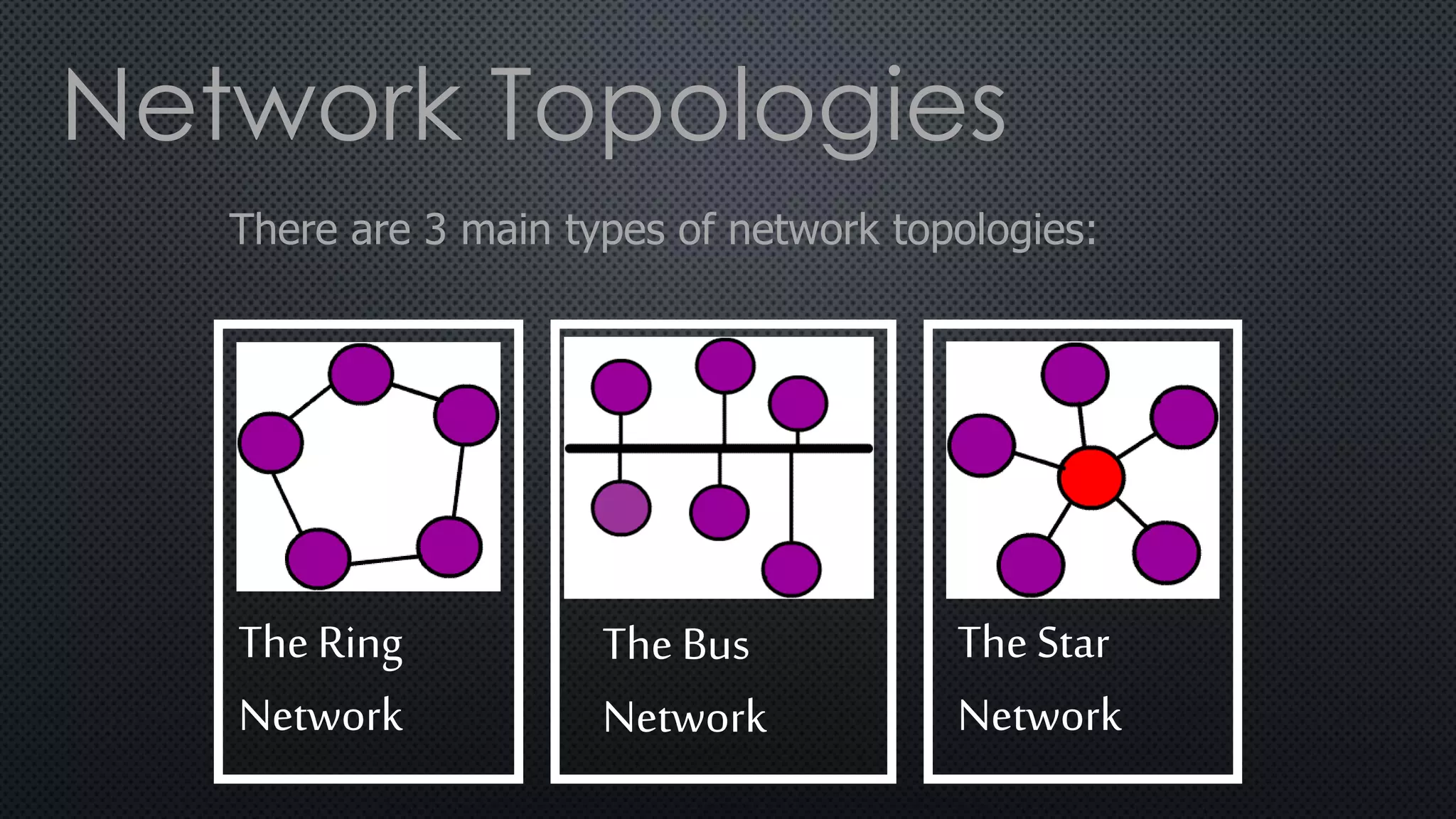
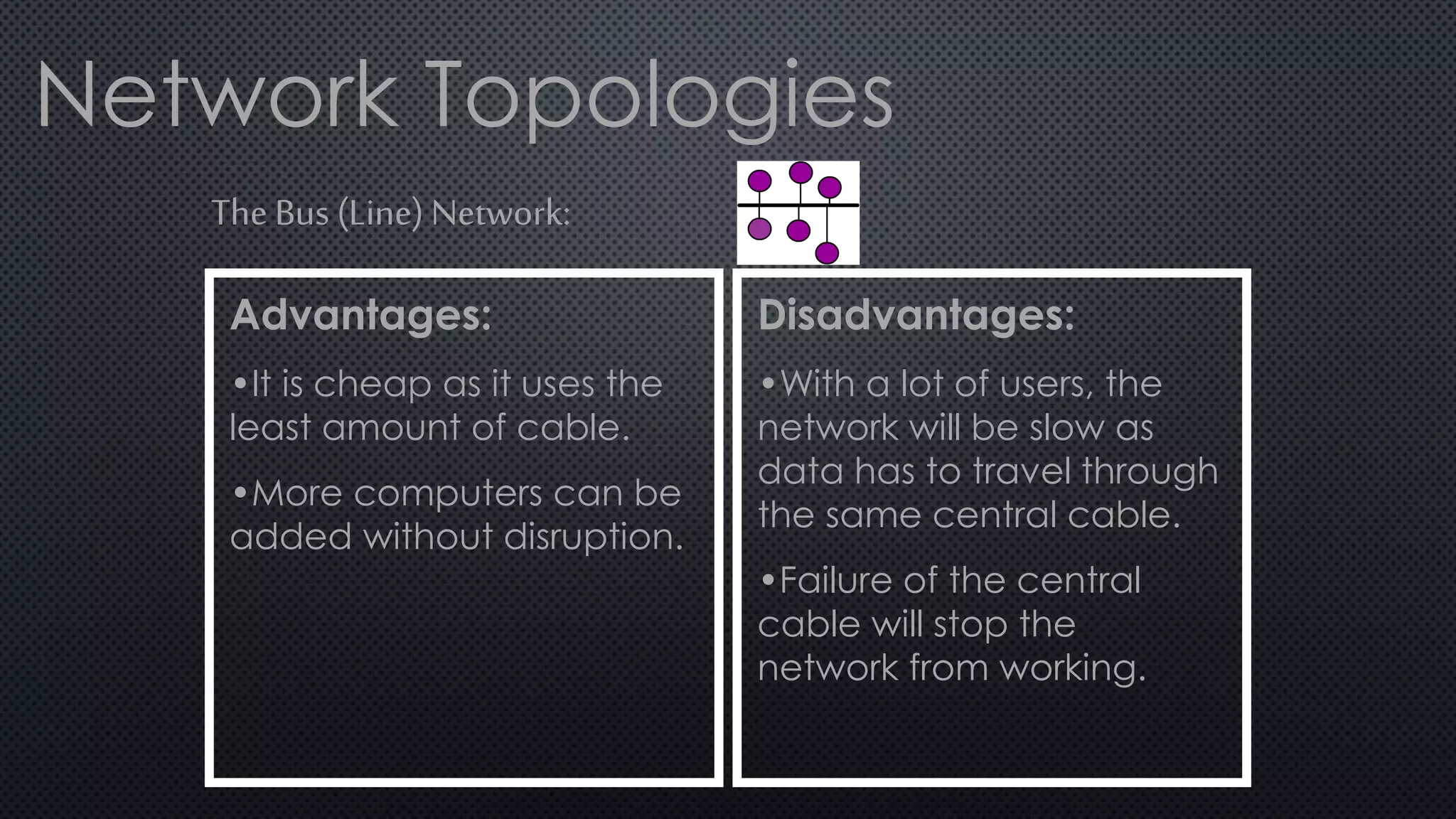
