This document presents a study comparing the fatigue performance of a steel leaf spring and a glass fiber/epoxy composite leaf spring used in automobiles. A finite element model was created of each leaf spring using ANSYS software. Static analysis showed the composite spring had higher stiffness but similar maximum stress compared to the steel spring. Fatigue analysis using the Gerber approach predicted the composite spring would have a longer fatigue life of 1.025*10 cycles compared to the steel spring. The document concludes the composite spring design and simulation validate methods for predicting fatigue performance without full physical testing.



![2. Background
Author Conclusion
Senthilkumar
Mouleeswaran [2]
Composite multi leaf spring using glass fibre reinforced polymer
compared to steel spring, found to have 67.35% lesser stress,
64.95% higher stiffness and 126.98% higher natural frequency and
also weight reduction of 68.15% is achieved compared to steel leaf
spring.
D.N.Dubey,
S.G.Mahakalkar [7]
Composite leaf springs would offer substantial weight savings by
using mono leaf spring in passenger cars. Mono parabolic leaf spring
of a Maruti Omni used HM and HS Carbon polymers composite
material.
Makarand B. Shirke and
Prof. V .D .Wakchaure [5]
The life of the spring is an important criterion. In this aspect as well
composite leaf spring proves to be much better than EN45 steel leaf
spring.
01/25/16 International Conference on Trends in Product Life Cycle, Modeling, Simulation and Synthesis 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plmsspresentation-160125183502/85/Composite-automobile-leaf-spring-Fatigue-life-4-320.jpg)
![2. Background
Author Conclusion
Shishay Amare Gebremeskel
[4]
Constant cross section design of mono leaf springs is employed to
take advantages of ease of design analysis and its manufacturing
process. Resulting design and simulation stresses are much below
the strength properties of the material, satisfying the maximum
stress failure criterion .
Sachin Kr. Patel,
A.K. Jain and
Pratik Gandhi [9]
Composite materials have high elastic strain energy storage capacity
and high strength to weight ratio Therefore, composite leaf spring is
an effective replacement for the existing steel leaf spring in
automobile.
J.A.M. Ferreira,
J.D.M. Costa,
P.N.B. Reis, M.O.W.
Richardson [8]
The fatigue strength is strongly influenced by the layer design.
0° laminate results have values 1.5-1.8 times higher than +45°/0°/-
45° and +30°/-30°/0° laminates which exhibit similar fatigue
strengths.
01/25/16 International Conference on Trends in Product Life Cycle, Modeling, Simulation and Synthesis 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plmsspresentation-160125183502/85/Composite-automobile-leaf-spring-Fatigue-life-5-320.jpg)
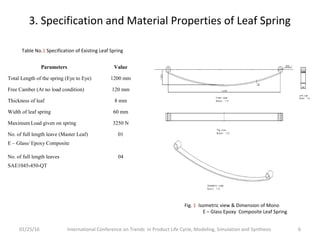
![3. Specification and Material Properties of Leaf Spring
01/25/16 International Conference on Trends in Product Life Cycle, Modeling, Simulation and Synthesis 7
Material Properties Value
Elastic Modulus (E), GPa 207
Yield Tensile Strength , MPa 1515
Ultimate Tensile Strength, MPa 1584
Cyclic Strength Coefficient (K’) 1874
Fatigue Strength Coefficient (Sf) 1686
Fatigue Strength Exponent (b) -0.06
Fatigue Ductility Exponent (c ) -0.83
Fatigue Ductility Coefficient (Ef) 0.79
Cyclic Strain Hardening Exponent (n’) 0.09
Density , Kg/m3
7.7 × 103
Possion’s ratio 0.266
Behaviour Isotropic
Table .2: Mechanical and Cyclic Properties of
SAE1045-450- QT [11,12]
Table .3: Mechanical and Cyclic Properties of E glass/ Epoxy
Composite material [11. 12]
Material Properties Value
Tensile modulus along X-direction (Ex), MPa 34000
Tensile modulus along Y-direction (Ey), MPa 6530
Tensile modulus along Z-direction (Ez), MPa 6530
Tensile strength of the material, MPa 900
Compressive strength of the material, MPa 450
Shear modulus along XY-direction (Gxy), MPa 2433
Shear modulus along YZ-direction (Gyz), MPa 1698
Shear modulus along ZX-direction (Gzx), MPa 2433
Poisson ratio along XY-direction (NUxy) 0.217
Poisson ratio along YZ-direction (NUyz) 0.366](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plmsspresentation-160125183502/85/Composite-automobile-leaf-spring-Fatigue-life-7-320.jpg)
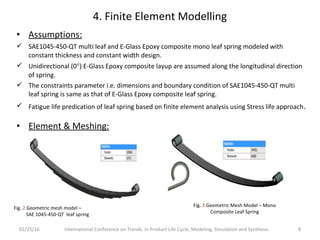
![5. Static Analysis and Ride Comfort
Parameters
Material
SAE1045-
450-QT
E-Glass Epoxy
Composite
Maximum load in N 3250 3250
Absolute Maximum
Stress , MPa
724.52 715
Stiffness, N/mm 24.33 53.59
01/25/16 International Conference on Trends in Product Life Cycle, Modeling, Simulation and Synthesis 10
Table. 5 Comparison result of Stress for
SAE 1045-450 - QT and E-Glass Epoxy Composite
Modes
SAE1045-450- QT
Frequency Hz
E- Glass Epoxy
Frequency Hz
1 13.13 17.15
2 54.55 56.16
3 78.59 72.19
4 116.89 119.36
5 178.49 202.78
6 243.27 288.43
Table 6 Natural frequency of SAE 1045-450-QT and
E-Glass Epoxy Composite material
Static Results :
Shear stress (τ12= 6.77 MPa) multiplied by a factor
of ‘9’ (9*3 = 60.93 MPa) is much less than the
shear strength (S = 68.95 MPa) of the specified
composite material, E-glass/Epoxy.
Specifying the criteria : (9*τ12< S),
Design is safe even for the flexural failure.
Ride Comfort :
To avoid resonant condition The road
irregularities usually have the maximum
frequency of 12 Hz. [7]
In modal analysis only boundary conditions are
applied and no load is acted on the leaf spring.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plmsspresentation-160125183502/85/Composite-automobile-leaf-spring-Fatigue-life-10-320.jpg)
![6. Finite Element Based Fatigue Analysis
• Main purpose of Finite Element Based Fatigue tool using for leaf spring
simulation – during the design stage of development process to enable
reliable fatigue life calculations.
• Input Parameter and Fatigue Analysis Cycle
01/25/16 International Conference on Trends in Product Life Cycle, Modeling, Simulation and Synthesis 11
Figure 5 Fatigue Analysis Prediction Strategies
Figure 6 FEM Based Fatigue Analysis Cycle [11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plmsspresentation-160125183502/85/Composite-automobile-leaf-spring-Fatigue-life-11-320.jpg)
![6. Finite Element Based Fatigue Analysis
• The life data analysis is a tool to be used here to predict the fatigue life of mono
composite leaf spring.
• Fatigue life results are based on analytical result and resulting S-N graph for
SAE1045-450-QT and E – Glass Composite as shown in Fig. 7 and 8
• E glass-epoxy figure is for tension, torsion or bending ? Specify ! ( Figure 7)
01/25/16 International Conference on Trends in Product Life Cycle, Modeling, Simulation and Synthesis 13
Figure 7 S-N curves for E-Glass/epoxy composite [2] Figure 8 S-N curves for SAE1045-450-QT spring [11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plmsspresentation-160125183502/85/Composite-automobile-leaf-spring-Fatigue-life-13-320.jpg)