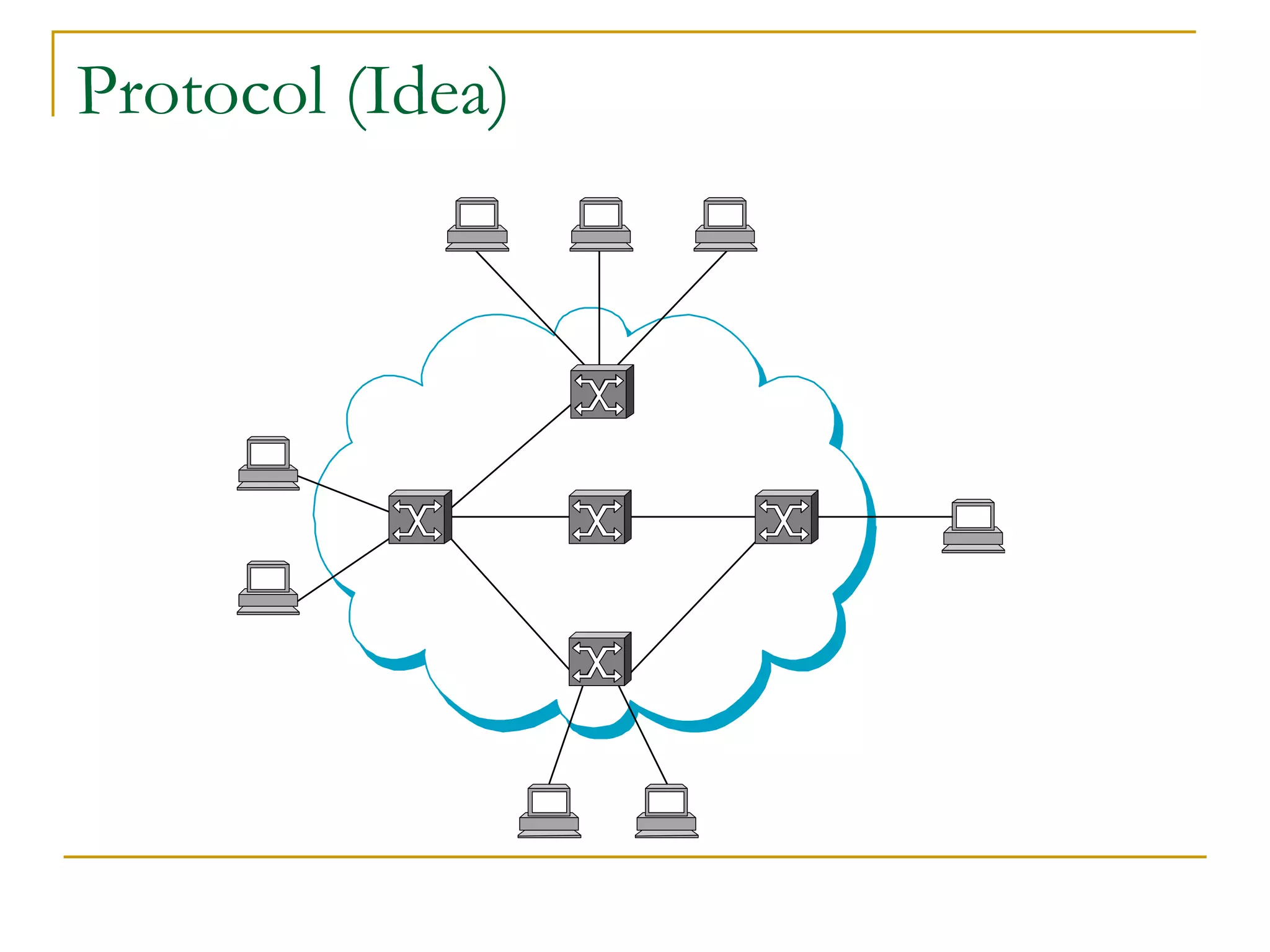
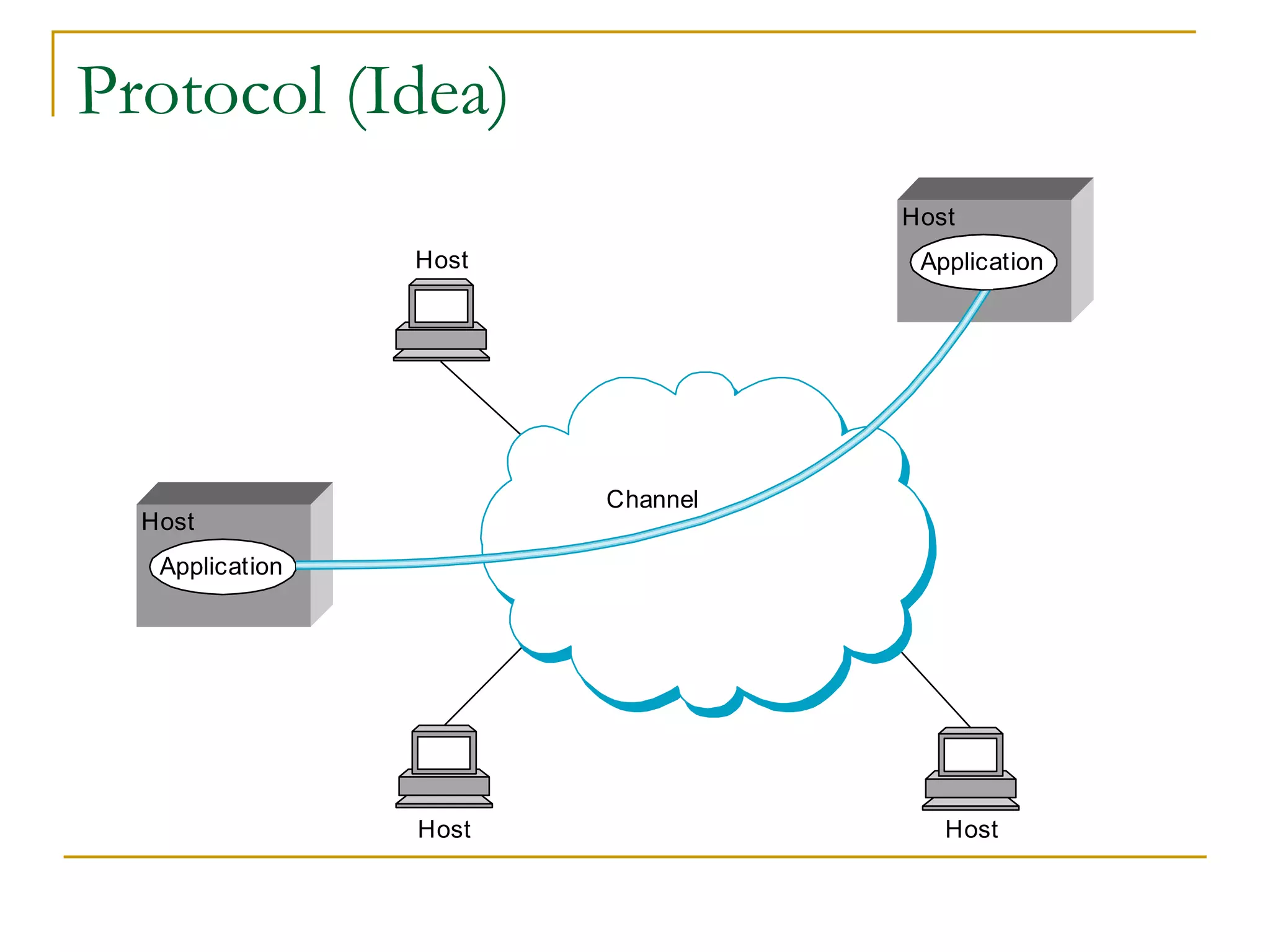
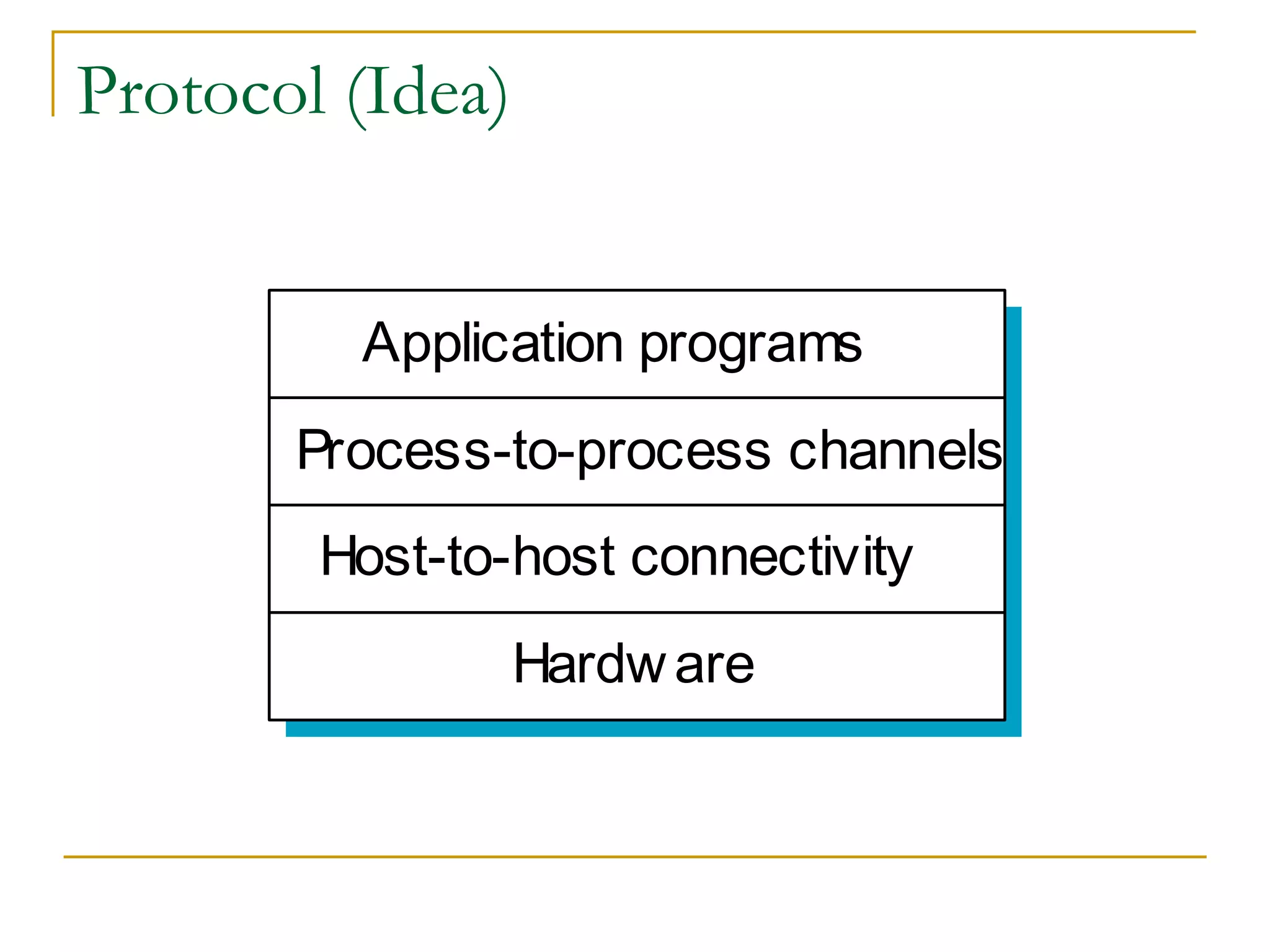
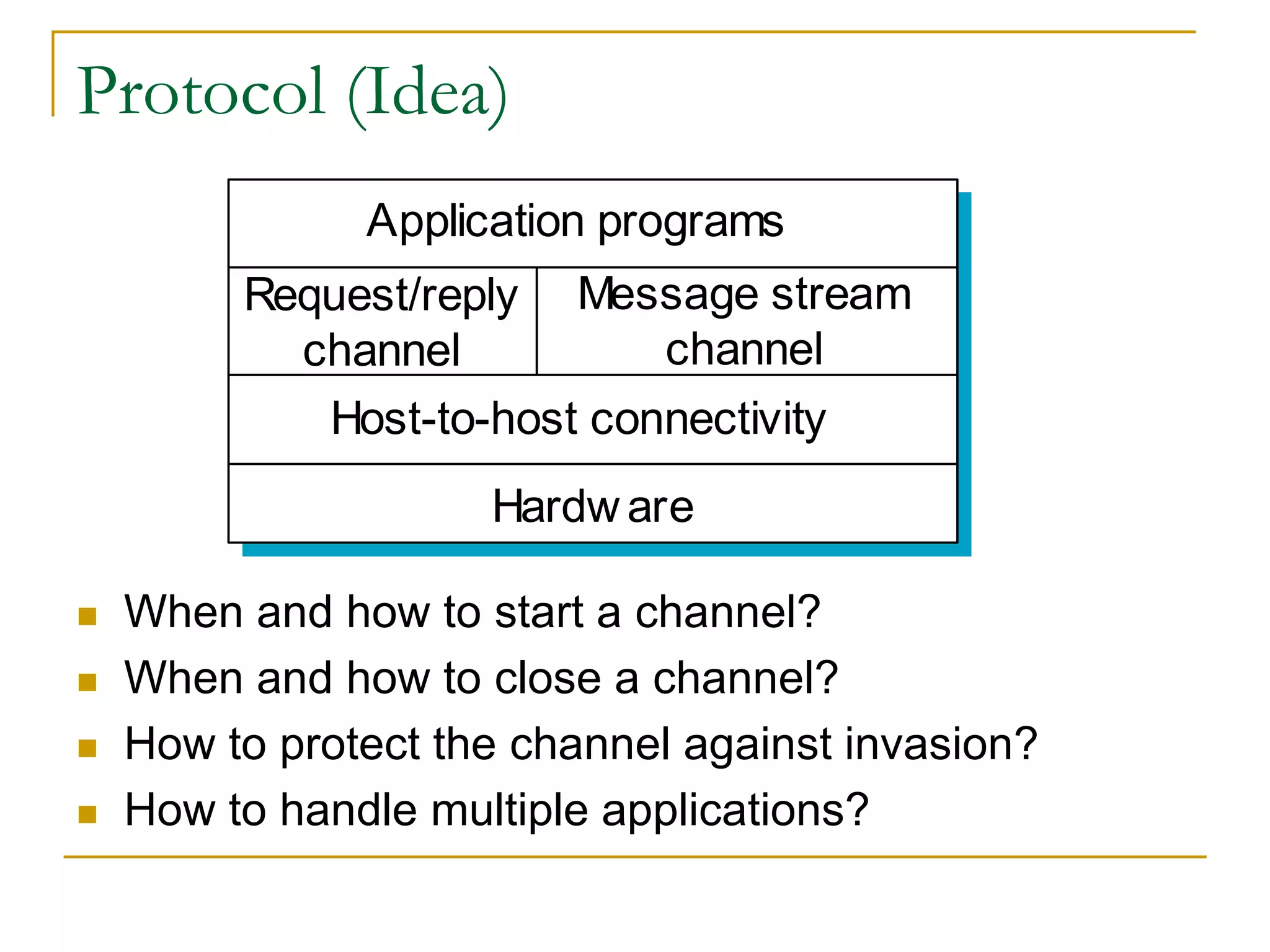
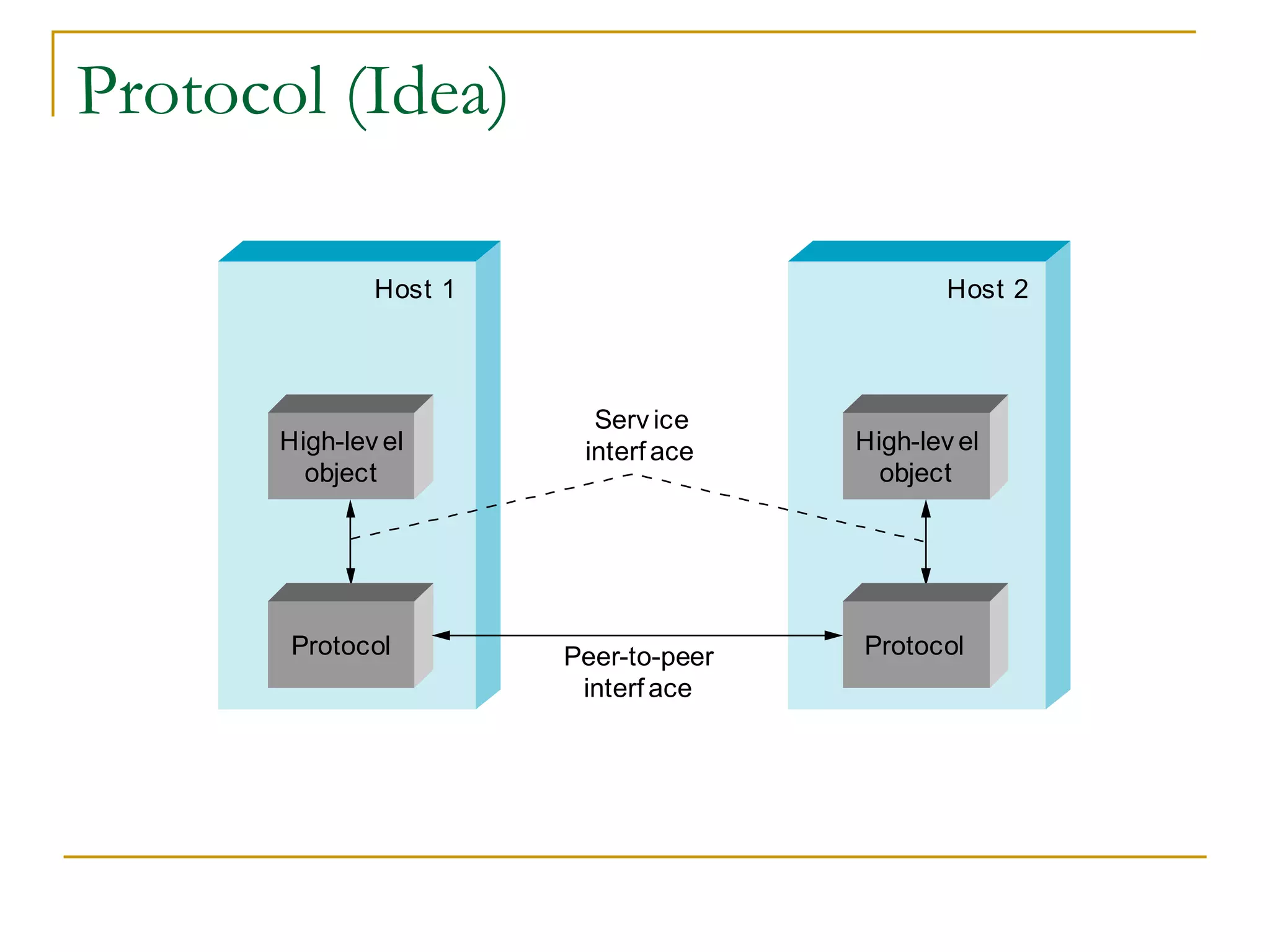