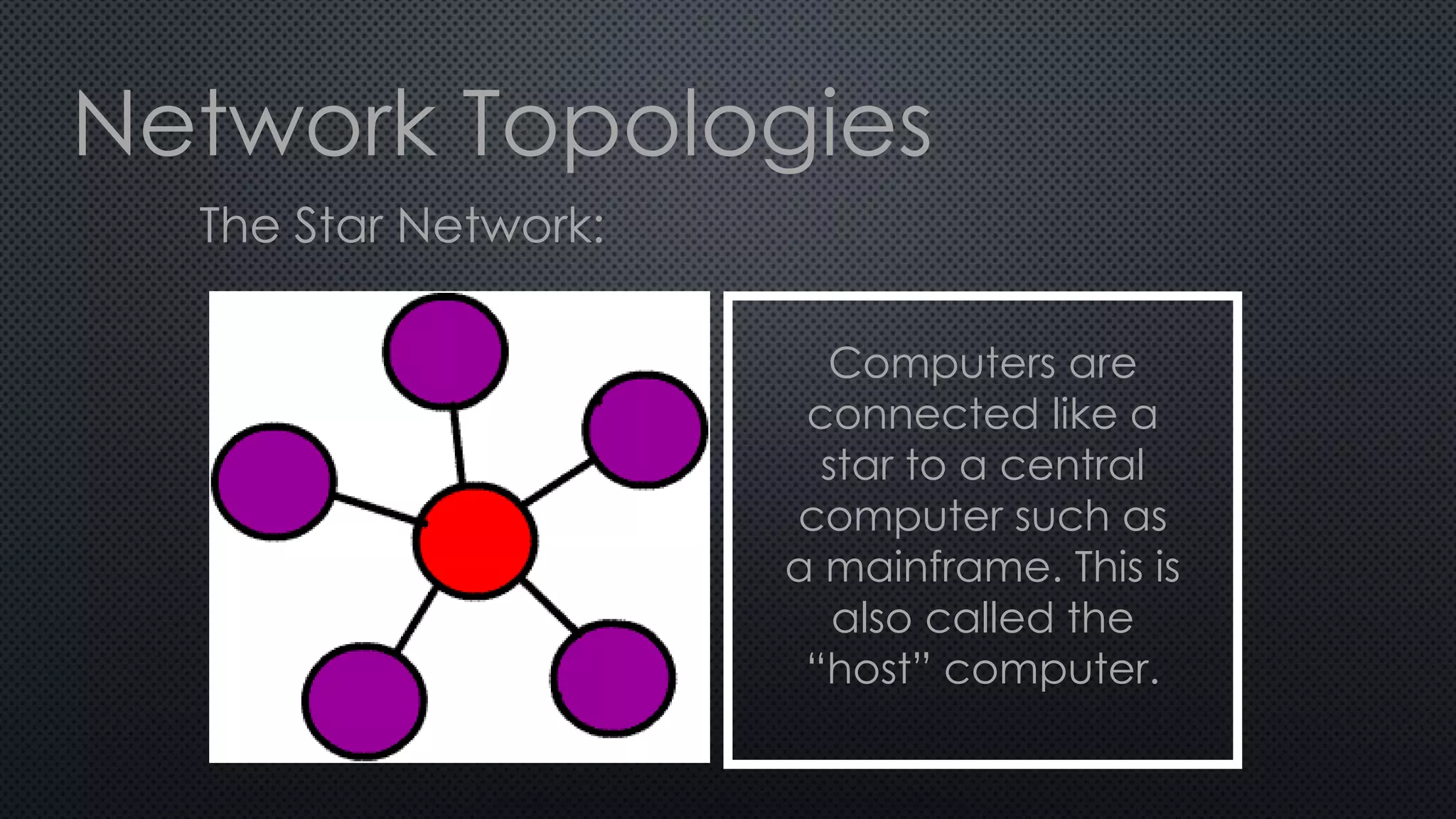
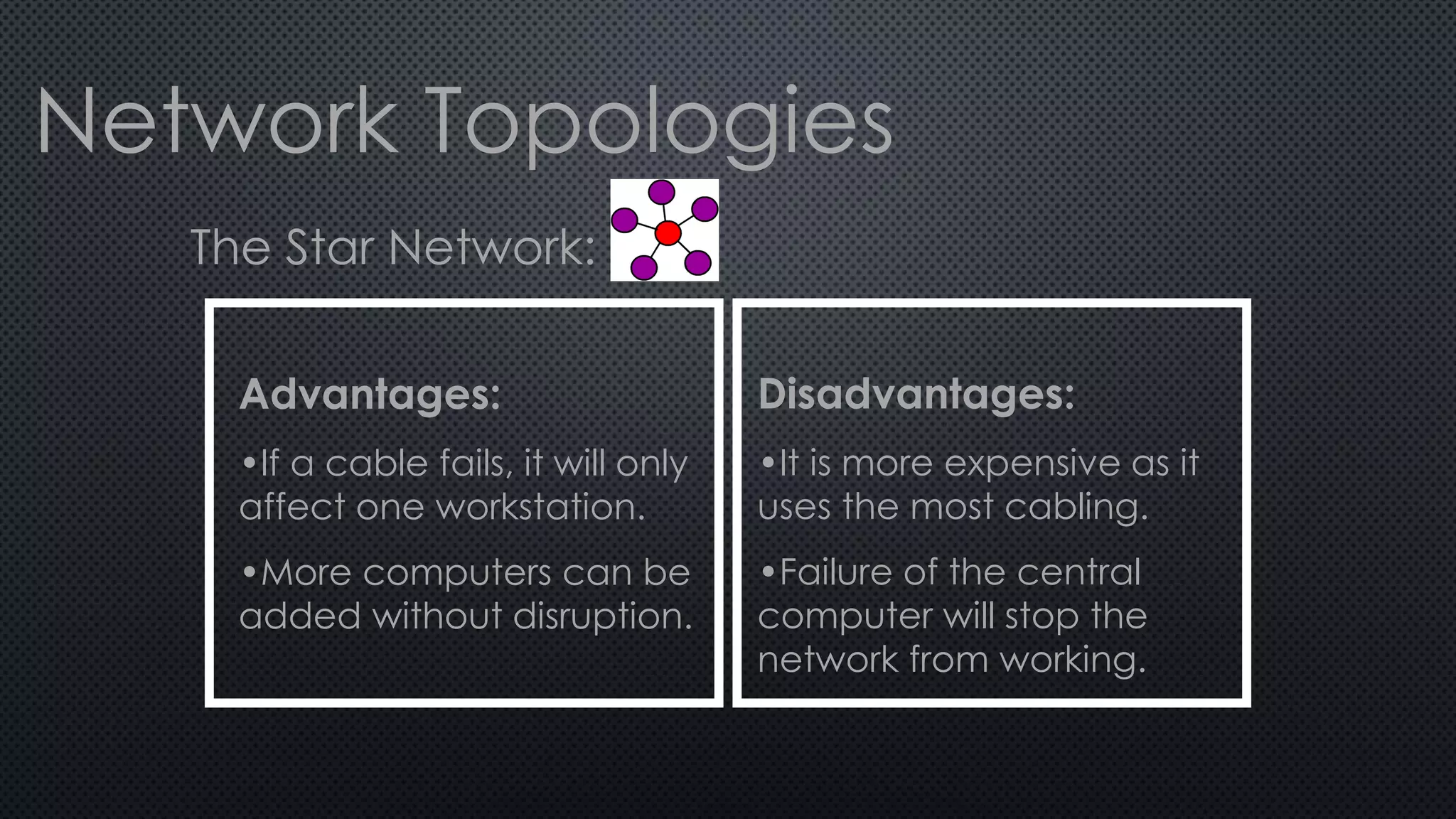
