This document discusses organizational communication and defines key concepts. It is divided into several sections:
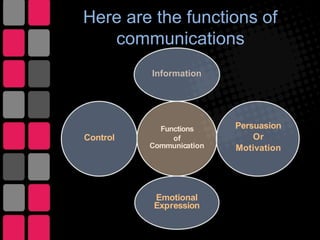
1) It defines communication and its main functions within organizations as conveying information, persuasion, motivation, and emotional expression.
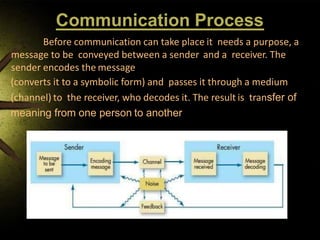
2) It describes the communication process including encoding, messaging, channels, decoding, feedback.
3) It outlines different directions of communication flow within organizations including downward, upward, and lateral.
4) It discusses interpersonal communication methods like oral, written, and nonverbal communication.
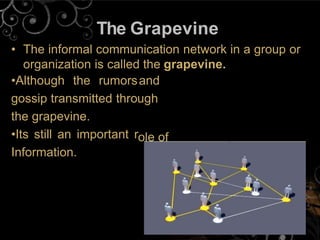
5) It examines organizational networks, the informal grapevine, and electronic communication methods.
6) Finally, it briefly mentions managing information and barriers to effective communication.