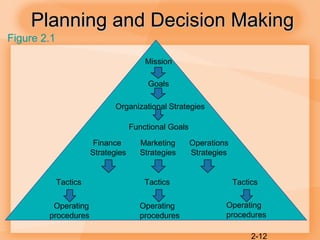
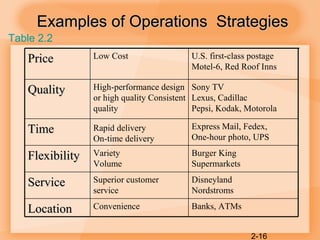
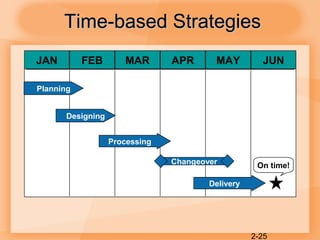
This document discusses competitiveness, strategy, and productivity. It defines key terms like competitiveness, strategy, tactics, and operations strategy. It explains that organizations compete through marketing and operations functions. Poor competitiveness can result from too much short-term focus, neglecting operations strategy, or failing to meet customer needs. Strategy involves achieving organizational goals through strategic plans, while tactics are the specific actions. Linking organizational and operations strategy is important. Time-based and quality-focused strategies are discussed as ways to improve competitiveness.