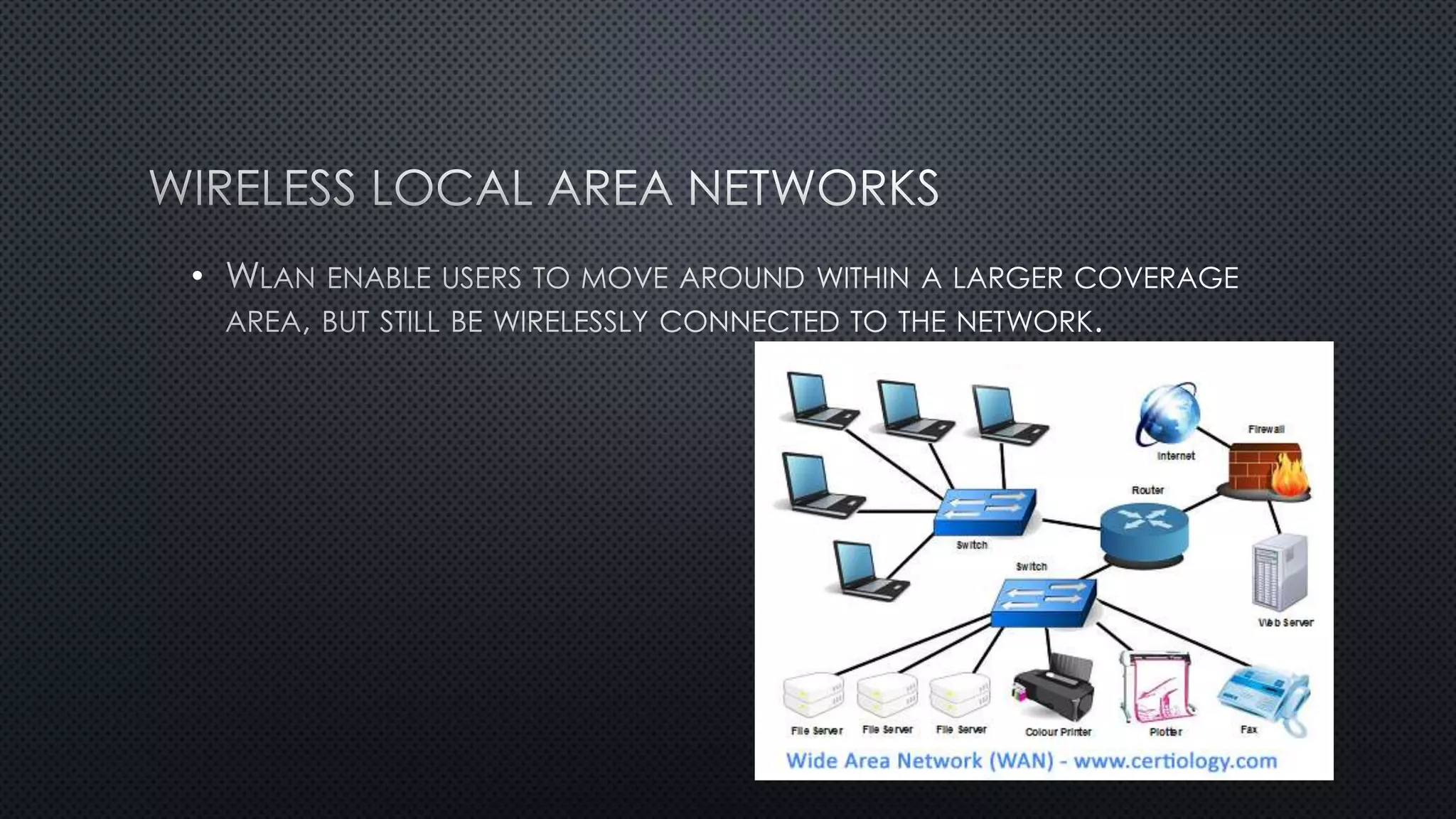
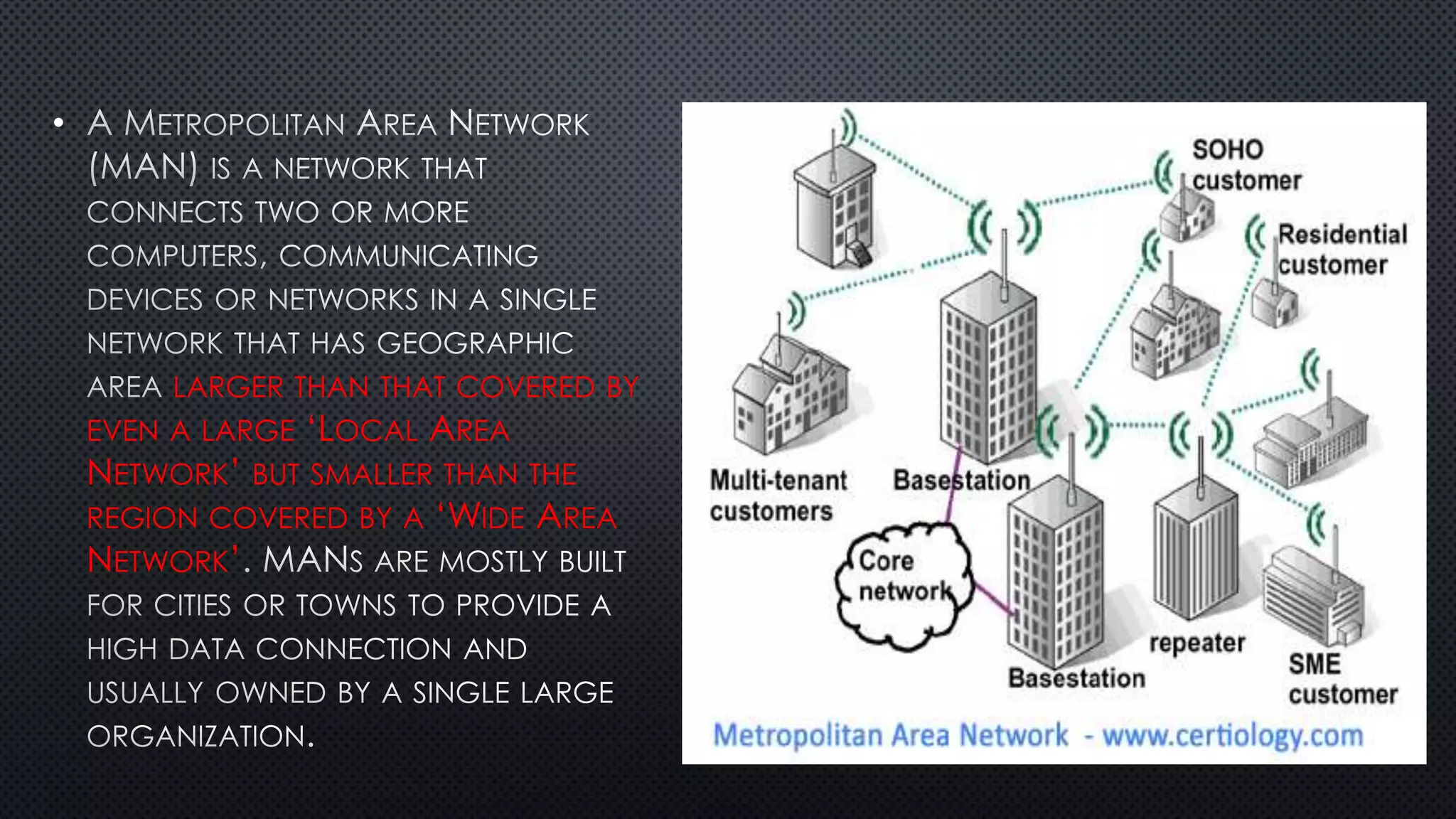
