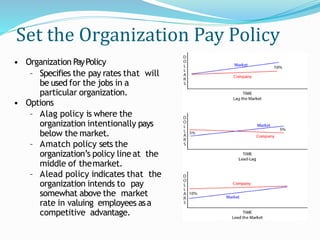
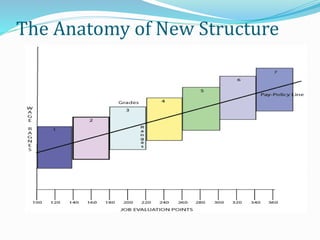
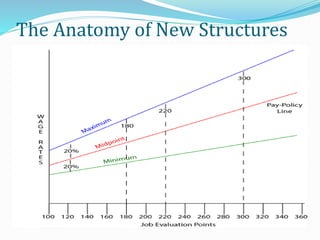
The document discusses compensation and total rewards. It defines compensation as the total payments provided to employees in exchange for work performed, including pay, incentives, and benefits. Total rewards refers to all aspects of an employee's work experience, including compensation, benefits, work environment, career development opportunities, and recognition. The purpose of a total rewards approach is to attract, motivate, and retain talented staff through an effective compensation strategy.