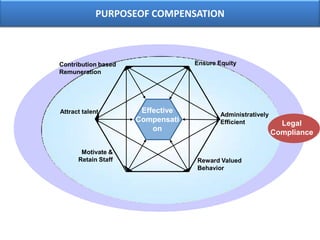
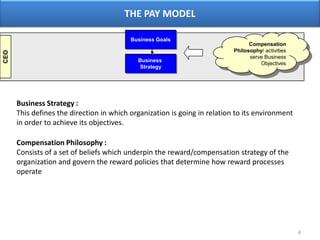
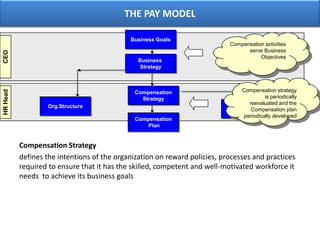
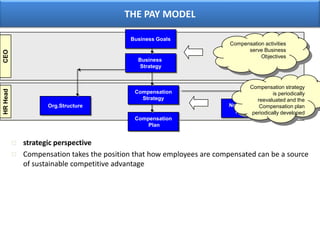
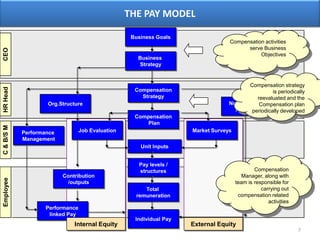
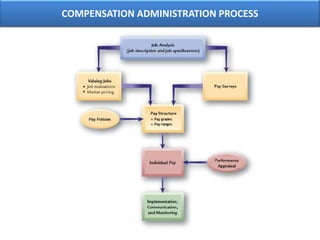
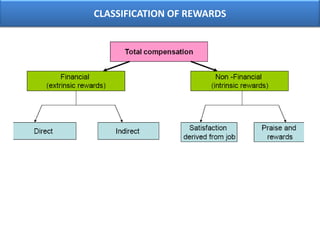
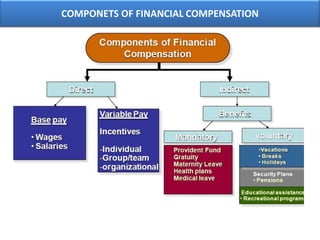
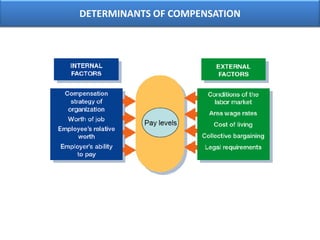
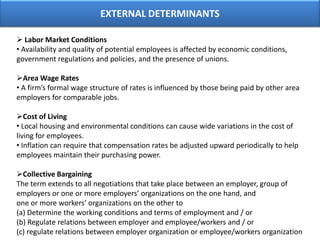
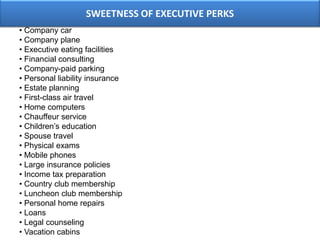
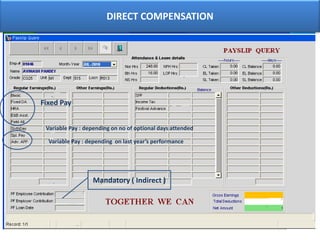
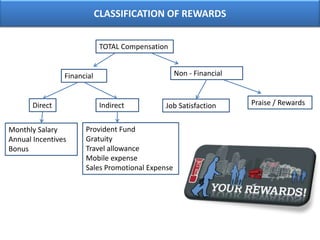
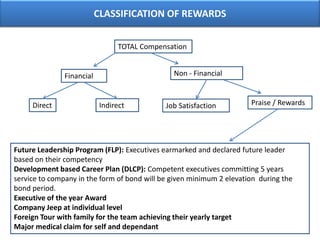
The document outlines various aspects of compensation practices, including definitions, purposes, and strategies for employee remuneration. It discusses the significance of equitable and effective compensation in achieving organizational objectives, along with the different types of financial and non-financial rewards. It also highlights the importance of aligning compensation strategies with business goals and the evolving trends in compensation management.