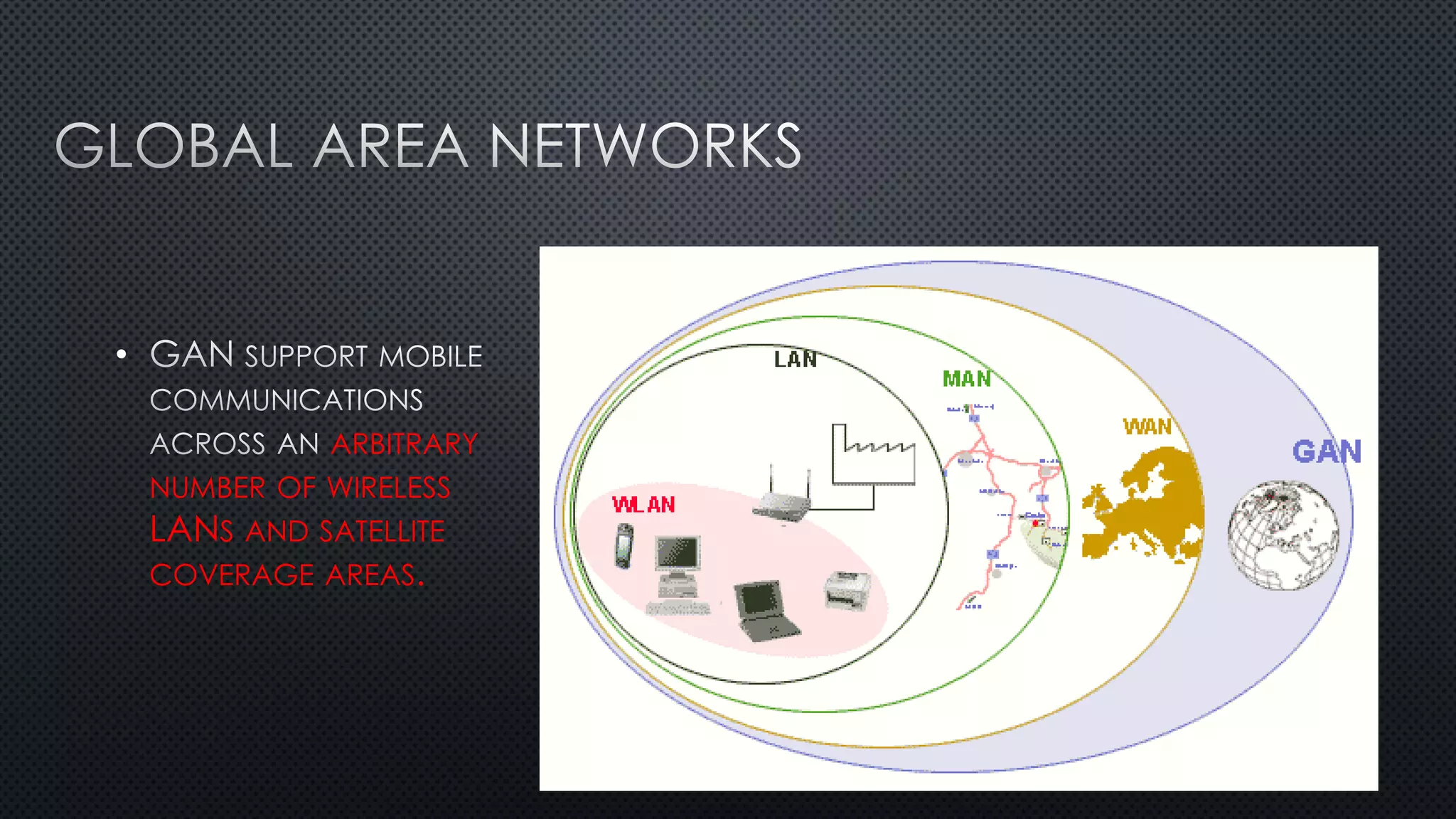
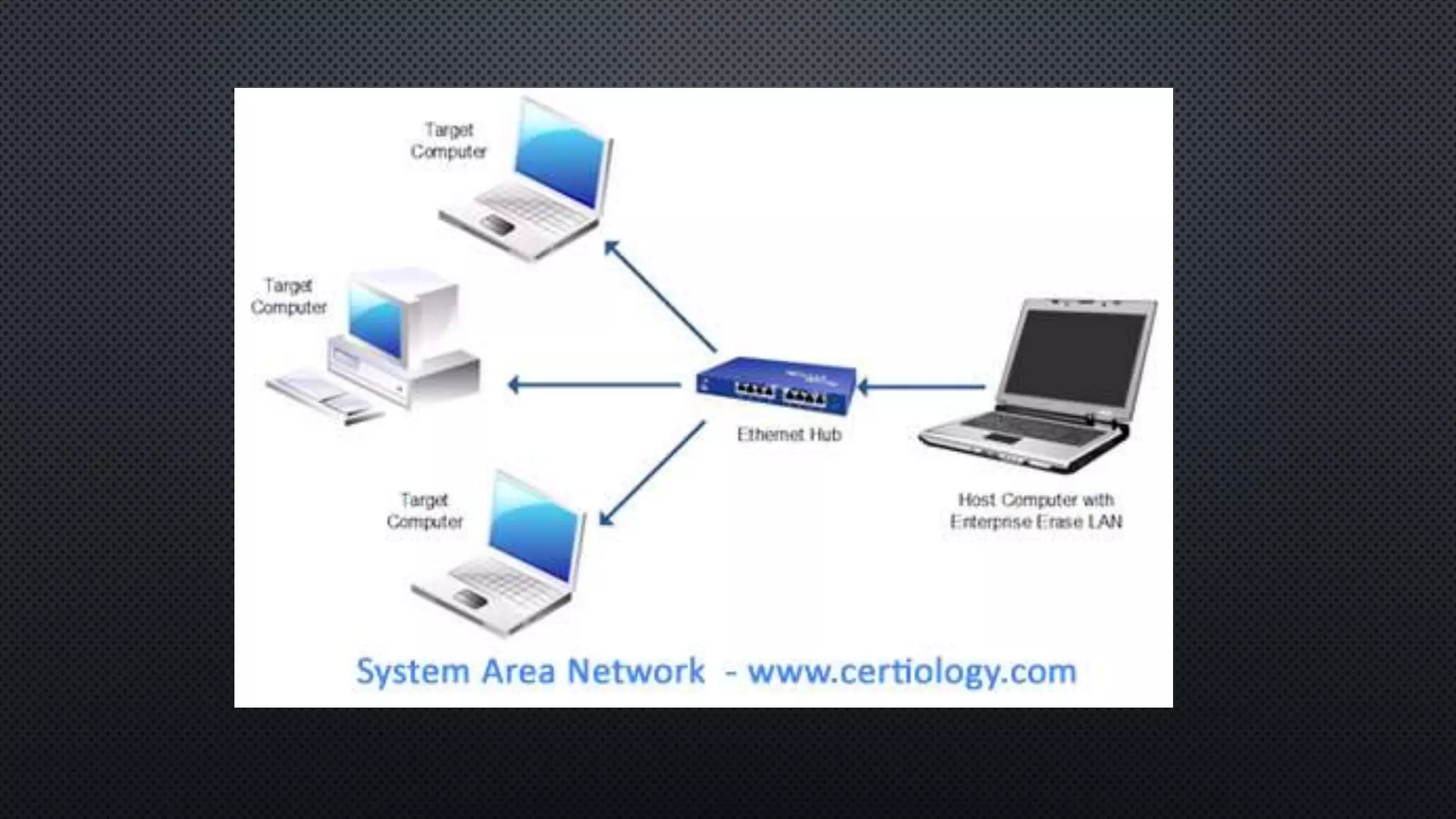
