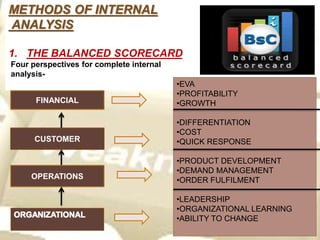
This document summarizes methods for conducting an internal analysis of an organization. It discusses frameworks for identifying areas to assess, including critical success factors, industry characteristics, and the value chain. Primary and support activities and core processes are examined. Quantitative methods like financial ratios, economic value added, and activity-based costing are outlined. Qualitative analysis of non-financial factors is also noted. The conclusion states that internal analysis along with external analysis helps formulate strategies by determining strengths and weaknesses.