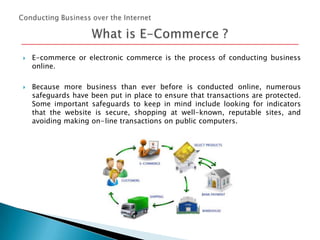
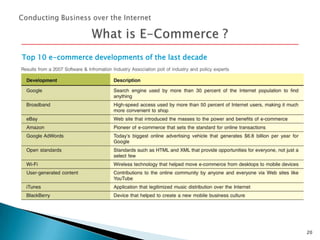
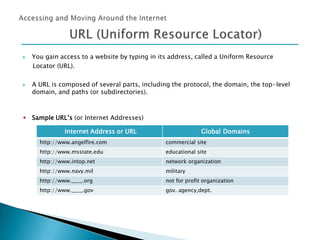
The document provides an overview of how to make the most of the web's resources. It discusses the origin and development of the internet from ARPANET to the world wide web. It describes how the internet works through a network of connected computers and servers that transmit data. It also summarizes key aspects of using the internet like social networking, e-commerce, web browsers, searching, and hyperlinks.