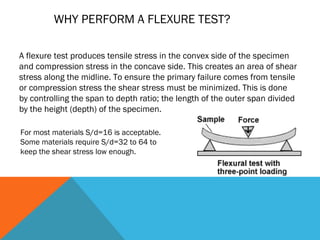
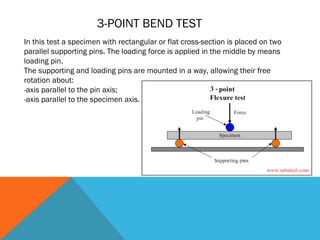
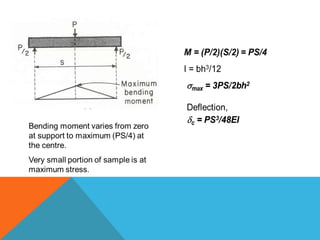
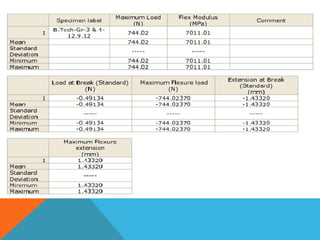
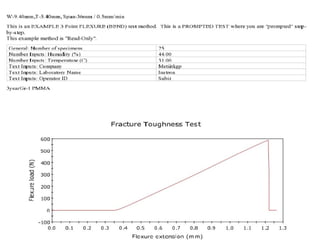
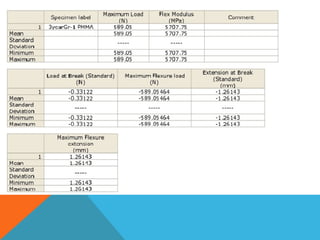
This document discusses the 3-point flexural test, which measures the flexural properties of materials. In a 3-point flexural test, a specimen is placed on two supporting pins and a loading pin is applied in the middle. Calculations are performed to determine flexural stress, strain, and modulus based on the load and deflection measurements. The test provides values for modulus of elasticity in bending, flexural stress, flexural strain, and flexural stress-strain response. It is a common test for evaluating a material's stiffness when flexed.