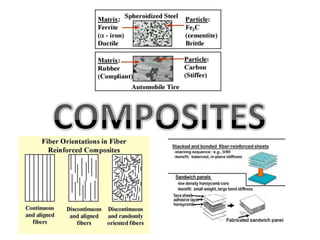
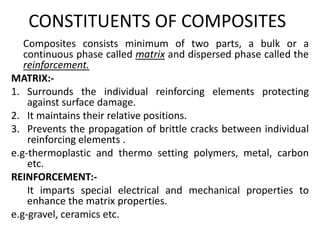
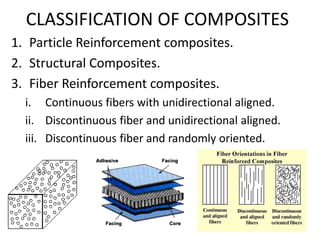
Composites are materials formed from two or more constituent materials that remain separate and distinct within a composite. Composites consist of a continuous matrix phase that surrounds and binds together a dispersed reinforcement phase. This gives composites properties that are superior to the individual components, such as high strength and stiffness. Composites can be classified based on the type of reinforcement, such as particle, structural, or fiber reinforcement composites which use particles, sheets, or fibers respectively to enhance the properties of the matrix material.