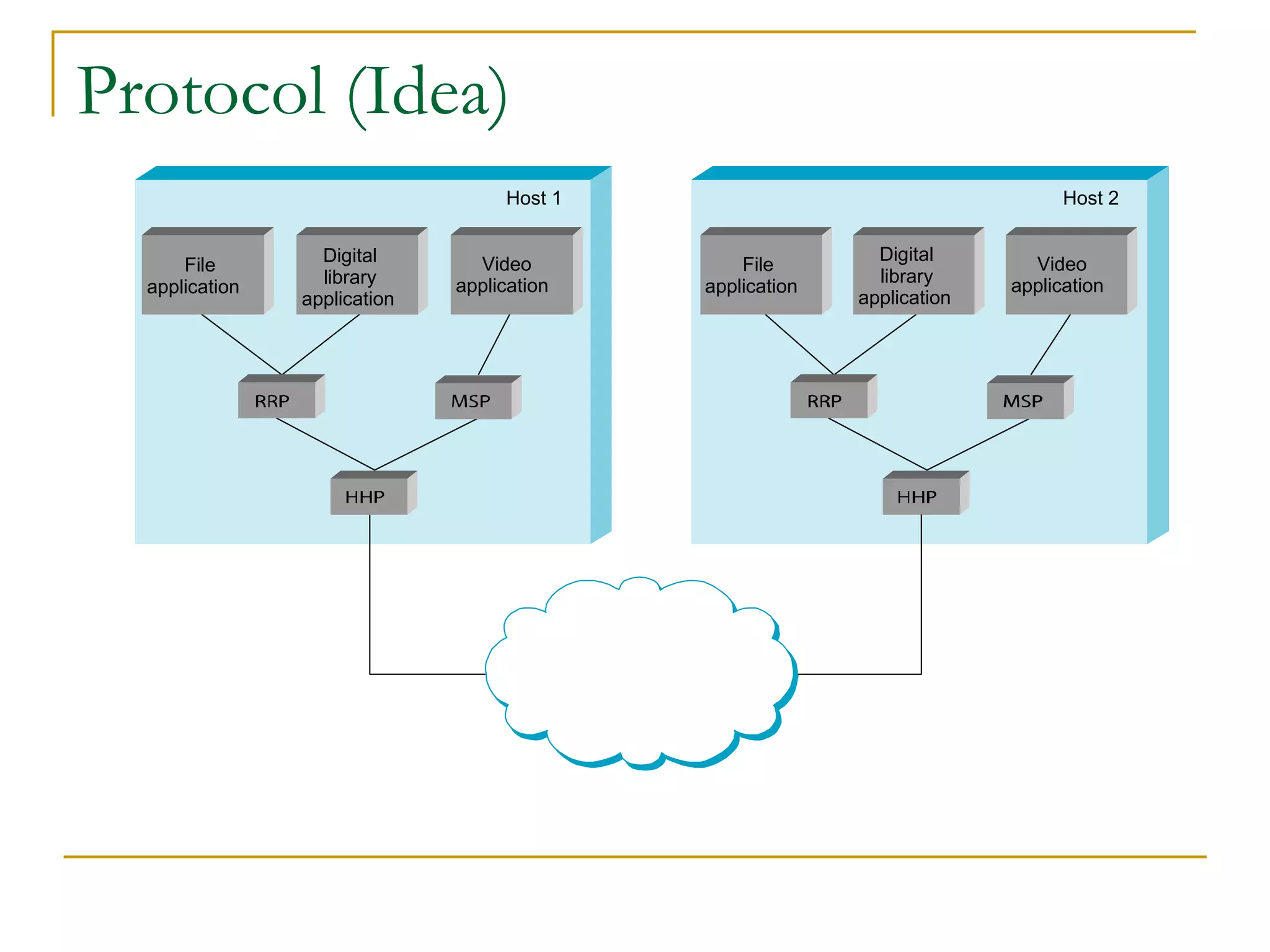
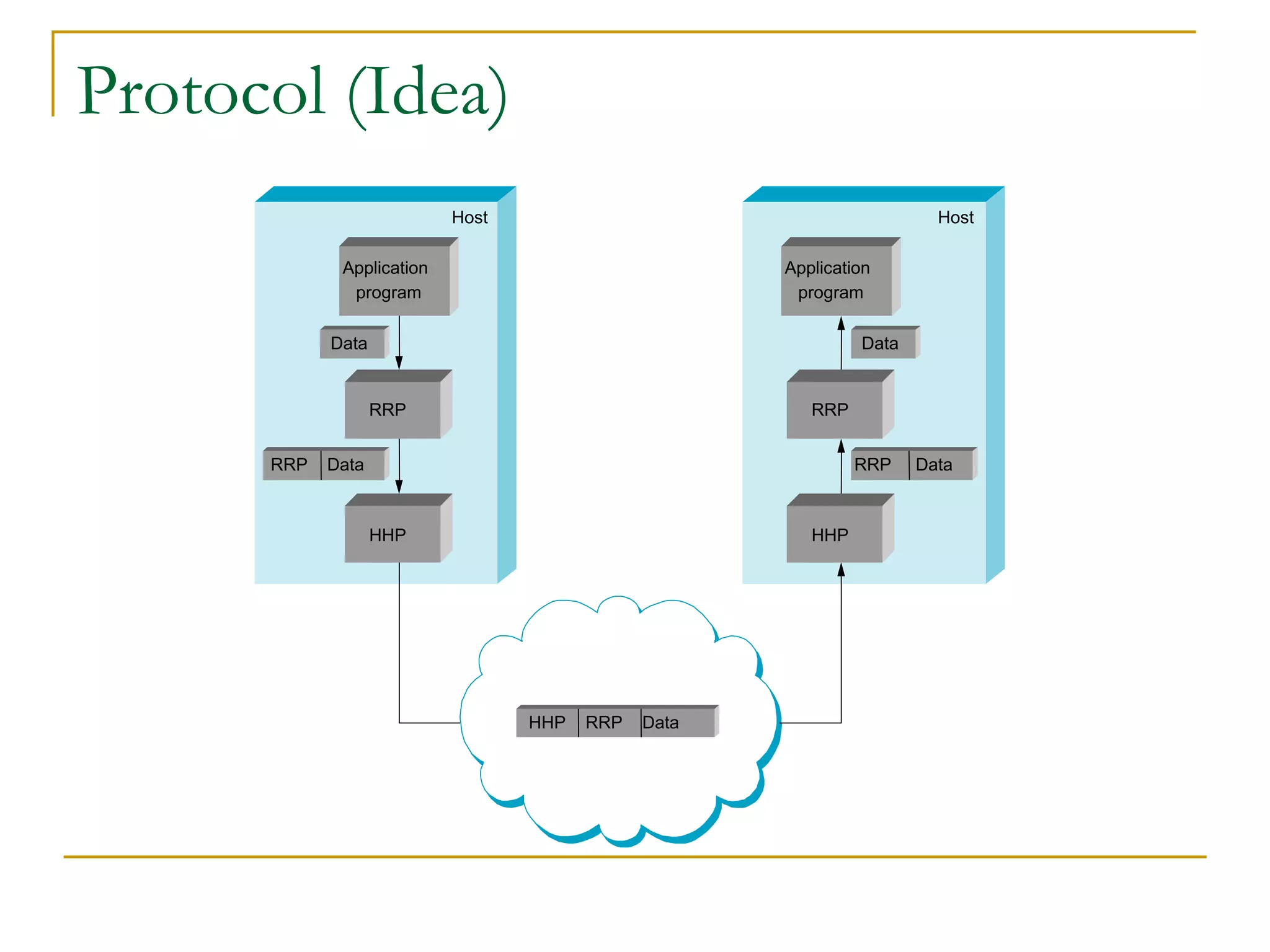
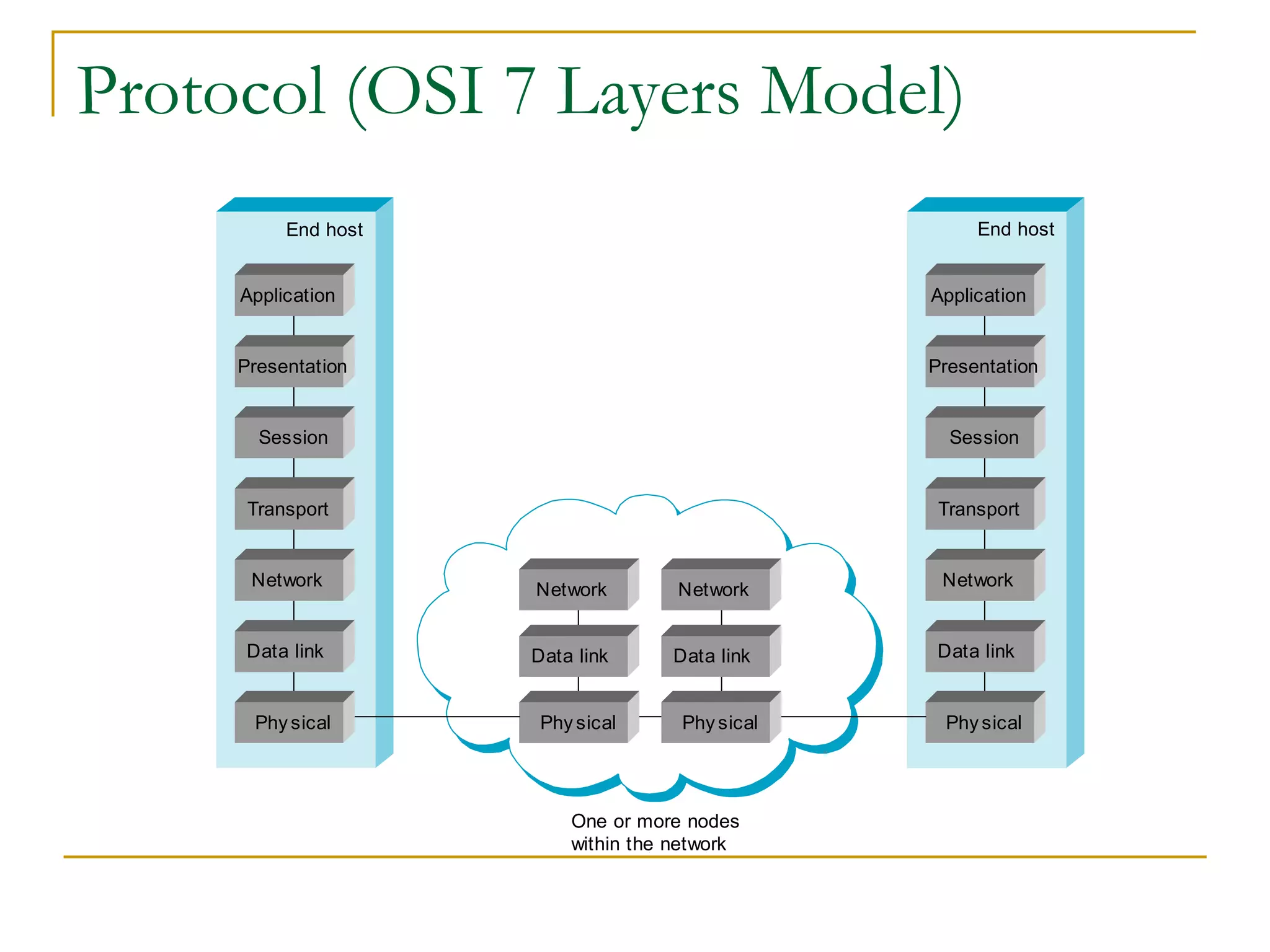
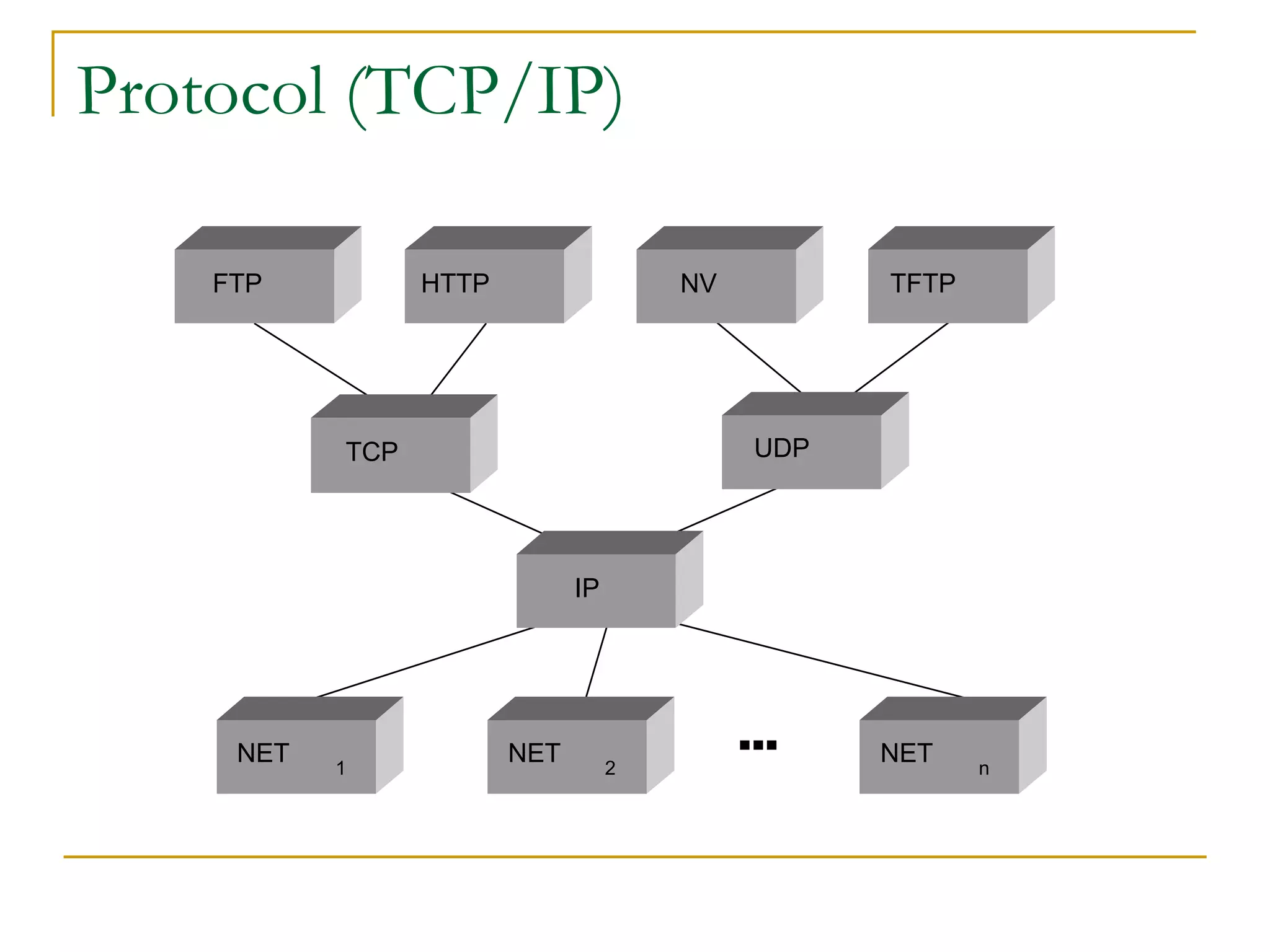
