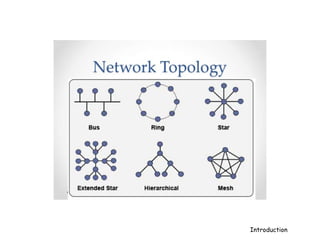
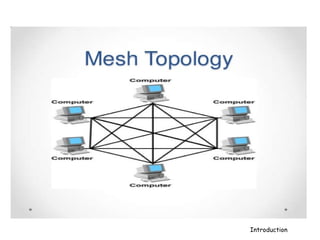
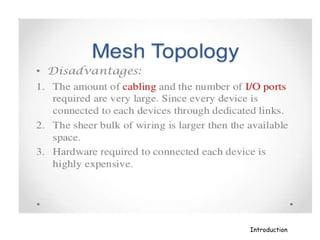
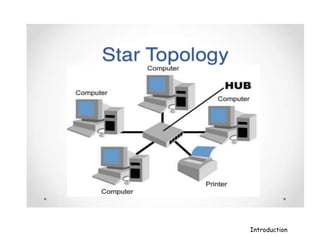
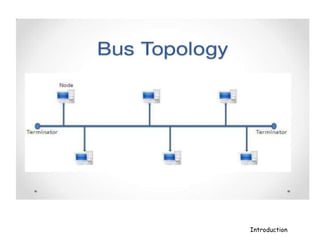
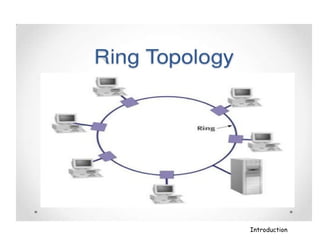
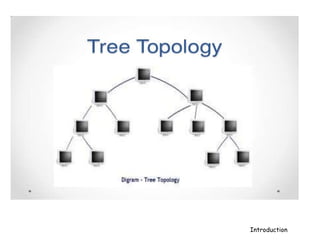
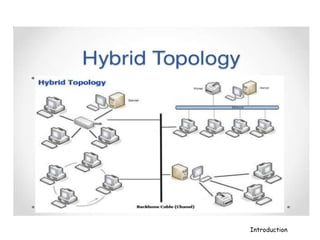
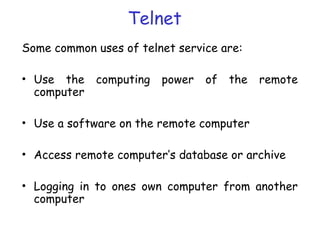
A computer network connects hardware and devices through communication channels to share resources and information. A local area network (LAN) connects devices in a small geographic area like a home or office through nodes. LANs can connect to wide area networks (WANs) using routers. A metropolitan area network (MAN) interconnects multiple LANs using high-capacity links to provide services to WANs and the Internet. The Internet is the largest global network of interconnected computers that allows sharing of information through services like email, file transfer, remote access, and discussion groups. The World Wide Web uses the Internet and hypertext transfer protocol to share hyperlinked documents through web servers and browsers.