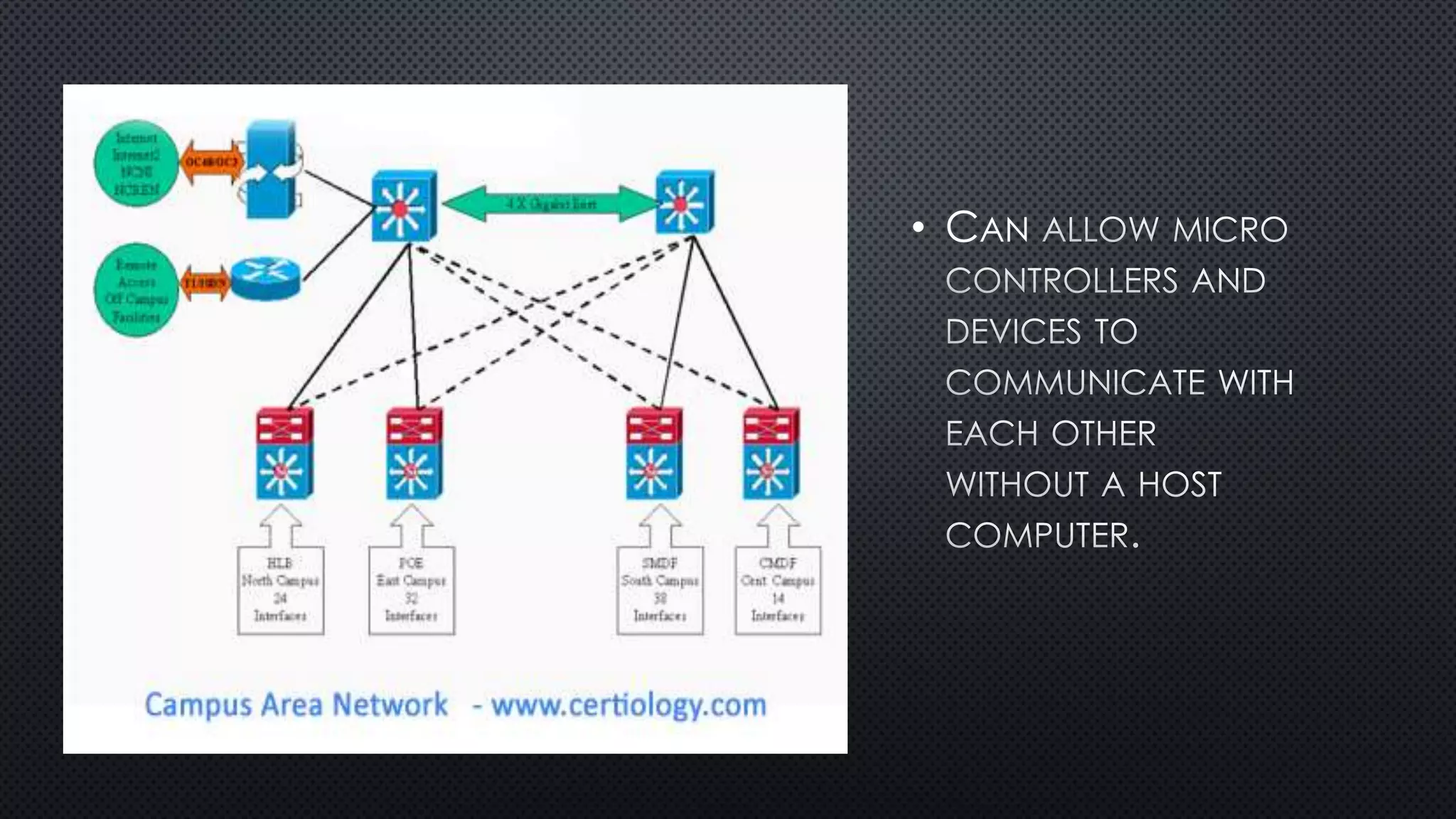
1. A network connects two or more computers so they can communicate with each other. There are three main network topologies: ring, bus, and star.
