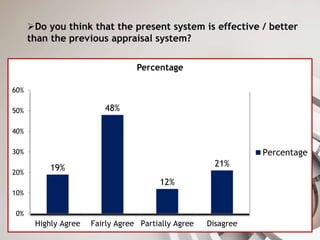
BHEL is a leading power generation and industrial equipment manufacturer in India. It has implemented an online performance management system called e-MAP for evaluating employees. The system consists of evaluating employees on key result areas (KRAs) and skills. Most employees are satisfied with e-MAP and feel it is an improvement over the previous appraisal system as the KRA evaluation is more transparent. However, some employees face issues in selecting the appropriate KRAs. Appraisers provide regular feedback to help employees improve performance.