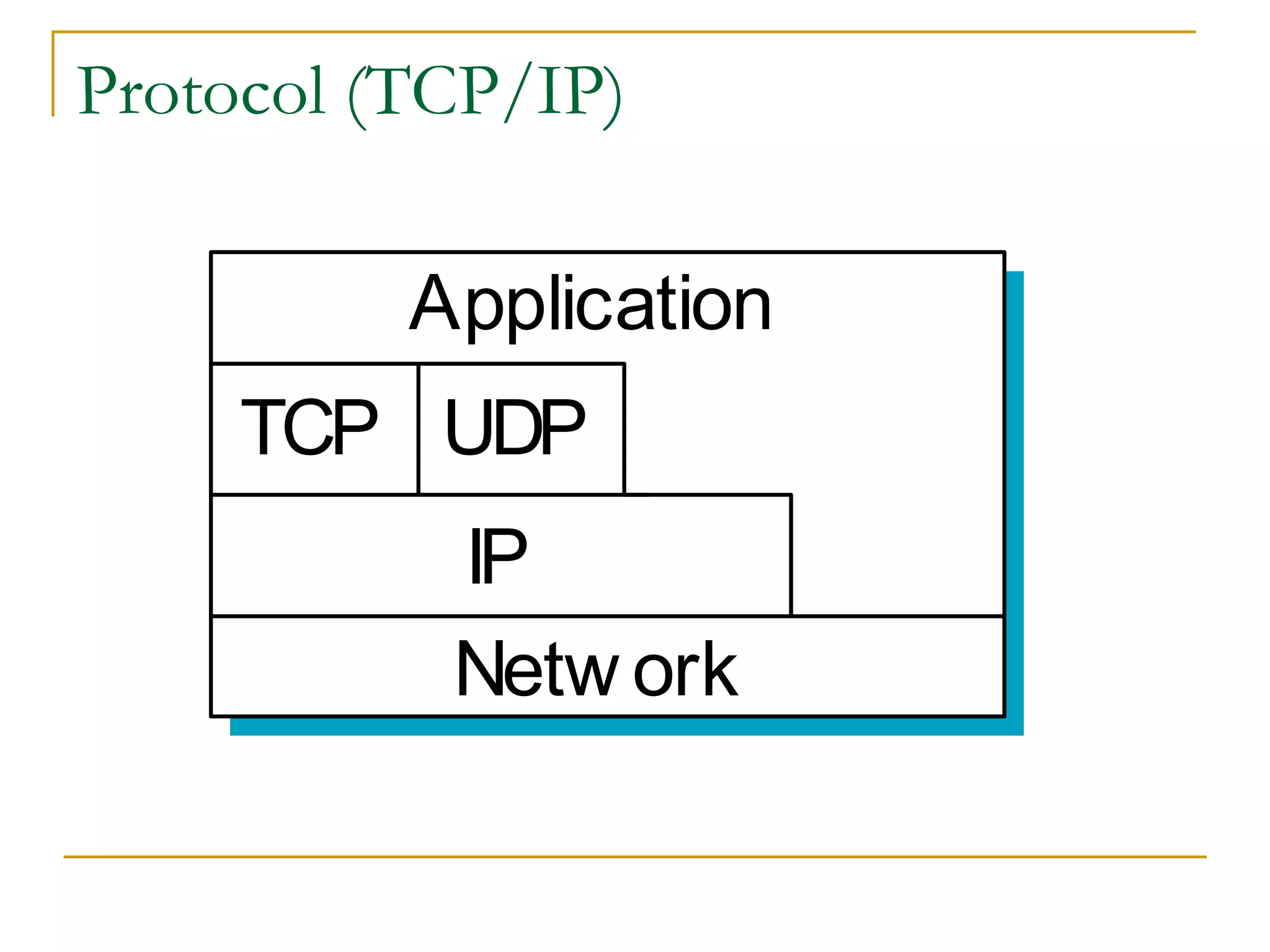
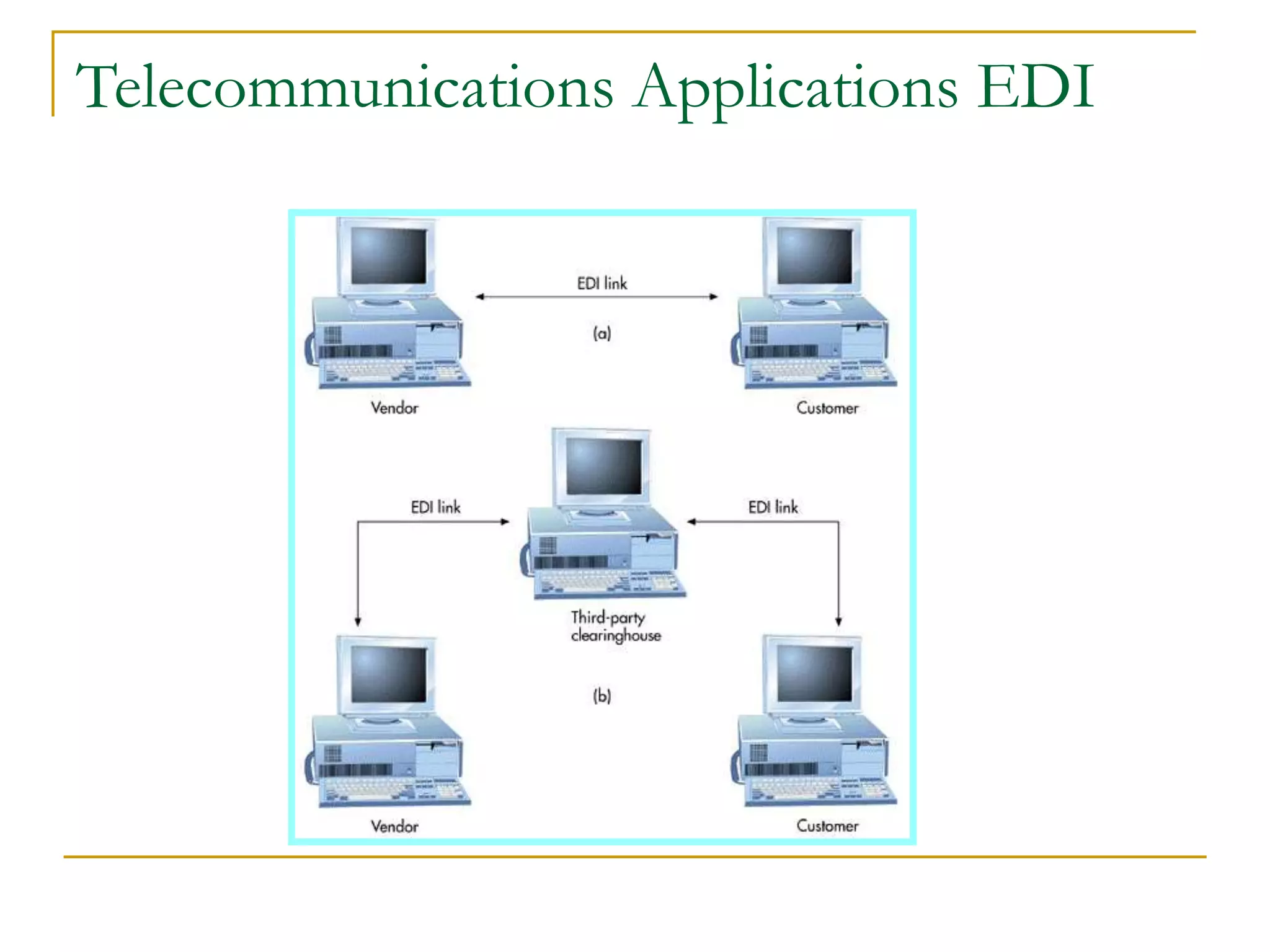
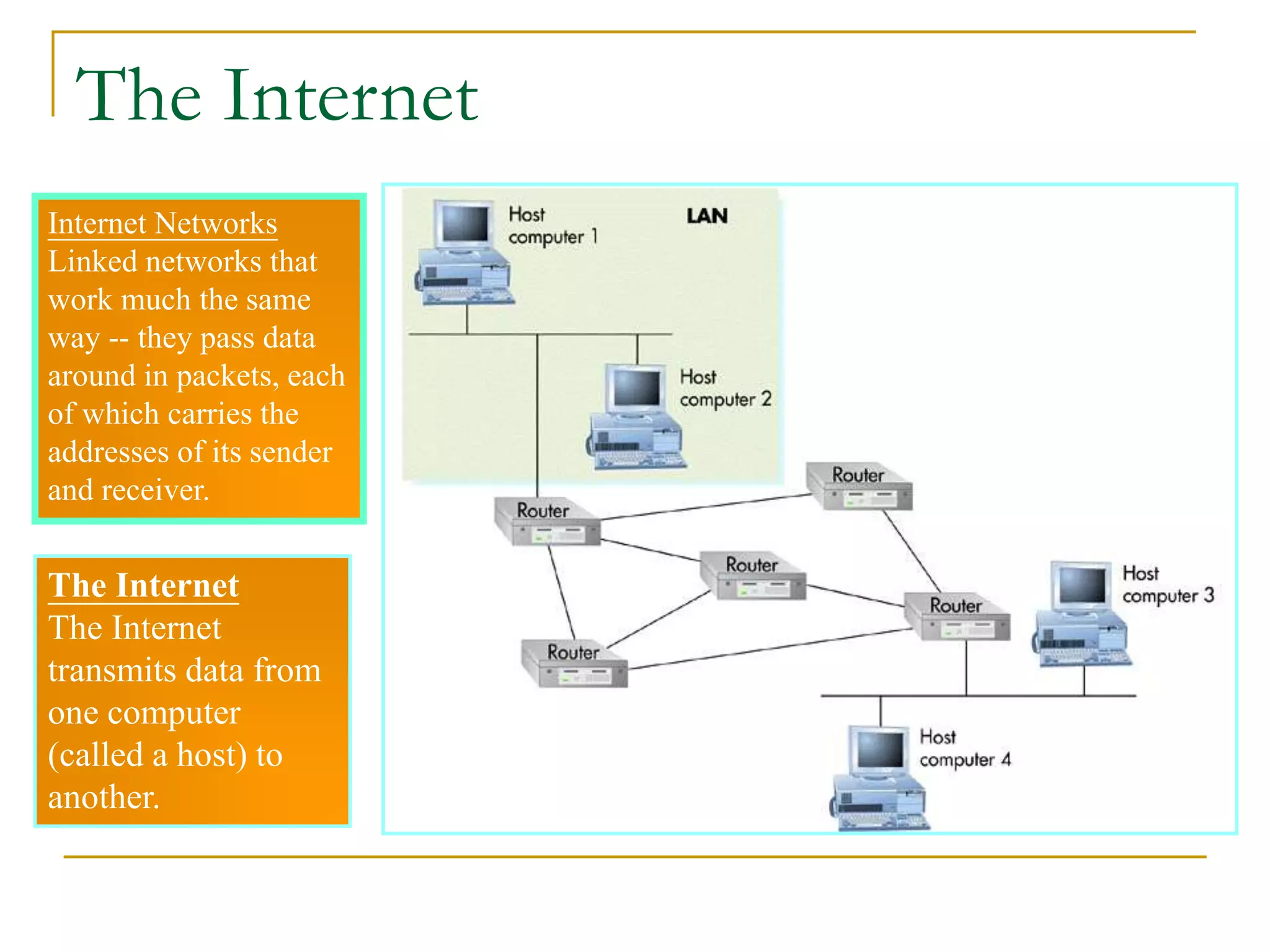
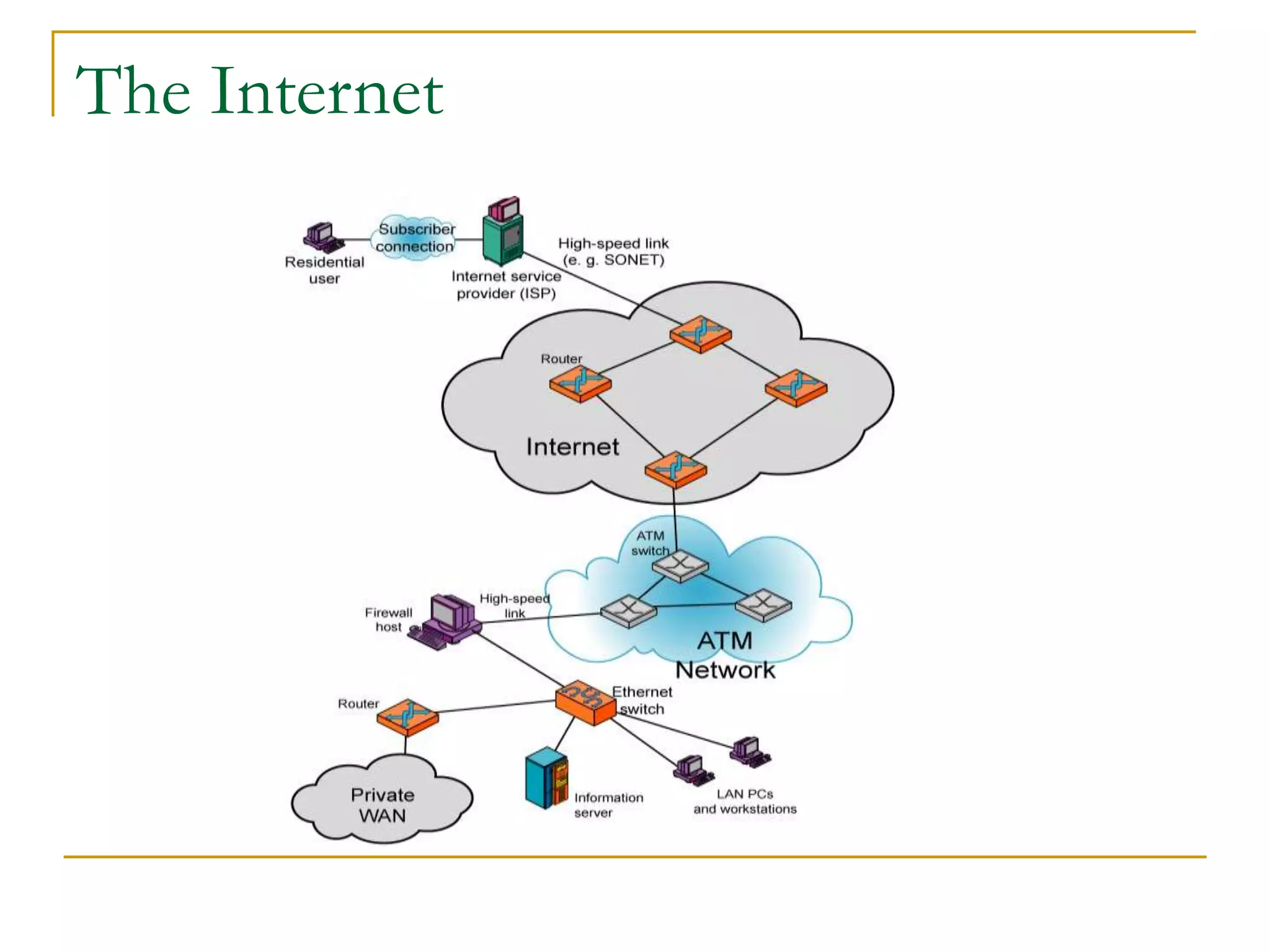
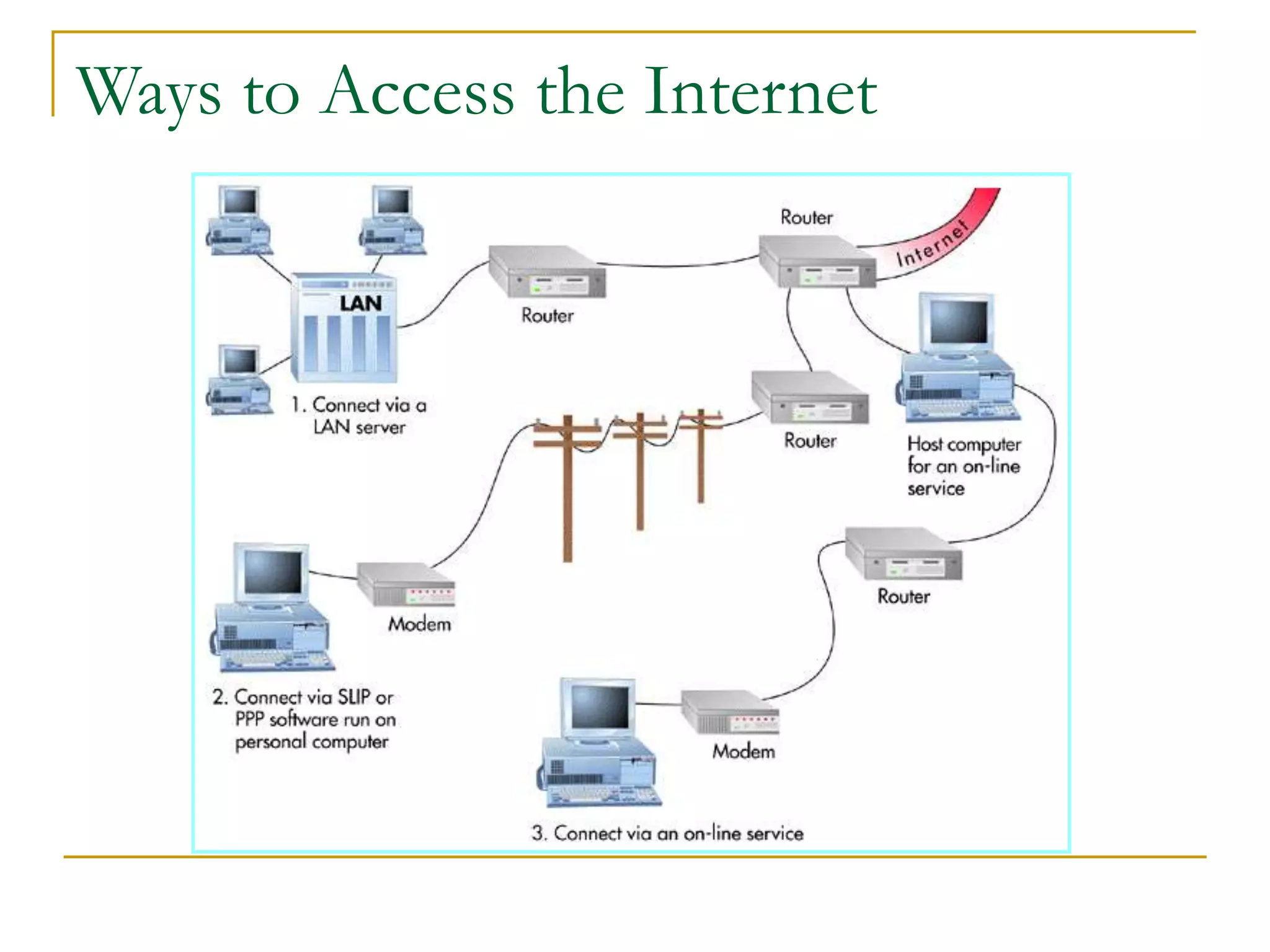