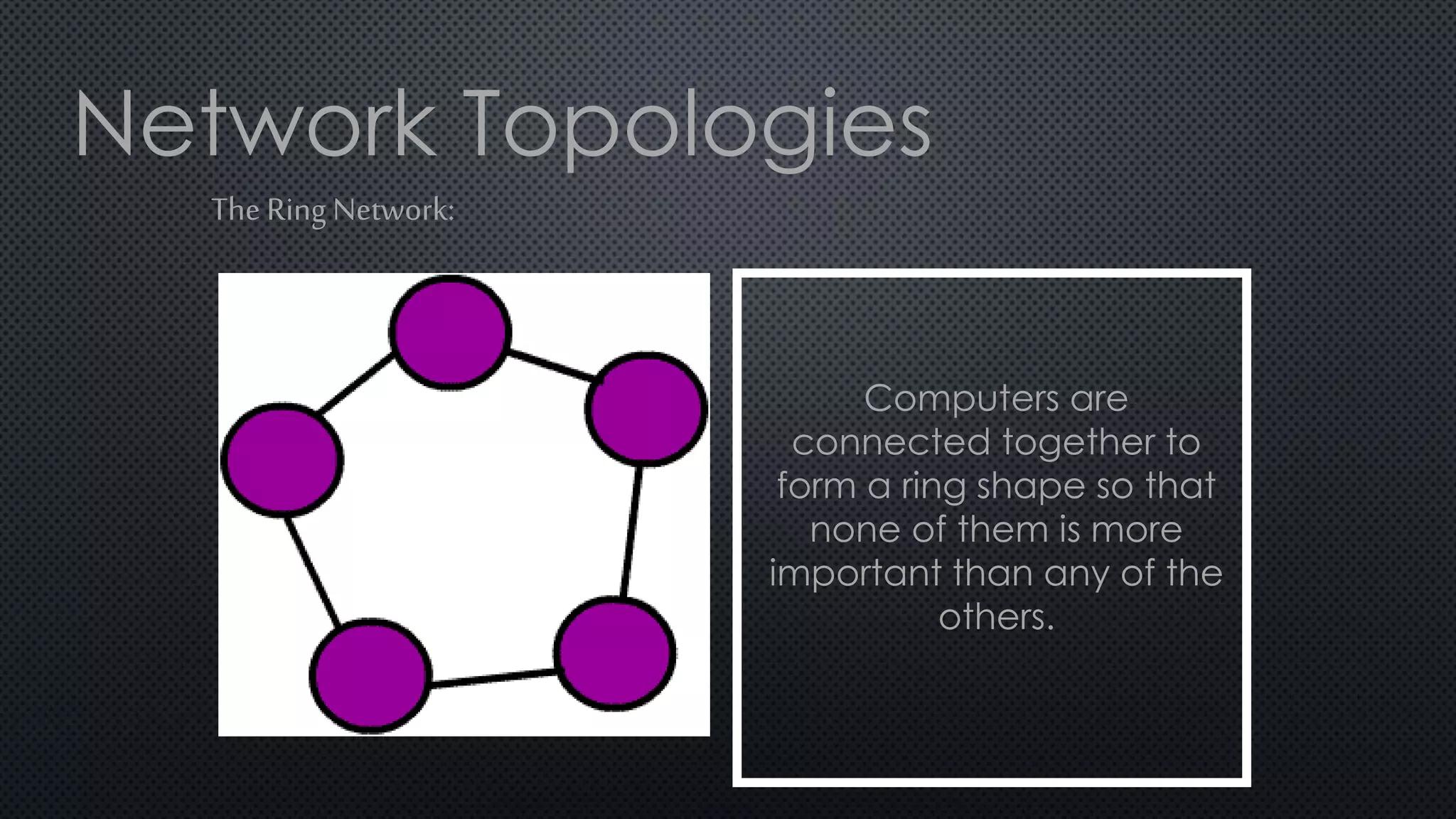
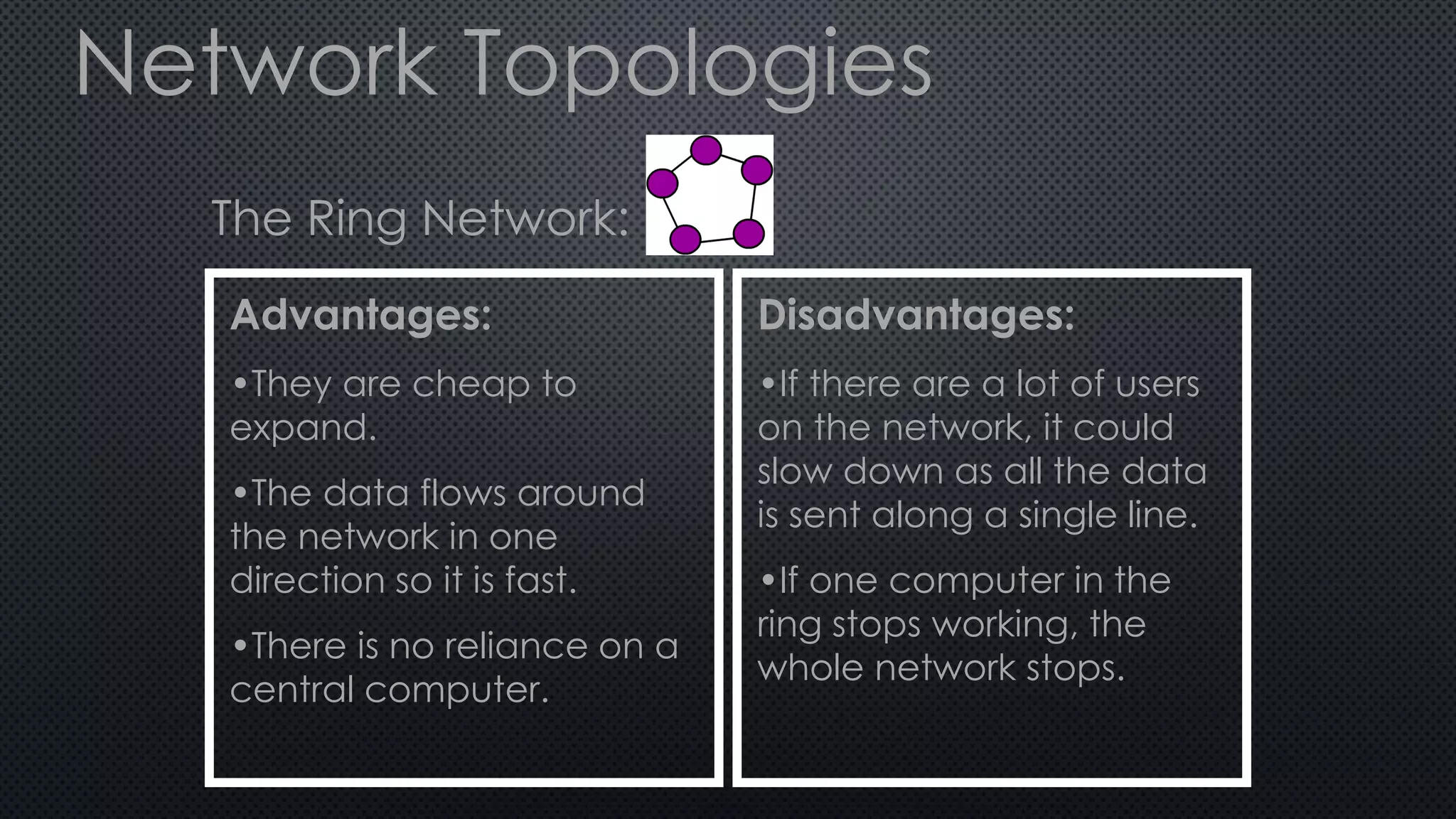
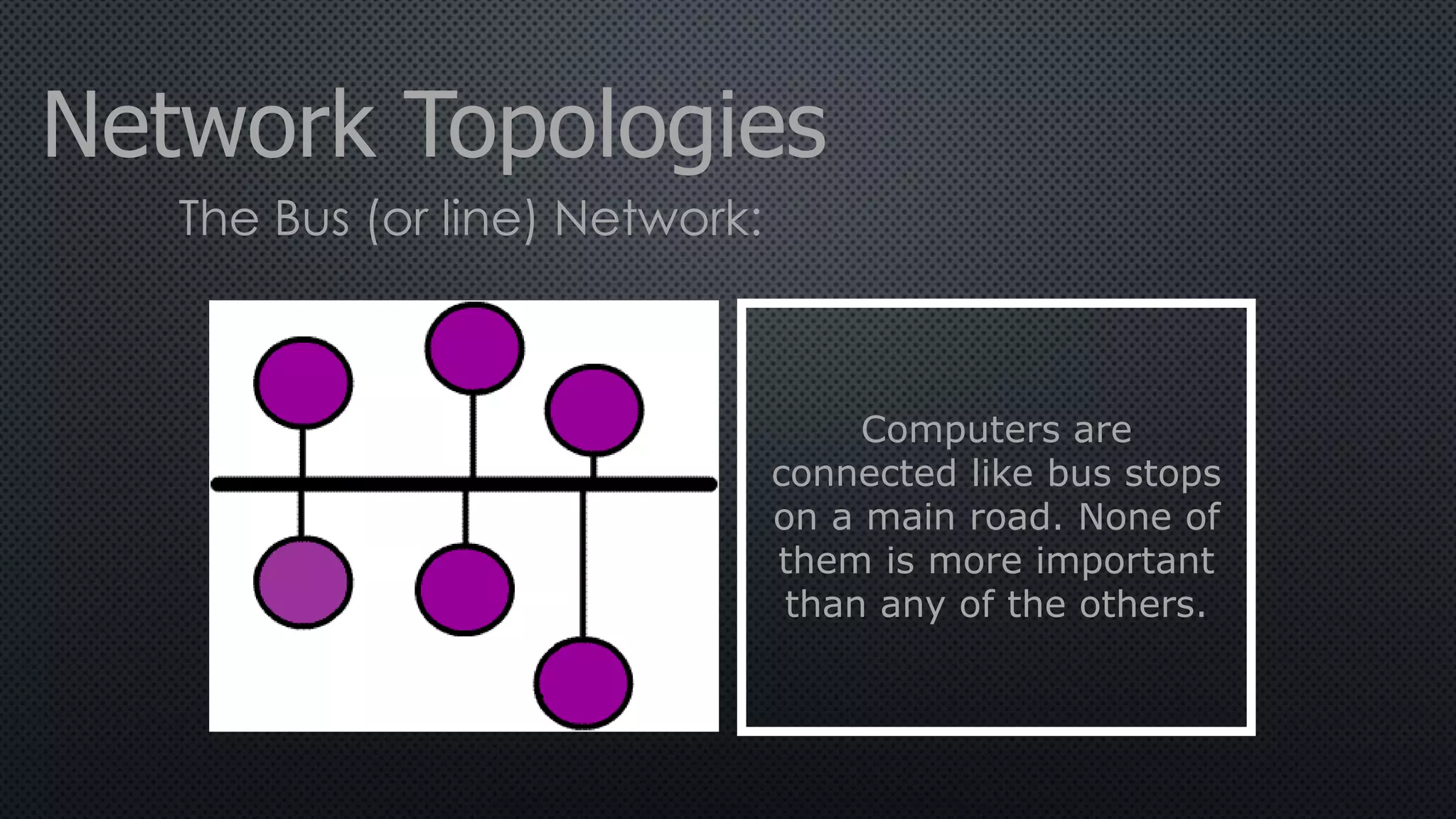
2. In a ring network, computers are connected in a ring shape with no central computer. In a bus network, computers are connected like bus stops to a main cable. In a star network, computers connect to a central host computer.
3. Network security includes physical, access, and data security. Physical security protects hardware from theft. Access security limits user access to information. Data security prevents data loss.