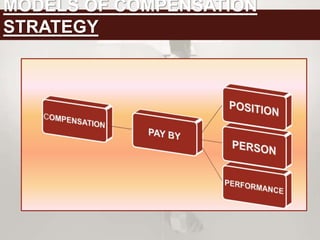
This document discusses compensation strategies in India. It outlines three main models of compensation strategy: position based, person based, and performance based. For each model, it describes the key aspects, benefits, and pitfalls. It also discusses compensation practices that are common in India, such as maintaining a lower cost of labor compared to other countries and offering double digit salary increases. The conclusion recommends that a performance based model is best for motivating employees and controlling work activities.