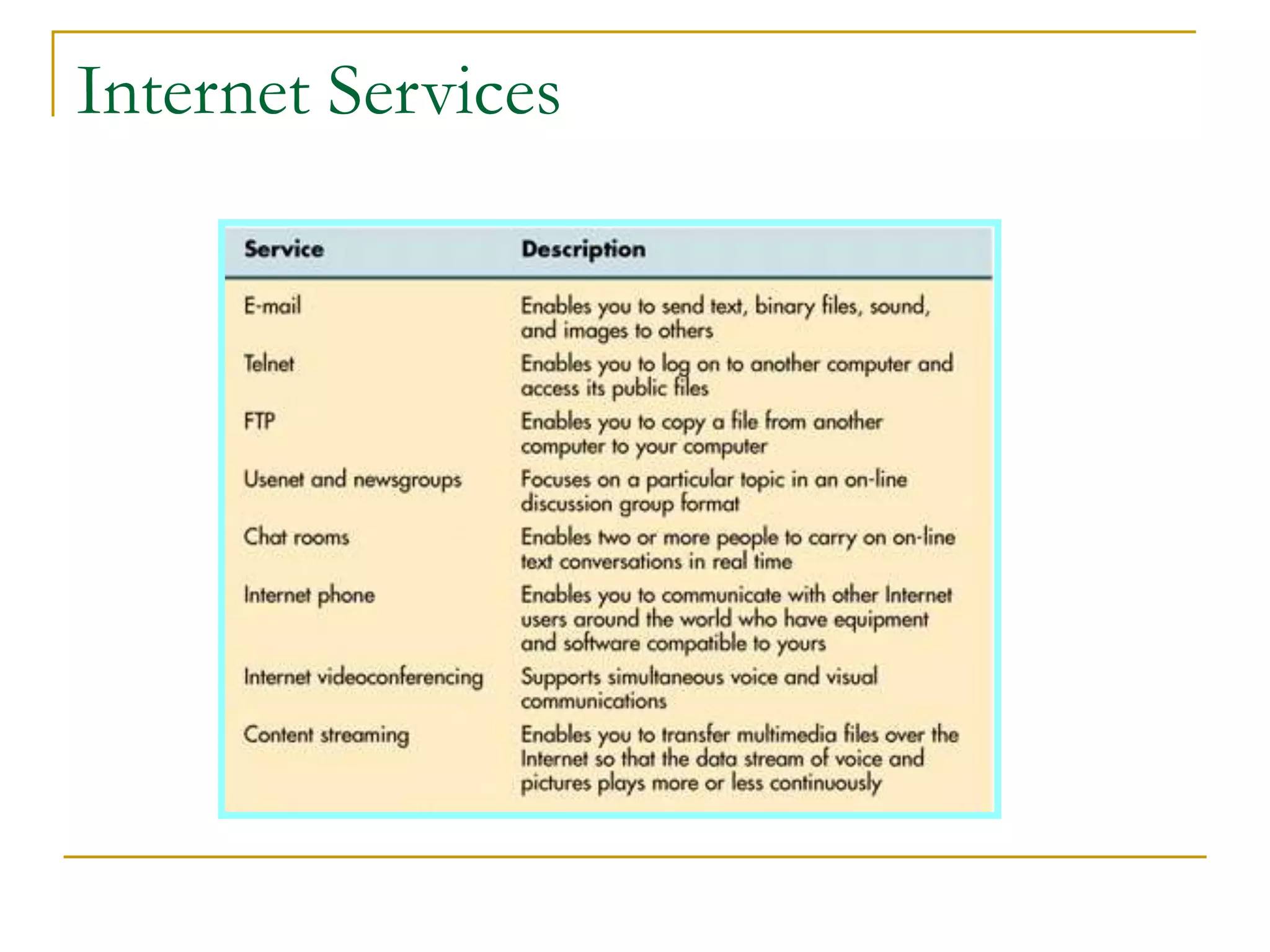
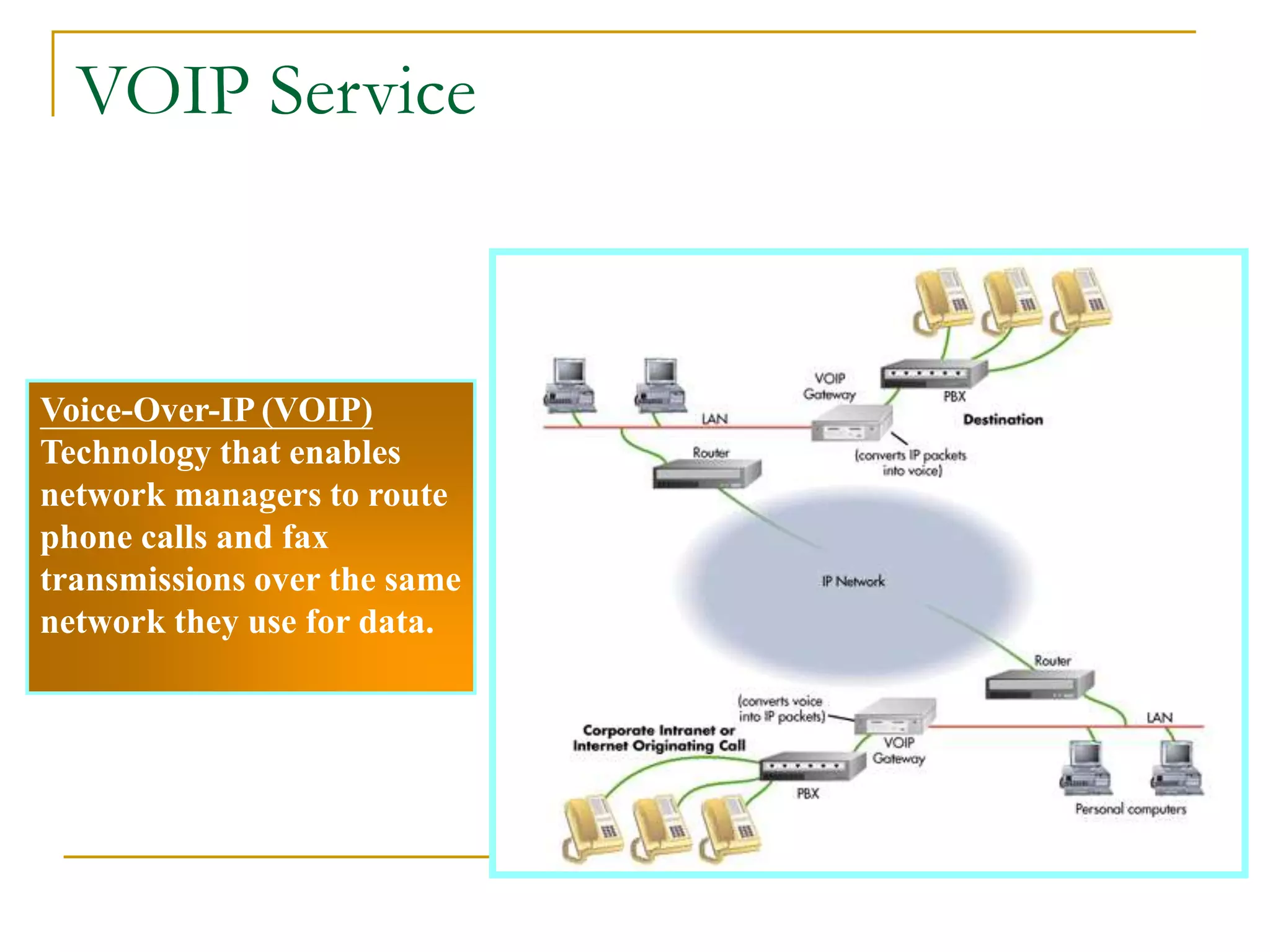
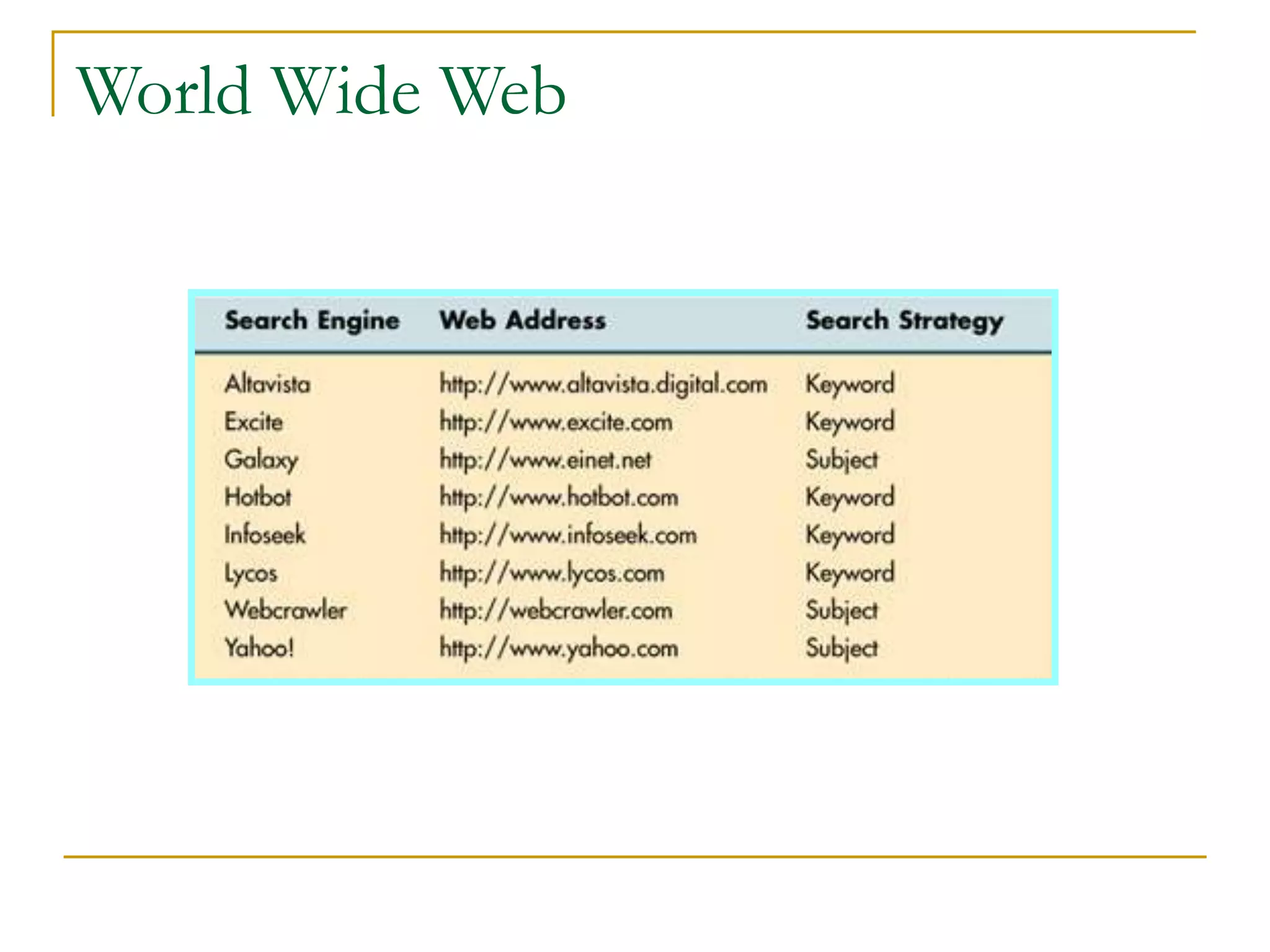
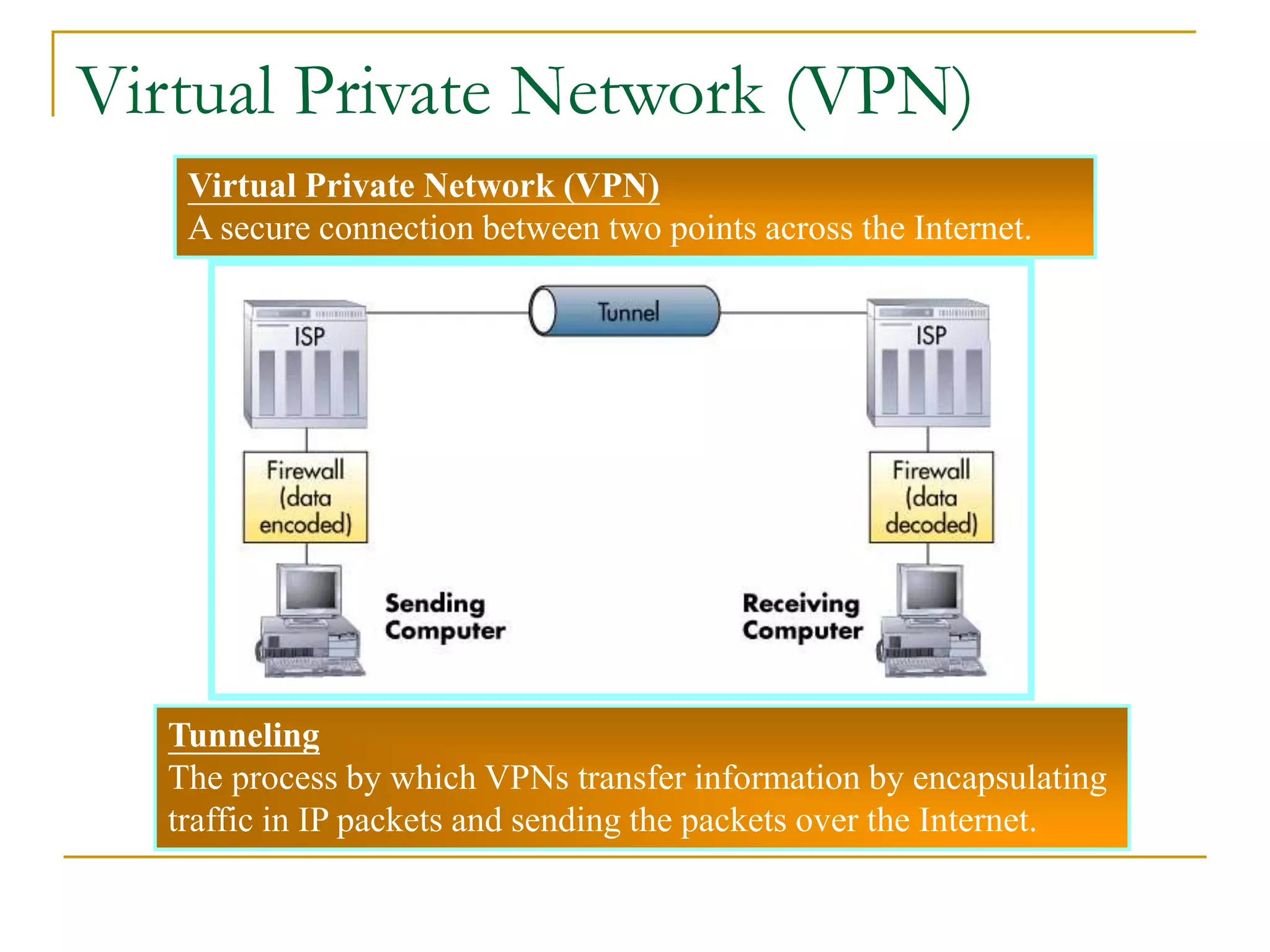
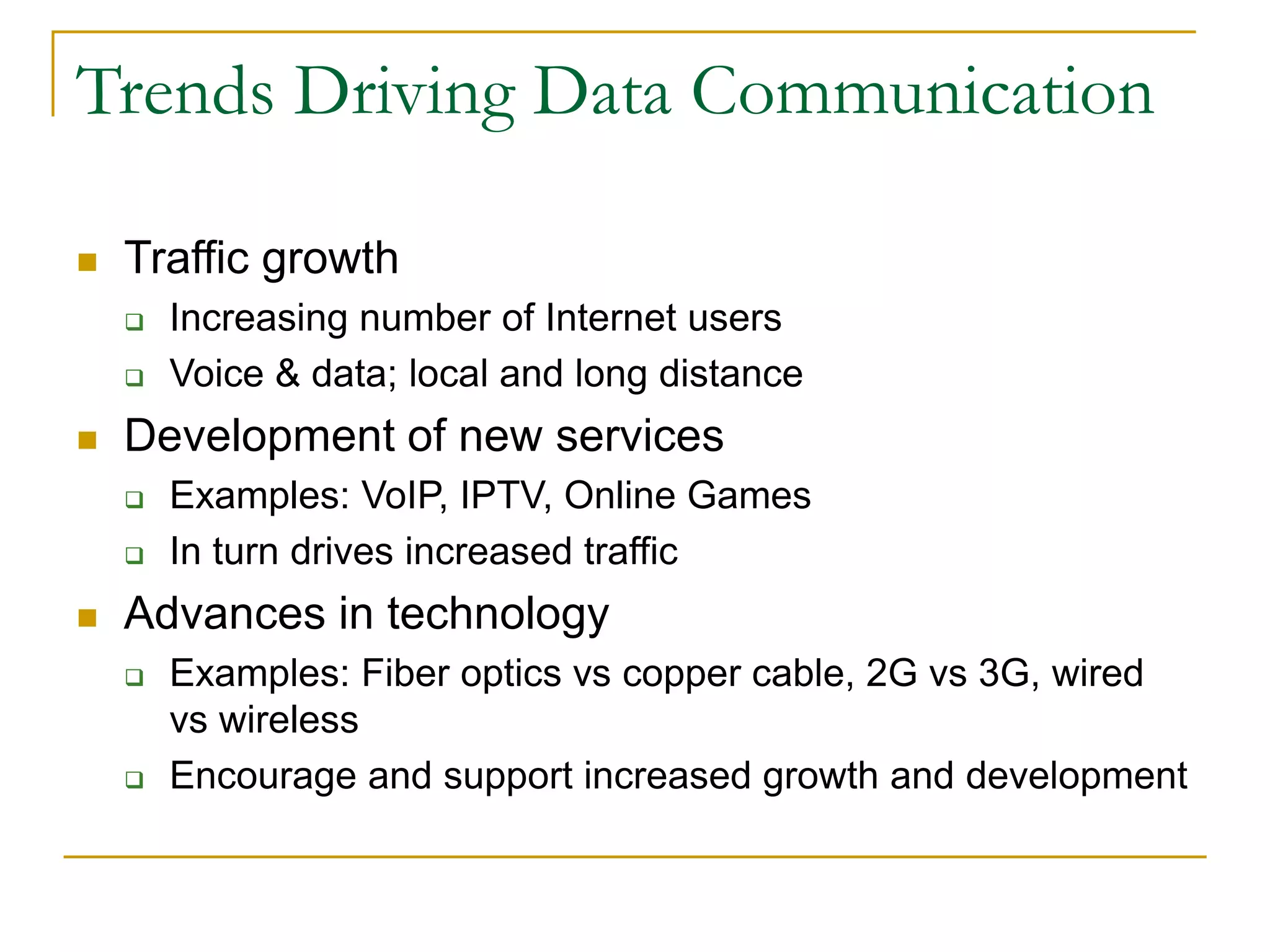
