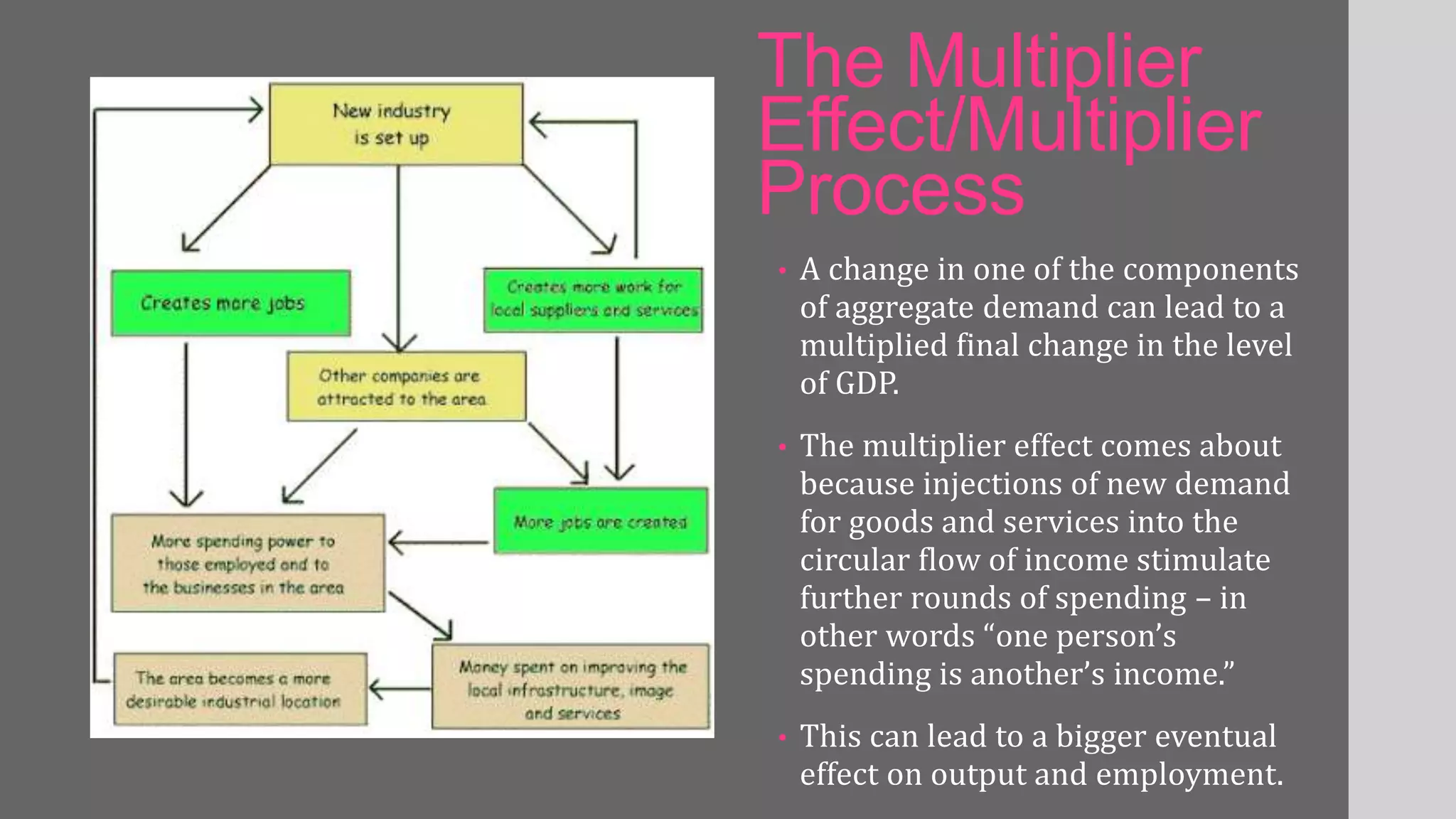
The document discusses the multiplier effect in economics. It defines the multiplier effect as how an initial injection of spending, such as increased government spending, creates a ripple effect that increases overall output and employment. It works through consumers receiving more income and spending more, which further increases income and demand. The multiplier is the ratio of the total change in income to the initial change in spending. The document also outlines the assumptions and limitations of the multiplier model, and describes how the multiplier effect can occur through both static and dynamic processes.