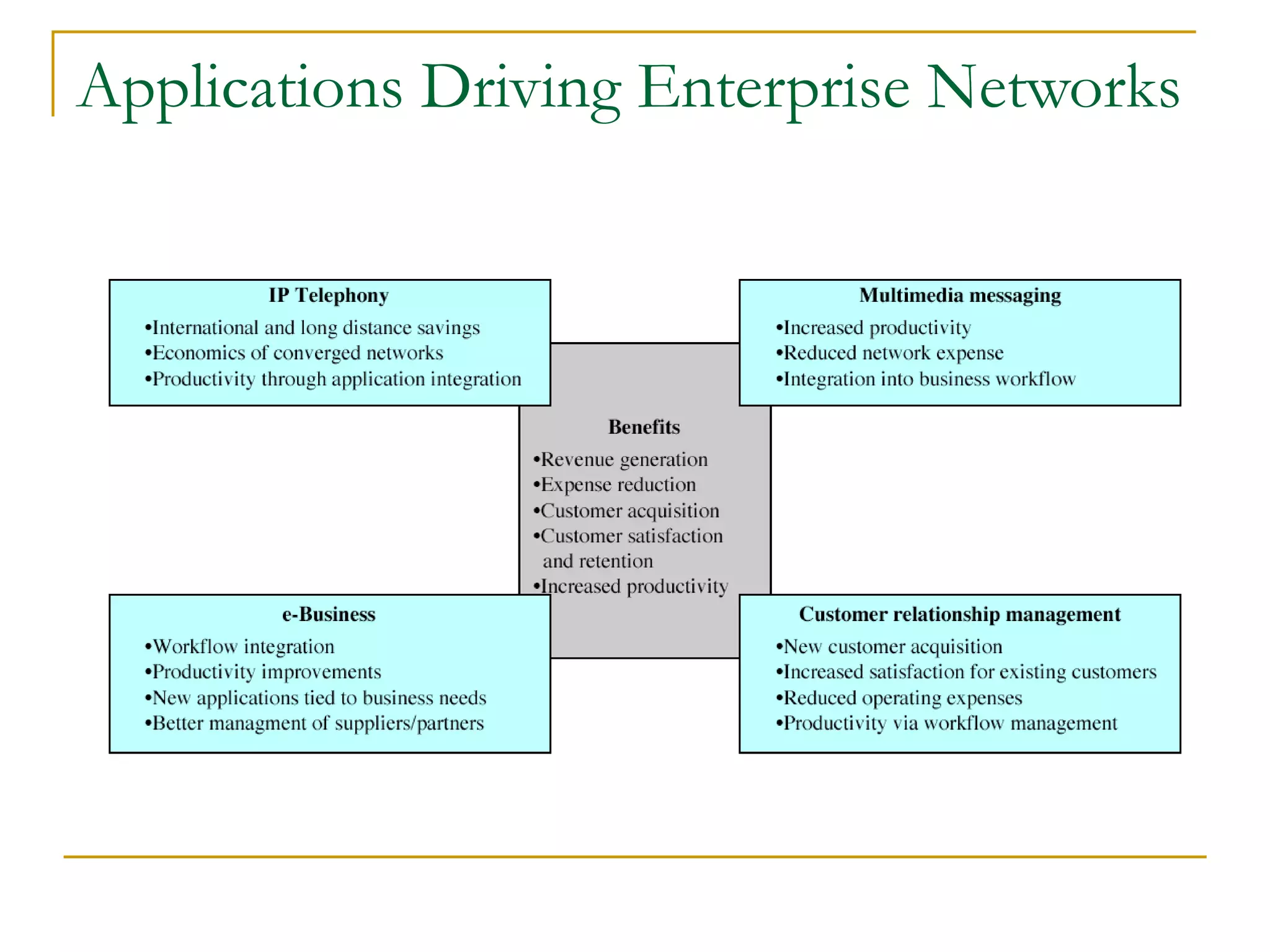
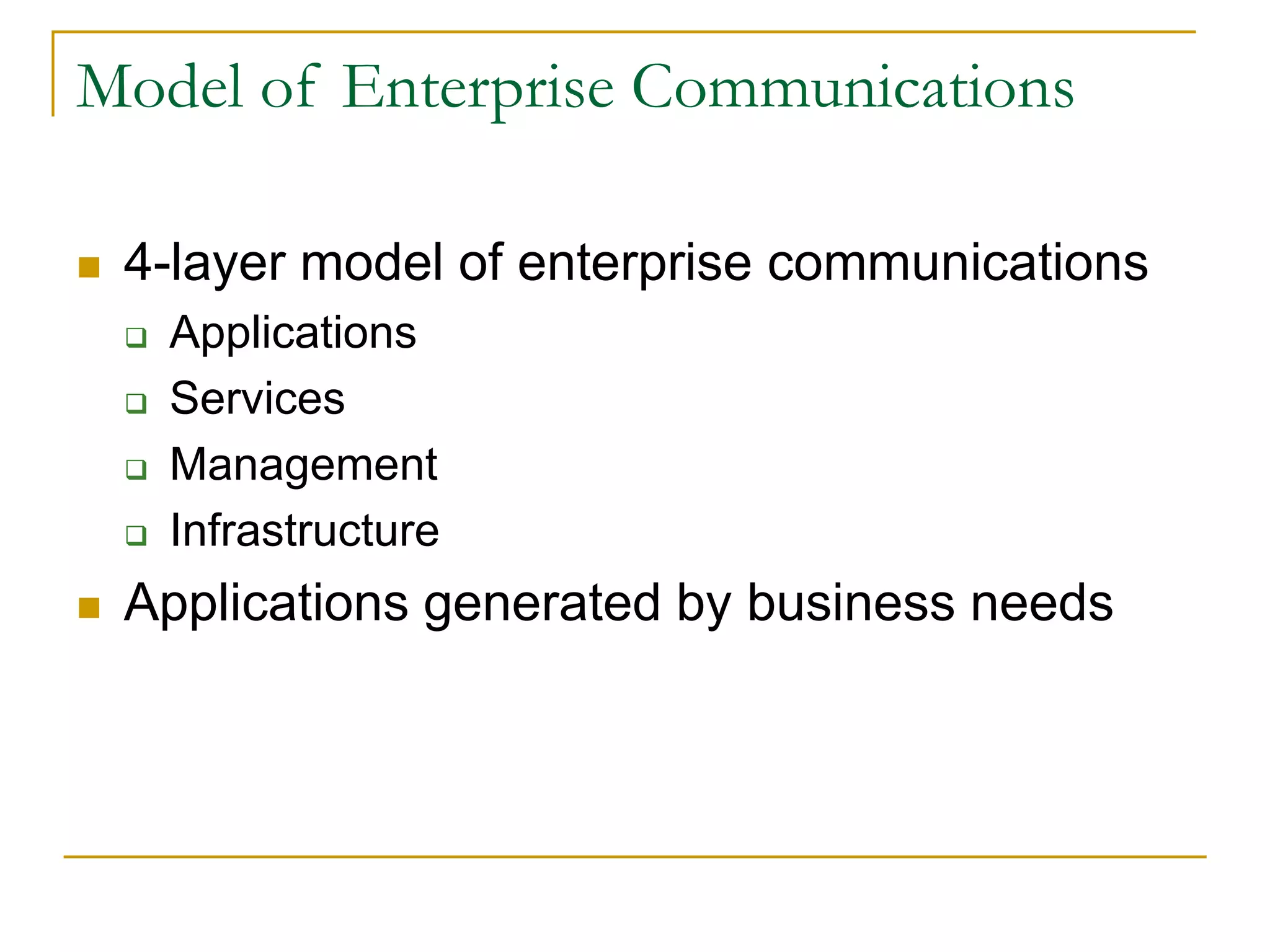
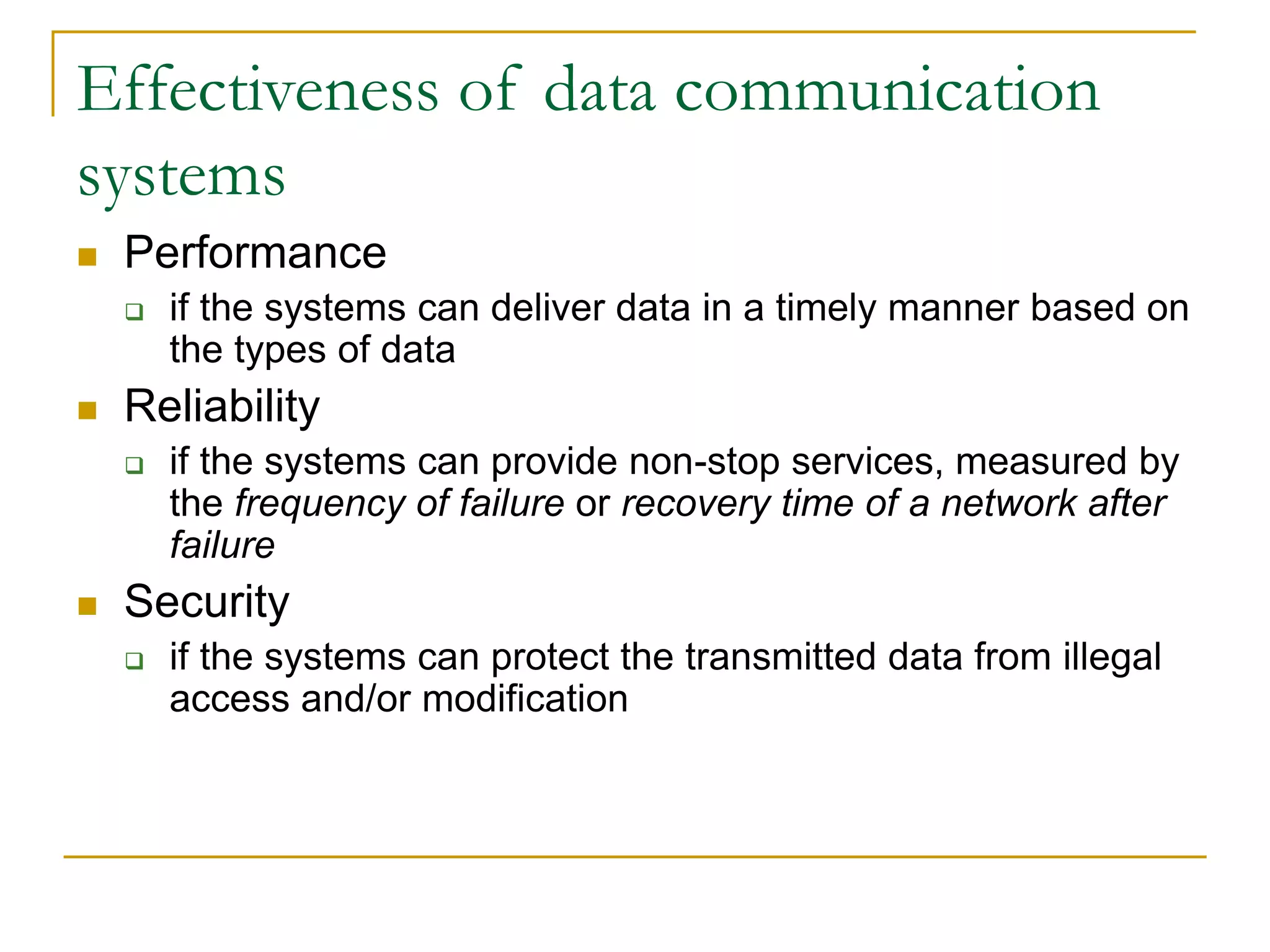
Dr. John Sum introduces various concepts related to telecommunications and computer networks. He discusses different types of telecommunication media that can transmit electronic signals including twisted pair wire, coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, microwave, satellite, cellular, and infrared transmission. He also examines network topologies like ring, bus, star, hierarchical and mobile ad-hoc networks. Finally, he covers protocols, applications, and the role of telecommunications in connecting computers and enabling functions like email, videoconferencing, electronic data interchange and more.